Najibul Haque Sarker
LAMP: Learning Universal Adversarial Perturbations for Multi-Image Tasks via Pre-trained Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable performance across vision-language tasks. Recent advancements allow these models to process multiple images as inputs. However, the vulnerabilities of multi-image MLLMs remain unexplored. Existing adversarial attacks focus on single-image settings and often assume a white-box threat model, which is impractical in many real-world scenarios. This paper introduces LAMP, a black-box method for learning Universal Adversarial Perturbations (UAPs) targeting multi-image MLLMs. LAMP applies an attention-based constraint that prevents the model from effectively aggregating information across images. LAMP also introduces a novel cross-image contagious constraint that forces perturbed tokens to influence clean tokens, spreading adversarial effects without requiring all inputs to be modified. Additionally, an index-attention suppression loss enables a robust position-invariant attack. Experimental results show that LAMP outperforms SOTA baselines and achieves the highest attack success rates across multiple vision-language tasks and models.
An Optimized YOLOv5 Based Approach For Real-time Vehicle Detection At Road Intersections Using Fisheye Cameras
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Real time vehicle detection is a challenging task for urban traffic surveillance. Increase in urbanization leads to increase in accidents and traffic congestion in junction areas resulting in delayed travel time. In order to solve these problems, an intelligent system utilizing automatic detection and tracking system is significant. But this becomes a challenging task at road intersection areas which require a wide range of field view. For this reason, fish eye cameras are widely used in real time vehicle detection purpose to provide large area coverage and 360 degree view at junctions. However, it introduces challenges such as light glare from vehicles and street lights, shadow, non-linear distortion, scaling issues of vehicles and proper localization of small vehicles. To overcome each of these challenges, a modified YOLOv5 object detection scheme is proposed. YOLOv5 is a deep learning oriented convolutional neural network (CNN) based object detection method. The proposed scheme for detecting vehicles in fish-eye images consists of a light-weight day-night CNN classifier so that two different solutions can be implemented to address the day-night detection issues. Furthurmore, challenging instances are upsampled in the dataset for proper localization of vehicles and later on the detection model is ensembled and trained in different combination of vehicle datasets for better generalization, detection and accuracy. For testing, a real world fisheye dataset provided by the Video and Image Processing (VIP) Cup organizer ISSD has been used which includes images from video clips of different fisheye cameras at junction of different cities during day and night time. Experimental results show that our proposed model has outperformed the YOLOv5 model on the dataset by 13.7% mAP @ 0.5.
ENTER: Event Based Interpretable Reasoning for VideoQA
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:In this paper, we present ENTER, an interpretable Video Question Answering (VideoQA) system based on event graphs. Event graphs convert videos into graphical representations, where video events form the nodes and event-event relationships (temporal/causal/hierarchical) form the edges. This structured representation offers many benefits: 1) Interpretable VideoQA via generated code that parses event-graph; 2) Incorporation of contextual visual information in the reasoning process (code generation) via event graphs; 3) Robust VideoQA via Hierarchical Iterative Update of the event graphs. Existing interpretable VideoQA systems are often top-down, disregarding low-level visual information in the reasoning plan generation, and are brittle. While bottom-up approaches produce responses from visual data, they lack interpretability. Experimental results on NExT-QA, IntentQA, and EgoSchema demonstrate that not only does our method outperform existing top-down approaches while obtaining competitive performance against bottom-up approaches, but more importantly, offers superior interpretability and explainability in the reasoning process.
SONICS: Synthetic Or Not -- Identifying Counterfeit Songs
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:The recent surge in AI-generated songs presents exciting possibilities and challenges. While these tools democratize music creation, they also necessitate the ability to distinguish between human-composed and AI-generated songs for safeguarding artistic integrity and content curation. Existing research and datasets in fake song detection only focus on singing voice deepfake detection (SVDD), where the vocals are AI-generated but the instrumental music is sourced from real songs. However, this approach is inadequate for contemporary end-to-end AI-generated songs where all components (vocals, lyrics, music, and style) could be AI-generated. Additionally, existing datasets lack lyrics-music diversity, long-duration songs, and open fake songs. To address these gaps, we introduce SONICS, a novel dataset for end-to-end Synthetic Song Detection (SSD), comprising over 97k songs with over 49k synthetic songs from popular platforms like Suno and Udio. Furthermore, we highlight the importance of modeling long-range temporal dependencies in songs for effective authenticity detection, an aspect overlooked in existing methods. To capture these patterns, we propose a novel model, SpecTTTra, that is up to 3 times faster and 6 times more memory efficient compared to popular CNN and Transformer-based models while maintaining competitive performance. Finally, we offer both AI-based and Human evaluation benchmarks, addressing another deficiency in current research.
Leveraging Generative Language Models for Weakly Supervised Sentence Component Analysis in Video-Language Joint Learning
Dec 10, 2023Abstract:A thorough comprehension of textual data is a fundamental element in multi-modal video analysis tasks. However, recent works have shown that the current models do not achieve a comprehensive understanding of the textual data during the training for the target downstream tasks. Orthogonal to the previous approaches to this limitation, we postulate that understanding the significance of the sentence components according to the target task can potentially enhance the performance of the models. Hence, we utilize the knowledge of a pre-trained large language model (LLM) to generate text samples from the original ones, targeting specific sentence components. We propose a weakly supervised importance estimation module to compute the relative importance of the components and utilize them to improve different video-language tasks. Through rigorous quantitative analysis, our proposed method exhibits significant improvement across several video-language tasks. In particular, our approach notably enhances video-text retrieval by a relative improvement of 8.3\% in video-to-text and 1.4\% in text-to-video retrieval over the baselines, in terms of R@1. Additionally, in video moment retrieval, average mAP shows a relative improvement ranging from 2.0\% to 13.7 \% across different baselines.
Syn-Att: Synthetic Speech Attribution via Semi-Supervised Unknown Multi-Class Ensemble of CNNs
Sep 15, 2023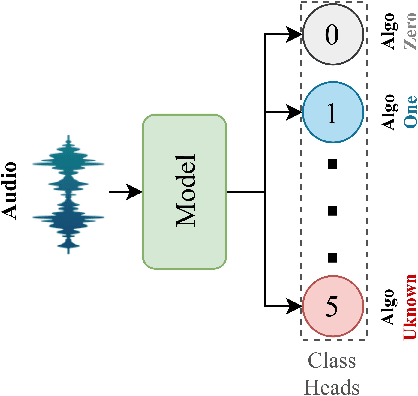
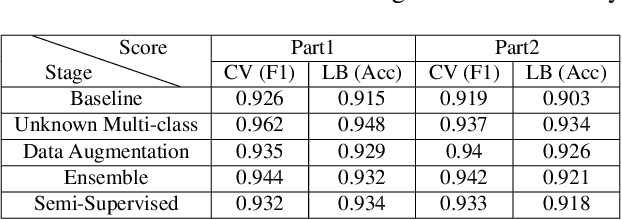
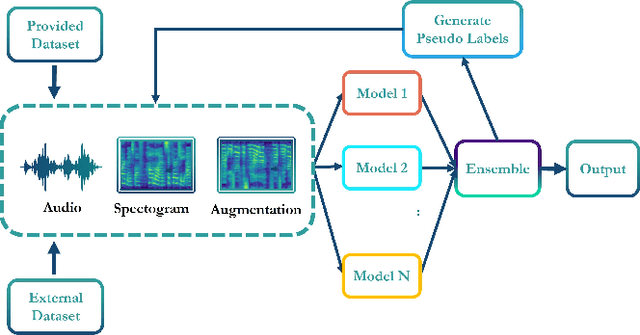
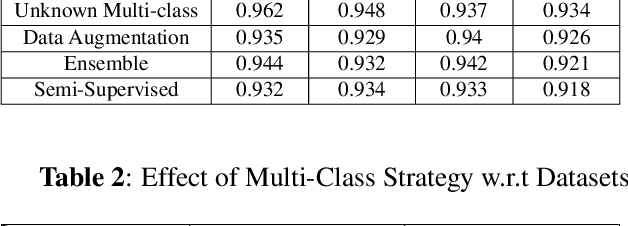
Abstract:With the huge technological advances introduced by deep learning in audio & speech processing, many novel synthetic speech techniques achieved incredible realistic results. As these methods generate realistic fake human voices, they can be used in malicious acts such as people imitation, fake news, spreading, spoofing, media manipulations, etc. Hence, the ability to detect synthetic or natural speech has become an urgent necessity. Moreover, being able to tell which algorithm has been used to generate a synthetic speech track can be of preeminent importance to track down the culprit. In this paper, a novel strategy is proposed to attribute a synthetic speech track to the generator that is used to synthesize it. The proposed detector transforms the audio into log-mel spectrogram, extracts features using CNN, and classifies it between five known and unknown algorithms, utilizing semi-supervision and ensemble to improve its robustness and generalizability significantly. The proposed detector is validated on two evaluation datasets consisting of a total of 18,000 weakly perturbed (Eval 1) & 10,000 strongly perturbed (Eval 2) synthetic speeches. The proposed method outperforms other top teams in accuracy by 12-13% on Eval 2 and 1-2% on Eval 1, in the IEEE SP Cup challenge at ICASSP 2022.
ArtiFact: A Large-Scale Dataset with Artificial and Factual Images for Generalizable and Robust Synthetic Image Detection
Feb 24, 2023



Abstract:Synthetic image generation has opened up new opportunities but has also created threats in regard to privacy, authenticity, and security. Detecting fake images is of paramount importance to prevent illegal activities, and previous research has shown that generative models leave unique patterns in their synthetic images that can be exploited to detect them. However, the fundamental problem of generalization remains, as even state-of-the-art detectors encounter difficulty when facing generators never seen during training. To assess the generalizability and robustness of synthetic image detectors in the face of real-world impairments, this paper presents a large-scale dataset named ArtiFact, comprising diverse generators, object categories, and real-world challenges. Moreover, the proposed multi-class classification scheme, combined with a filter stride reduction strategy addresses social platform impairments and effectively detects synthetic images from both seen and unseen generators. The proposed solution significantly outperforms other top teams by 8.34% on Test 1, 1.26% on Test 2, and 15.08% on Test 3 in the IEEE VIP Cup challenge at ICIP 2022, as measured by the accuracy metric.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge