Chris Thomas
Virginia Tech, USA
Applying Ground Robot Fleets in Urban Search: Understanding Professionals' Operational Challenges and Design Opportunities
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Urban searches demand rapid, defensible decisions and sustained physical effort under high cognitive and situational load. Incident commanders must plan, coordinate, and document time-critical operations, while field searchers execute evolving tasks in uncertain environments. With recent advances in technology, ground-robot fleets paired with computer-vision-based situational awareness and LLM-powered interfaces offer the potential to ease these operational burdens. However, no dedicated studies have examined how public safety professionals perceive such technologies or envision their integration into existing practices, risking building technically sophisticated yet impractical solutions. To address this gap, we conducted focus-group sessions with eight police officers across five local departments in Virginia. Our findings show that ground robots could reduce professionals' reliance on paper references, mental calculations, and ad-hoc coordination, alleviating cognitive and physical strain in four key challenge areas: (1) partitioning the workforce across multiple search hypotheses, (2) retaining group awareness and situational awareness, (3) building route planning that fits the lost-person profile, and (4) managing cognitive and physical fatigue under uncertainty. We further identify four design opportunities and requirements for future ground-robot fleet integration in public-safety operations: (1) scalable multi-robot planning and control interfaces, (2) agency-specific route optimization, (3) real-time replanning informed by debrief updates, and (4) vision-assisted cueing that preserves operational trust while reducing cognitive workload. We conclude with design implications for deployable, accountable, and human-centered urban-search support systems
LAMP: Learning Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Multi-Image Tasks via Pre-trained Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable performance across vision-language tasks. Recent advancements allow these models to process multiple images as inputs. However, the vulnerabilities of multi-image MLLMs remain unexplored. Existing adversarial attacks focus on single-image settings and often assume a white-box threat model, which is impractical in many real-world scenarios. This paper introduces LAMP, a black-box method for learning Universal Adversarial Perturbations (UAPs) targeting multi-image MLLMs. LAMP applies an attention-based constraint that prevents the model from effectively aggregating information across images. LAMP also introduces a novel cross-image contagious constraint that forces perturbed tokens to influence clean tokens, spreading adversarial effects without requiring all inputs to be modified. Additionally, an index-attention suppression loss enables a robust position-invariant attack. Experimental results show that LAMP outperforms SOTA baselines and achieves the highest attack success rates across multiple vision-language tasks and models.
SoundBreak: A Systematic Study of Audio-Only Adversarial Attacks on Trimodal Models
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Multimodal foundation models that integrate audio, vision, and language achieve strong performance on reasoning and generation tasks, yet their robustness to adversarial manipulation remains poorly understood. We study a realistic and underexplored threat model: untargeted, audio-only adversarial attacks on trimodal audio-video-language models. We analyze six complementary attack objectives that target different stages of multimodal processing, including audio encoder representations, cross-modal attention, hidden states, and output likelihoods. Across three state-of-the-art models and multiple benchmarks, we show that audio-only perturbations can induce severe multimodal failures, achieving up to 96% attack success rate. We further show that attacks can be successful at low perceptual distortions (LPIPS <= 0.08, SI-SNR >= 0) and benefit more from extended optimization than increased data scale. Transferability across models and encoders remains limited, while speech recognition systems such as Whisper primarily respond to perturbation magnitude, achieving >97% attack success under severe distortion. These results expose a previously overlooked single-modality attack surface in multimodal systems and motivate defenses that enforce cross-modal consistency.
SteerVLM: Robust Model Control through Lightweight Activation Steering for Vision Language Models
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:This work introduces SteerVLM, a lightweight steering module designed to guide Vision-Language Models (VLMs) towards outputs that better adhere to desired instructions. Our approach learns from the latent embeddings of paired prompts encoding target and converse behaviors to dynamically adjust activations connecting the language modality with image context. This allows for fine-grained, inference-time control over complex output semantics without modifying model weights while preserving performance on off-target tasks. Our steering module requires learning parameters equal to 0.14% of the original VLM's size. Our steering module gains model control through dimension-wise activation modulation and adaptive steering across layers without requiring pre-extracted static vectors or manual tuning of intervention points. Furthermore, we introduce VNIA (Visual Narrative Intent Alignment), a multimodal dataset specifically created to facilitate the development and evaluation of VLM steering techniques. Our method outperforms existing intervention techniques on steering and hallucination mitigation benchmarks for VLMs and proposes a robust solution for multimodal model control through activation engineering.
Maximal Matching Matters: Preventing Representation Collapse for Robust Cross-Modal Retrieval
Jun 26, 2025
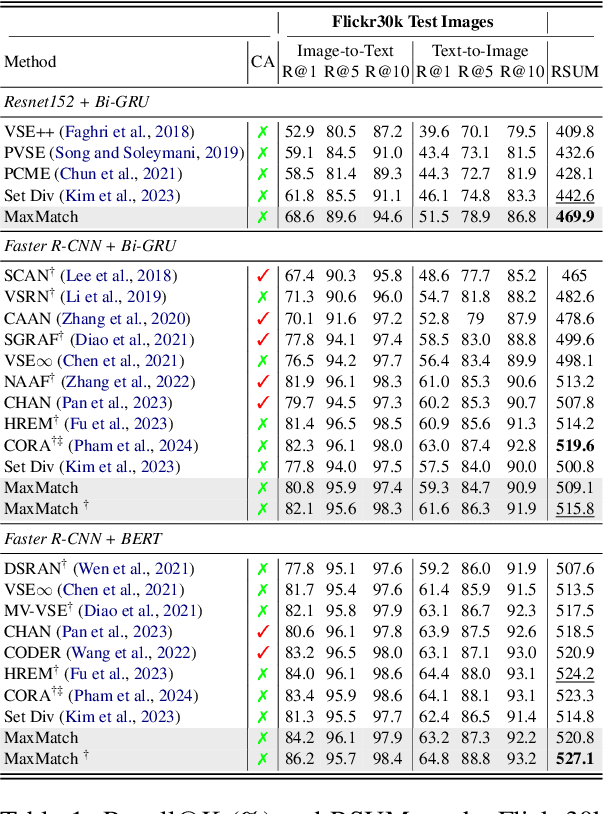


Abstract:Cross-modal image-text retrieval is challenging because of the diverse possible associations between content from different modalities. Traditional methods learn a single-vector embedding to represent semantics of each sample, but struggle to capture nuanced and diverse relationships that can exist across modalities. Set-based approaches, which represent each sample with multiple embeddings, offer a promising alternative, as they can capture richer and more diverse relationships. In this paper, we show that, despite their promise, these set-based representations continue to face issues including sparse supervision and set collapse, which limits their effectiveness. To address these challenges, we propose Maximal Pair Assignment Similarity to optimize one-to-one matching between embedding sets which preserve semantic diversity within the set. We also introduce two loss functions to further enhance the representations: Global Discriminative Loss to enhance distinction among embeddings, and Intra-Set Divergence Loss to prevent collapse within each set. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on MS-COCO and Flickr30k without relying on external data.
Flexible-length Text Infilling for Discrete Diffusion Models
Jun 16, 2025
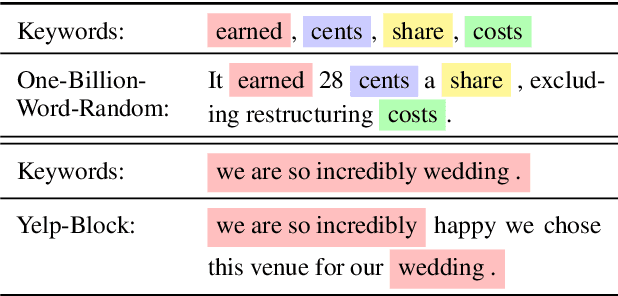
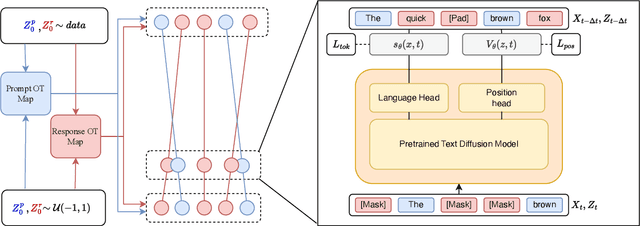

Abstract:Discrete diffusion models are a new class of text generators that offer advantages such as bidirectional context use, parallelizable generation, and flexible prompting compared to autoregressive models. However, a critical limitation of discrete diffusion models is their inability to perform flexible-length or flexible-position text infilling without access to ground-truth positional data. We introduce \textbf{DDOT} (\textbf{D}iscrete \textbf{D}iffusion with \textbf{O}ptimal \textbf{T}ransport Position Coupling), the first discrete diffusion model to overcome this challenge. DDOT jointly denoises token values and token positions, employing a novel sample-level Optimal Transport (OT) coupling. This coupling preserves relative token ordering while dynamically adjusting the positions and length of infilled segments, a capability previously missing in text diffusion. Our method is orthogonal to existing discrete text diffusion methods and is compatible with various pretrained text denoisers. Extensive experiments on text infilling benchmarks such as One-Billion-Word and Yelp demonstrate that DDOT outperforms naive diffusion baselines. Furthermore, DDOT achieves performance on par with state-of-the-art non-autoregressive models and enables significant improvements in training efficiency and flexibility.
ENTER: Event Based Interpretable Reasoning for VideoQA
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we present ENTER, an interpretable Video Question Answering (VideoQA) system based on event graphs. Event graphs convert videos into graphical representations, where video events form the nodes and event-event relationships (temporal/causal/hierarchical) form the edges. This structured representation offers many benefits: 1) Interpretable VideoQA via generated code that parses event-graph; 2) Incorporation of contextual visual information in the reasoning process (code generation) via event graphs; 3) Robust VideoQA via Hierarchical Iterative Update of the event graphs. Existing interpretable VideoQA systems are often top-down, disregarding low-level visual information in the reasoning plan generation, and are brittle. While bottom-up approaches produce responses from visual data, they lack interpretability. Experimental results on NExT-QA, IntentQA, and EgoSchema demonstrate that not only does our method outperform existing top-down approaches while obtaining competitive performance against bottom-up approaches, but more importantly, offers superior interpretability and explainability in the reasoning process.
Fixing Imbalanced Attention to Mitigate In-Context Hallucination of Large Vision-Language Model
Jan 21, 2025Abstract:Large Vision Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding and describing visual content, achieving state-of-the-art performance across various vision-language tasks. However, these models frequently exhibit hallucination behavior, where they generate descriptions containing objects or details absent in the input image. Our work investigates this phenomenon by analyzing attention patterns across transformer layers and heads, revealing that hallucinations often stem from progressive degradation of visual grounding in deeper layers. We propose a novel attention modification approach that combines selective token emphasis and head-specific modulation to maintain visual grounding throughout the generation process. Our method introduces two key components: (1) a dual-stream token selection mechanism that identifies and prioritizes both locally informative and spatially significant visual tokens, and (2) an attention head-specific modulation strategy that differentially amplifies visual information processing based on measured visual sensitivity of individual attention heads. Through extensive experimentation on the MSCOCO dataset, we demonstrate that our approach reduces hallucination rates by up to 62.3\% compared to baseline models while maintaining comparable task performance. Our analysis reveals that selectively modulating tokens across attention heads with varying levels of visual sensitivity can significantly improve visual grounding without requiring model retraining.
Advancing Chart Question Answering with Robust Chart Component Recognition
Jul 19, 2024Abstract:Chart comprehension presents significant challenges for machine learning models due to the diverse and intricate shapes of charts. Existing multimodal methods often overlook these visual features or fail to integrate them effectively for chart question answering (ChartQA). To address this, we introduce Chartformer, a unified framework that enhances chart component recognition by accurately identifying and classifying components such as bars, lines, pies, titles, legends, and axes. Additionally, we propose a novel Question-guided Deformable Co-Attention (QDCAt) mechanism, which fuses chart features encoded by Chartformer with the given question, leveraging the question's guidance to ground the correct answer. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed approaches significantly outperform baseline models in chart component recognition and ChartQA tasks, achieving improvements of 3.2% in mAP and 15.4% in accuracy, respectively. These results underscore the robustness of our solution for detailed visual data interpretation across various applications.
MetaSumPerceiver: Multimodal Multi-Document Evidence Summarization for Fact-Checking
Jul 18, 2024Abstract:Fact-checking real-world claims often requires reviewing multiple multimodal documents to assess a claim's truthfulness, which is a highly laborious and time-consuming task. In this paper, we present a summarization model designed to generate claim-specific summaries useful for fact-checking from multimodal, multi-document datasets. The model takes inputs in the form of documents, images, and a claim, with the objective of assisting in fact-checking tasks. We introduce a dynamic perceiver-based model that can handle inputs from multiple modalities of arbitrary lengths. To train our model, we leverage a novel reinforcement learning-based entailment objective to generate summaries that provide evidence distinguishing between different truthfulness labels. To assess the efficacy of our approach, we conduct experiments on both an existing benchmark and a new dataset of multi-document claims that we contribute. Our approach outperforms the SOTA approach by 4.6% in the claim verification task on the MOCHEG dataset and demonstrates strong performance on our new Multi-News-Fact-Checking dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge