Guangzhen Liu
WenLan: Bridging Vision and Language by Large-Scale Multi-Modal Pre-Training
Mar 19, 2021
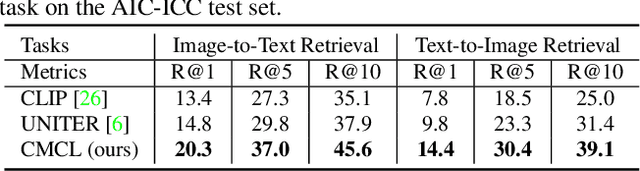
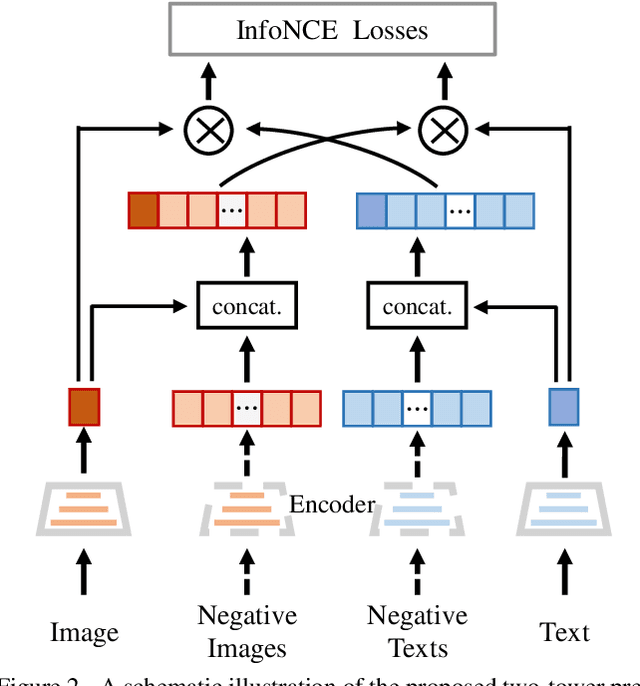
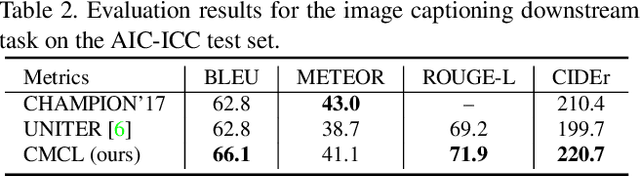
Abstract:Multi-modal pre-training models have been intensively explored to bridge vision and language in recent years. However, most of them explicitly model the cross-modal interaction between image-text pairs, by assuming that there exists strong semantic correlation between the text and image modalities. Since this strong assumption is often invalid in real-world scenarios, we choose to implicitly model the cross-modal correlation for large-scale multi-modal pre-training, which is the focus of the Chinese project `WenLan' led by our team. Specifically, with the weak correlation assumption over image-text pairs, we propose a two-tower pre-training model called BriVL within the cross-modal contrastive learning framework. Unlike OpenAI CLIP that adopts a simple contrastive learning method, we devise a more advanced algorithm by adapting the latest method MoCo into the cross-modal scenario. By building a large queue-based dictionary, our BriVL can incorporate more negative samples in limited GPU resources. We further construct a large Chinese multi-source image-text dataset called RUC-CAS-WenLan for pre-training our BriVL model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the pre-trained BriVL model outperforms both UNITER and OpenAI CLIP on various downstream tasks.
Contrastive Prototype Learning with Augmented Embeddings for Few-Shot Learning
Jan 23, 2021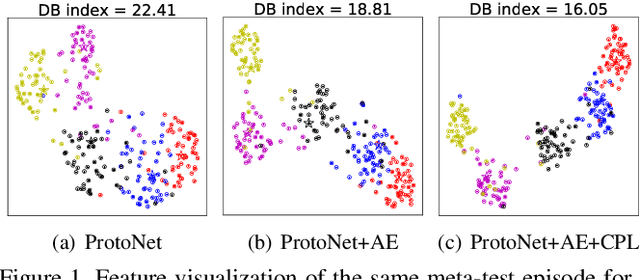
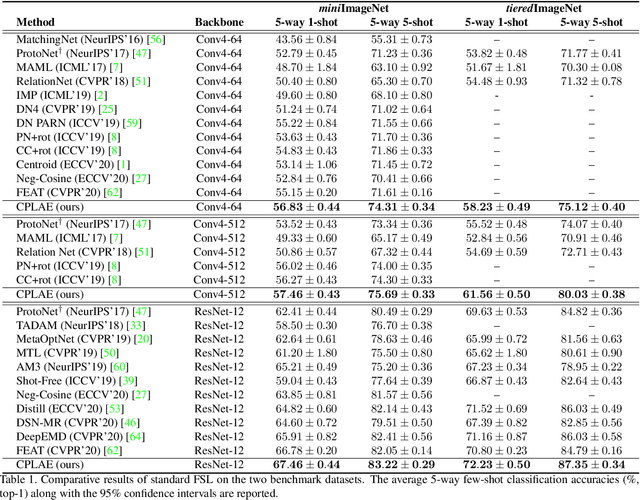
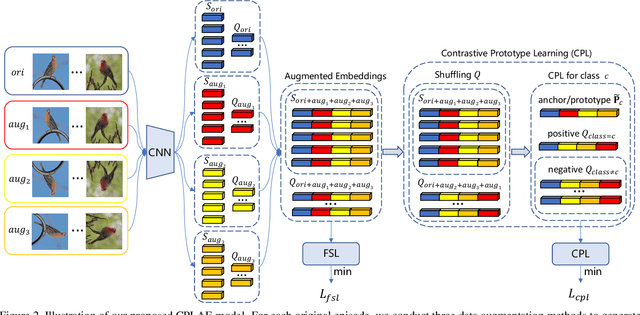
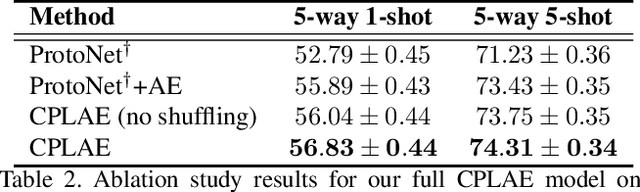
Abstract:Most recent few-shot learning (FSL) methods are based on meta-learning with episodic training. In each meta-training episode, a discriminative feature embedding and/or classifier are first constructed from a support set in an inner loop, and then evaluated in an outer loop using a query set for model updating. This query set sample centered learning objective is however intrinsically limited in addressing the lack of training data problem in the support set. In this paper, a novel contrastive prototype learning with augmented embeddings (CPLAE) model is proposed to overcome this limitation. First, data augmentations are introduced to both the support and query sets with each sample now being represented as an augmented embedding (AE) composed of concatenated embeddings of both the original and augmented versions. Second, a novel support set class prototype centered contrastive loss is proposed for contrastive prototype learning (CPL). With a class prototype as an anchor, CPL aims to pull the query samples of the same class closer and those of different classes further away. This support set sample centered loss is highly complementary to the existing query centered loss, fully exploiting the limited training data in each episode. Extensive experiments on several benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed CPLAE achieves new state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge