Ali Dabouei
GIF: Generative Inspiration for Face Recognition at Scale
May 05, 2025



Abstract:Aiming to reduce the computational cost of Softmax in massive label space of Face Recognition (FR) benchmarks, recent studies estimate the output using a subset of identities. Although promising, the association between the computation cost and the number of identities in the dataset remains linear only with a reduced ratio. A shared characteristic among available FR methods is the employment of atomic scalar labels during training. Consequently, the input to label matching is through a dot product between the feature vector of the input and the Softmax centroids. Inspired by generative modeling, we present a simple yet effective method that substitutes scalar labels with structured identity code, i.e., a sequence of integers. Specifically, we propose a tokenization scheme that transforms atomic scalar labels into structured identity codes. Then, we train an FR backbone to predict the code for each input instead of its scalar label. As a result, the associated computational cost becomes logarithmic w.r.t. number of identities. We demonstrate the benefits of the proposed method by conducting experiments. In particular, our method outperforms its competitors by 1.52%, and 0.6% at TAR@FAR$=1e-4$ on IJB-B and IJB-C, respectively, while transforming the association between computational cost and the number of identities from linear to logarithmic. See code at https://github.com/msed-Ebrahimi/GIF
Decomposed Distribution Matching in Dataset Condensation
Dec 06, 2024
Abstract:Dataset Condensation (DC) aims to reduce deep neural networks training efforts by synthesizing a small dataset such that it will be as effective as the original large dataset. Conventionally, DC relies on a costly bi-level optimization which prohibits its practicality. Recent research formulates DC as a distribution matching problem which circumvents the costly bi-level optimization. However, this efficiency sacrifices the DC performance. To investigate this performance degradation, we decomposed the dataset distribution into content and style. Our observations indicate two major shortcomings of: 1) style discrepancy between original and condensed data, and 2) limited intra-class diversity of condensed dataset. We present a simple yet effective method to match the style information between original and condensed data, employing statistical moments of feature maps as well-established style indicators. Moreover, we enhance the intra-class diversity by maximizing the Kullback-Leibler divergence within each synthetic class, i.e., content. We demonstrate the efficacy of our method through experiments on diverse datasets of varying size and resolution, achieving improvements of up to 4.1% on CIFAR10, 4.2% on CIFAR100, 4.3% on TinyImageNet, 2.0% on ImageNet-1K, 3.3% on ImageWoof, 2.5% on ImageNette, and 5.5% in continual learning accuracy.
Cross-Domain Learning for Video Anomaly Detection with Limited Supervision
Aug 09, 2024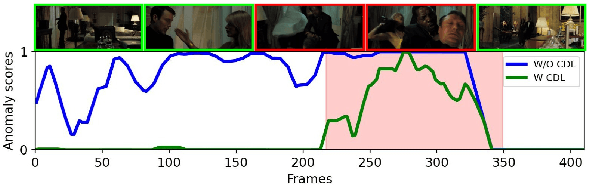

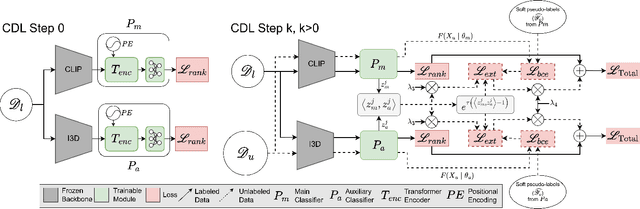
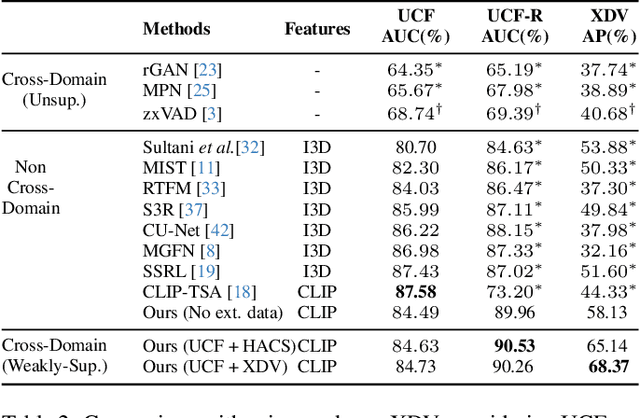
Abstract:Video Anomaly Detection (VAD) automates the identification of unusual events, such as security threats in surveillance videos. In real-world applications, VAD models must effectively operate in cross-domain settings, identifying rare anomalies and scenarios not well-represented in the training data. However, existing cross-domain VAD methods focus on unsupervised learning, resulting in performance that falls short of real-world expectations. Since acquiring weak supervision, i.e., video-level labels, for the source domain is cost-effective, we conjecture that combining it with external unlabeled data has notable potential to enhance cross-domain performance. To this end, we introduce a novel weakly-supervised framework for Cross-Domain Learning (CDL) in VAD that incorporates external data during training by estimating its prediction bias and adaptively minimizing that using the predicted uncertainty. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed CDL framework through comprehensive experiments conducted in various configurations on two large-scale VAD datasets: UCF-Crime and XD-Violence. Our method significantly surpasses the state-of-the-art works in cross-domain evaluations, achieving an average absolute improvement of 19.6% on UCF-Crime and 12.87% on XD-Violence.
ARoFace: Alignment Robustness to Improve Low-Quality Face Recognition
Jul 20, 2024



Abstract:Aiming to enhance Face Recognition (FR) on Low-Quality (LQ) inputs, recent studies suggest incorporating synthetic LQ samples into training. Although promising, the quality factors that are considered in these works are general rather than FR-specific, \eg, atmospheric turbulence, resolution, \etc. Motivated by the observation of the vulnerability of current FR models to even small Face Alignment Errors (FAE) in LQ images, we present a simple yet effective method that considers FAE as another quality factor that is tailored to FR. We seek to improve LQ FR by enhancing FR models' robustness to FAE. To this aim, we formalize the problem as a combination of differentiable spatial transformations and adversarial data augmentation in FR. We perturb the alignment of the training samples using a controllable spatial transformation and enrich the training with samples expressing FAE. We demonstrate the benefits of the proposed method by conducting evaluations on IJB-B, IJB-C, IJB-S (+4.3\% Rank1), and TinyFace (+2.63\%). \href{https://github.com/msed-Ebrahimi/ARoFace}{https://github.com/msed-Ebrahimi/ARoFace}
UFQA: Utility guided Fingerphoto Quality Assessment
Jul 15, 2024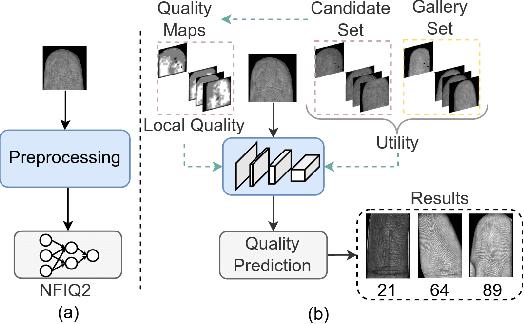
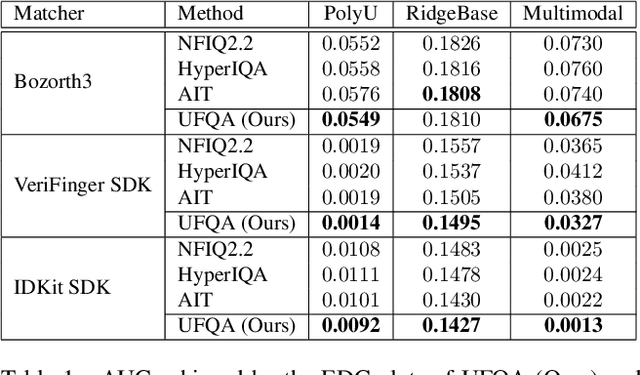
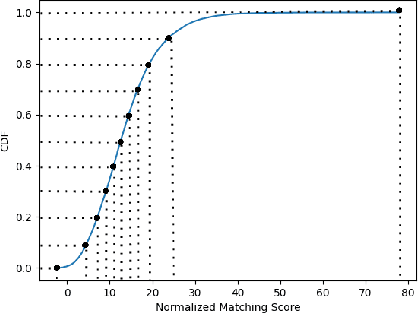
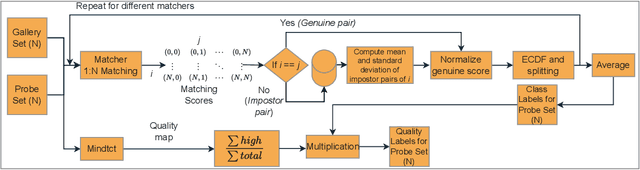
Abstract:Quality assessment of fingerprints captured using digital cameras and smartphones, also called fingerphotos, is a challenging problem in biometric recognition systems. As contactless biometric modalities are gaining more attention, their reliability should also be improved. Many factors, such as illumination, image contrast, camera angle, etc., in fingerphoto acquisition introduce various types of distortion that may render the samples useless. Current quality estimation methods developed for fingerprints collected using contact-based sensors are inadequate for fingerphotos. We propose Utility guided Fingerphoto Quality Assessment (UFQA), a self-supervised dual encoder framework to learn meaningful feature representations to assess fingerphoto quality. A quality prediction model is trained to assess fingerphoto quality with additional supervision of quality maps. The quality metric is a predictor of the utility of fingerphotos in matching scenarios. Therefore, we use a holistic approach by including fingerphoto utility and local quality when labeling the training data. Experimental results verify that our approach performs better than the widely used fingerprint quality metric NFIQ2.2 and state-of-the-art image quality assessment algorithms on multiple publicly available fingerphoto datasets.
Distilling Aggregated Knowledge for Weakly-Supervised Video Anomaly Detection
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Video anomaly detection aims to develop automated models capable of identifying abnormal events in surveillance videos. The benchmark setup for this task is extremely challenging due to: i) the limited size of the training sets, ii) weak supervision provided in terms of video-level labels, and iii) intrinsic class imbalance induced by the scarcity of abnormal events. In this work, we show that distilling knowledge from aggregated representations of multiple backbones into a relatively simple model achieves state-of-the-art performance. In particular, we develop a bi-level distillation approach along with a novel disentangled cross-attention-based feature aggregation network. Our proposed approach, DAKD (Distilling Aggregated Knowledge with Disentangled Attention), demonstrates superior performance compared to existing methods across multiple benchmark datasets. Notably, we achieve significant improvements of 1.36%, 0.78%, and 7.02% on the UCF-Crime, ShanghaiTech, and XD-Violence datasets, respectively.
Hyperspherical Classification with Dynamic Label-to-Prototype Assignment
Mar 25, 2024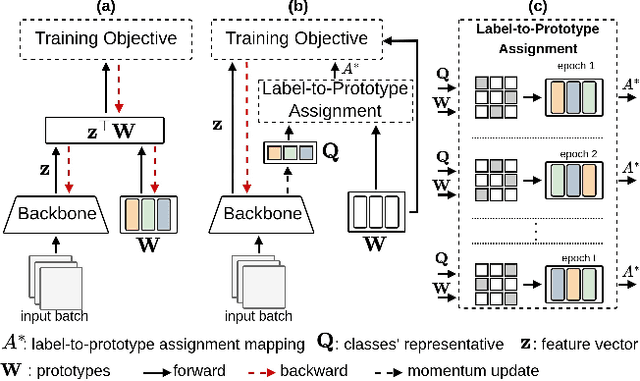
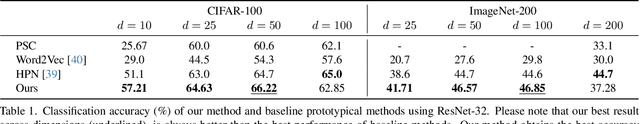
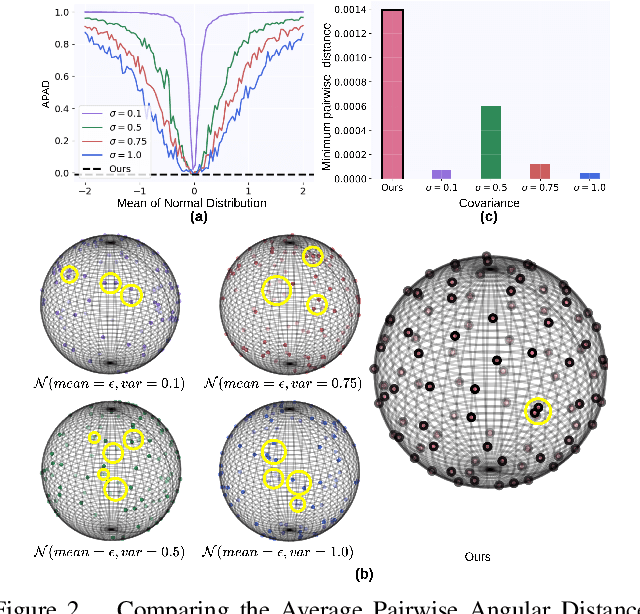
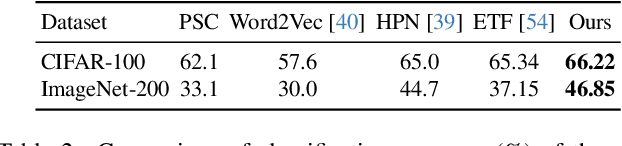
Abstract:Aiming to enhance the utilization of metric space by the parametric softmax classifier, recent studies suggest replacing it with a non-parametric alternative. Although a non-parametric classifier may provide better metric space utilization, it introduces the challenge of capturing inter-class relationships. A shared characteristic among prior non-parametric classifiers is the static assignment of labels to prototypes during the training, ie, each prototype consistently represents a class throughout the training course. Orthogonal to previous works, we present a simple yet effective method to optimize the category assigned to each prototype (label-to-prototype assignment) during the training. To this aim, we formalize the problem as a two-step optimization objective over network parameters and label-to-prototype assignment mapping. We solve this optimization using a sequential combination of gradient descent and Bipartide matching. We demonstrate the benefits of the proposed approach by conducting experiments on balanced and long-tail classification problems using different backbone network architectures. In particular, our method outperforms its competitors by 1.22\% accuracy on CIFAR-100, and 2.15\% on ImageNet-200 using a metric space dimension half of the size of its competitors. Code: https://github.com/msed-Ebrahimi/DL2PA_CVPR24
Leveraging Generative Language Models for Weakly Supervised Sentence Component Analysis in Video-Language Joint Learning
Dec 10, 2023Abstract:A thorough comprehension of textual data is a fundamental element in multi-modal video analysis tasks. However, recent works have shown that the current models do not achieve a comprehensive understanding of the textual data during the training for the target downstream tasks. Orthogonal to the previous approaches to this limitation, we postulate that understanding the significance of the sentence components according to the target task can potentially enhance the performance of the models. Hence, we utilize the knowledge of a pre-trained large language model (LLM) to generate text samples from the original ones, targeting specific sentence components. We propose a weakly supervised importance estimation module to compute the relative importance of the components and utilize them to improve different video-language tasks. Through rigorous quantitative analysis, our proposed method exhibits significant improvement across several video-language tasks. In particular, our approach notably enhances video-text retrieval by a relative improvement of 8.3\% in video-to-text and 1.4\% in text-to-video retrieval over the baselines, in terms of R@1. Additionally, in video moment retrieval, average mAP shows a relative improvement ranging from 2.0\% to 13.7 \% across different baselines.
Synthetic Latent Fingerprint Generation Using Style Transfer
Sep 27, 2023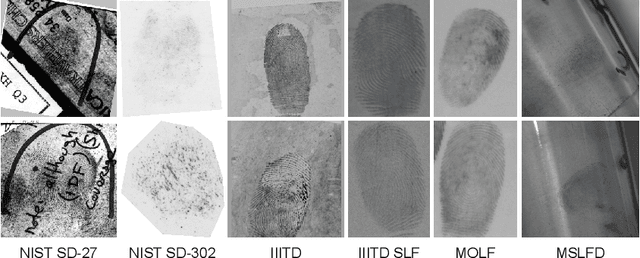
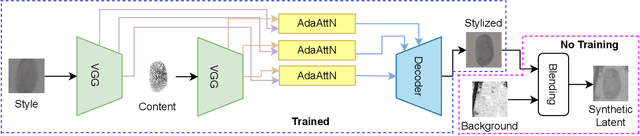
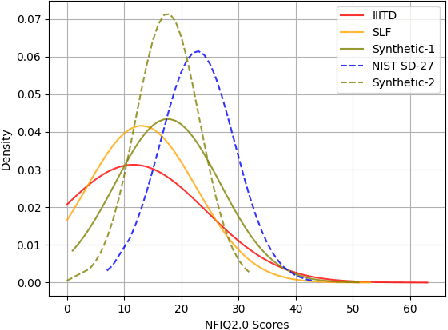
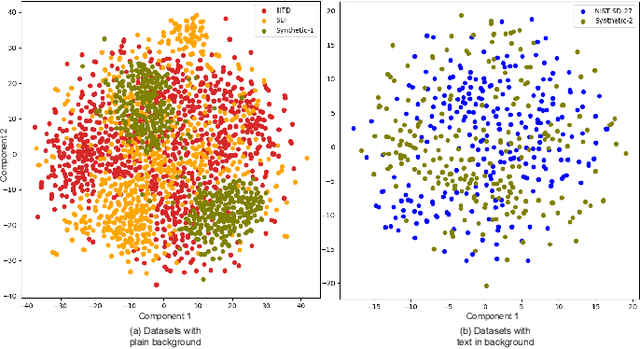
Abstract:Limited data availability is a challenging problem in the latent fingerprint domain. Synthetically generated fingerprints are vital for training data-hungry neural network-based algorithms. Conventional methods distort clean fingerprints to generate synthetic latent fingerprints. We propose a simple and effective approach using style transfer and image blending to synthesize realistic latent fingerprints. Our evaluation criteria and experiments demonstrate that the generated synthetic latent fingerprints preserve the identity information from the input contact-based fingerprints while possessing similar characteristics as real latent fingerprints. Additionally, we show that the generated fingerprints exhibit several qualities and styles, suggesting that the proposed method can generate multiple samples from a single fingerprint.
Revisiting Outer Optimization in Adversarial Training
Sep 02, 2022
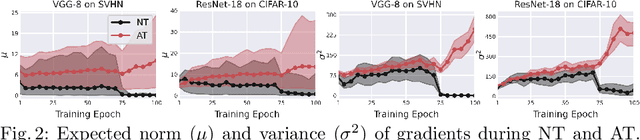
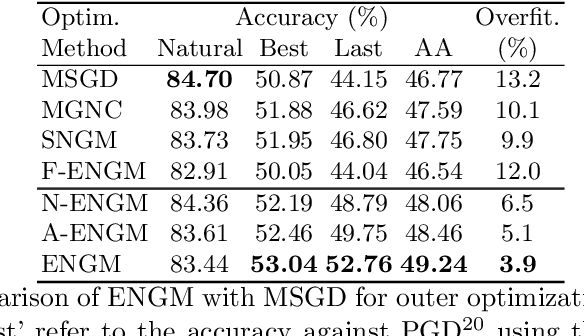
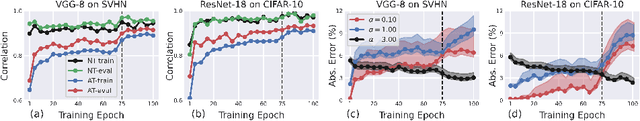
Abstract:Despite the fundamental distinction between adversarial and natural training (AT and NT), AT methods generally adopt momentum SGD (MSGD) for the outer optimization. This paper aims to analyze this choice by investigating the overlooked role of outer optimization in AT. Our exploratory evaluations reveal that AT induces higher gradient norm and variance compared to NT. This phenomenon hinders the outer optimization in AT since the convergence rate of MSGD is highly dependent on the variance of the gradients. To this end, we propose an optimization method called ENGM which regularizes the contribution of each input example to the average mini-batch gradients. We prove that the convergence rate of ENGM is independent of the variance of the gradients, and thus, it is suitable for AT. We introduce a trick to reduce the computational cost of ENGM using empirical observations on the correlation between the norm of gradients w.r.t. the network parameters and input examples. Our extensive evaluations and ablation studies on CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and TinyImageNet demonstrate that ENGM and its variants consistently improve the performance of a wide range of AT methods. Furthermore, ENGM alleviates major shortcomings of AT including robust overfitting and high sensitivity to hyperparameter settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge