Chuhao Jin
Pave the Way to Grasp Anything: Transferring Foundation Models for Universal Pick-Place Robots
Jun 25, 2023Abstract:Improving the generalization capabilities of general-purpose robotic agents has long been a significant challenge actively pursued by research communities. Existing approaches often rely on collecting large-scale real-world robotic data, such as the RT-1 dataset. However, these approaches typically suffer from low efficiency, limiting their capability in open-domain scenarios with new objects, and diverse backgrounds. In this paper, we propose a novel paradigm that effectively leverages language-grounded segmentation masks generated by state-of-the-art foundation models, to address a wide range of pick-and-place robot manipulation tasks in everyday scenarios. By integrating precise semantics and geometries conveyed from masks into our multi-view policy model, our approach can perceive accurate object poses and enable sample-efficient learning. Besides, such design facilitates effective generalization for grasping new objects with similar shapes observed during training. Our approach consists of two distinct steps. First, we introduce a series of foundation models to accurately ground natural language demands across multiple tasks. Second, we develop a Multi-modal Multi-view Policy Model that incorporates inputs such as RGB images, semantic masks, and robot proprioception states to jointly predict precise and executable robot actions. Extensive real-world experiments conducted on a Franka Emika robot arm validate the effectiveness of our proposed paradigm. Real-world demos are shown in YouTube (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1m9wNzfp_4E ) and Bilibili (https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV178411Z7H2/ ).
AlphaBlock: Embodied Finetuning for Vision-Language Reasoning in Robot Manipulation
May 30, 2023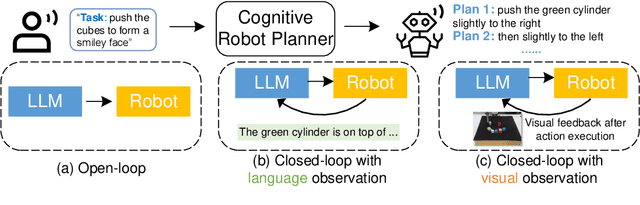
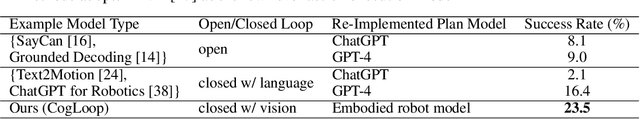
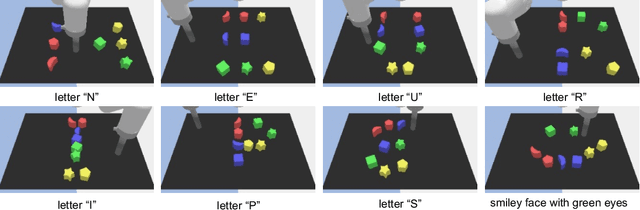
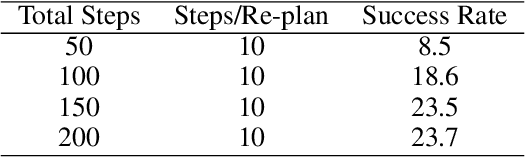
Abstract:We propose a novel framework for learning high-level cognitive capabilities in robot manipulation tasks, such as making a smiley face using building blocks. These tasks often involve complex multi-step reasoning, presenting significant challenges due to the limited paired data connecting human instructions (e.g., making a smiley face) and robot actions (e.g., end-effector movement). Existing approaches relieve this challenge by adopting an open-loop paradigm decomposing high-level instructions into simple sub-task plans, and executing them step-by-step using low-level control models. However, these approaches are short of instant observations in multi-step reasoning, leading to sub-optimal results. To address this issue, we propose to automatically collect a cognitive robot dataset by Large Language Models (LLMs). The resulting dataset AlphaBlock consists of 35 comprehensive high-level tasks of multi-step text plans and paired observation sequences. To enable efficient data acquisition, we employ elaborated multi-round prompt designs that effectively reduce the burden of extensive human involvement. We further propose a closed-loop multi-modal embodied planning model that autoregressively generates plans by taking image observations as input. To facilitate effective learning, we leverage MiniGPT-4 with a frozen visual encoder and LLM, and finetune additional vision adapter and Q-former to enable fine-grained spatial perception for manipulation tasks. We conduct experiments to verify the superiority over existing open and closed-loop methods, and achieve a significant increase in success rate by 21.4% and 14.5% over ChatGPT and GPT-4 based robot tasks. Real-world demos are shown in https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ayAzID1_qQk .
Text2Poster: Laying out Stylized Texts on Retrieved Images
Jan 06, 2023Abstract:Poster generation is a significant task for a wide range of applications, which is often time-consuming and requires lots of manual editing and artistic experience. In this paper, we propose a novel data-driven framework, called \textit{Text2Poster}, to automatically generate visually-effective posters from textual information. Imitating the process of manual poster editing, our framework leverages a large-scale pretrained visual-textual model to retrieve background images from given texts, lays out the texts on the images iteratively by cascaded auto-encoders, and finally, stylizes the texts by a matching-based method. We learn the modules of the framework by weakly- and self-supervised learning strategies, mitigating the demand for labeled data. Both objective and subjective experiments demonstrate that our Text2Poster outperforms state-of-the-art methods, including academic research and commercial software, on the quality of generated posters.
WenLan: Bridging Vision and Language by Large-Scale Multi-Modal Pre-Training
Mar 19, 2021
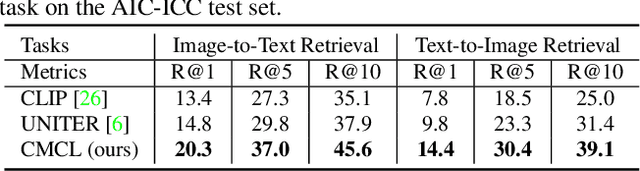
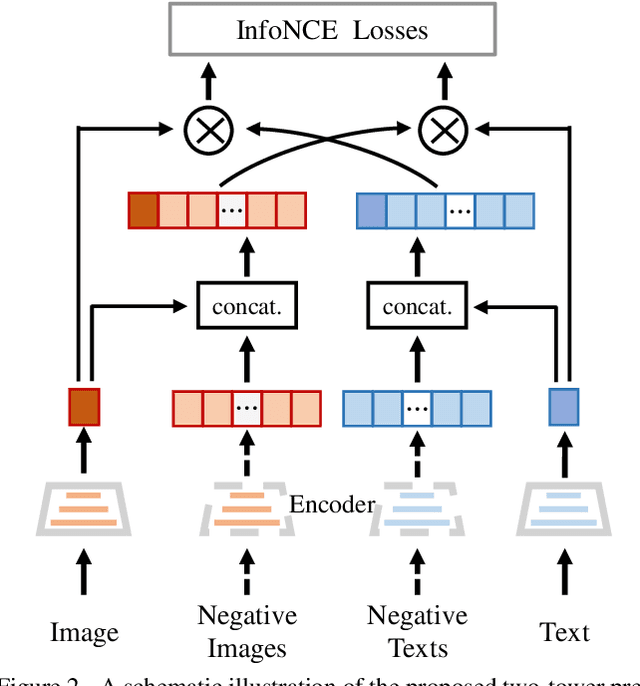
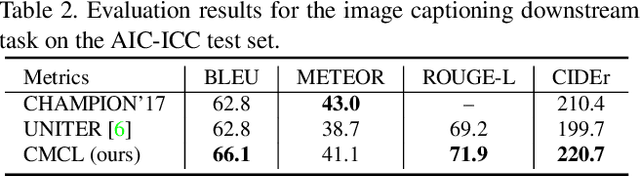
Abstract:Multi-modal pre-training models have been intensively explored to bridge vision and language in recent years. However, most of them explicitly model the cross-modal interaction between image-text pairs, by assuming that there exists strong semantic correlation between the text and image modalities. Since this strong assumption is often invalid in real-world scenarios, we choose to implicitly model the cross-modal correlation for large-scale multi-modal pre-training, which is the focus of the Chinese project `WenLan' led by our team. Specifically, with the weak correlation assumption over image-text pairs, we propose a two-tower pre-training model called BriVL within the cross-modal contrastive learning framework. Unlike OpenAI CLIP that adopts a simple contrastive learning method, we devise a more advanced algorithm by adapting the latest method MoCo into the cross-modal scenario. By building a large queue-based dictionary, our BriVL can incorporate more negative samples in limited GPU resources. We further construct a large Chinese multi-source image-text dataset called RUC-CAS-WenLan for pre-training our BriVL model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the pre-trained BriVL model outperforms both UNITER and OpenAI CLIP on various downstream tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge