Nasser Nasrabadi
CLFace: A Scalable and Resource-Efficient Continual Learning Framework for Lifelong Face Recognition
Nov 21, 2024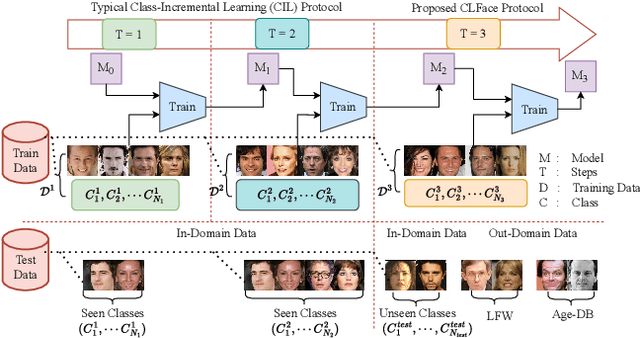
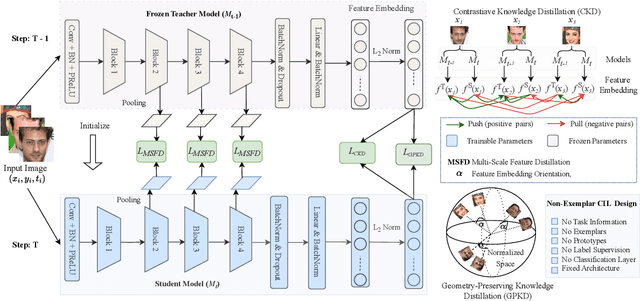
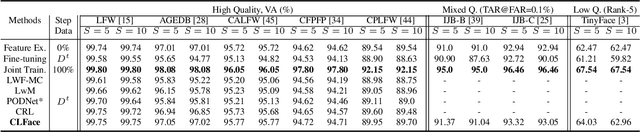
Abstract:An important aspect of deploying face recognition (FR) algorithms in real-world applications is their ability to learn new face identities from a continuous data stream. However, the online training of existing deep neural network-based FR algorithms, which are pre-trained offline on large-scale stationary datasets, encounter two major challenges: (I) catastrophic forgetting of previously learned identities, and (II) the need to store past data for complete retraining from scratch, leading to significant storage constraints and privacy concerns. In this paper, we introduce CLFace, a continual learning framework designed to preserve and incrementally extend the learned knowledge. CLFace eliminates the classification layer, resulting in a resource-efficient FR model that remains fixed throughout lifelong learning and provides label-free supervision to a student model, making it suitable for open-set face recognition during incremental steps. We introduce an objective function that employs feature-level distillation to reduce drift between feature maps of the student and teacher models across multiple stages. Additionally, it incorporates a geometry-preserving distillation scheme to maintain the orientation of the teacher model's feature embedding. Furthermore, a contrastive knowledge distillation is incorporated to continually enhance the discriminative power of the feature representation by matching similarities between new identities. Experiments on several benchmark FR datasets demonstrate that CLFace outperforms baseline approaches and state-of-the-art methods on unseen identities using both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets.
HF-Diff: High-Frequency Perceptual Loss and Distribution Matching for One-Step Diffusion-Based Image Super-Resolution
Nov 20, 2024Abstract:Although recent diffusion-based single-step super-resolution methods achieve better performance as compared to SinSR, they are computationally complex. To improve the performance of SinSR, we investigate preserving the high-frequency detail features during super-resolution (SR) because the downgraded images lack detailed information. For this purpose, we introduce a high-frequency perceptual loss by utilizing an invertible neural network (INN) pretrained on the ImageNet dataset. Different feature maps of pretrained INN produce different high-frequency aspects of an image. During the training phase, we impose to preserve the high-frequency features of super-resolved and ground truth (GT) images that improve the SR image quality during inference. Furthermore, we also utilize the Jenson-Shannon divergence between GT and SR images in the pretrained DINO-v2 embedding space to match their distribution. By introducing the $\textbf{h}igh$- $\textbf{f}requency$ preserving loss and distribution matching constraint in the single-step $\textbf{diff}usion-based$ SR ($\textbf{HF-Diff}$), we achieve a state-of-the-art CLIPIQA score in the benchmark RealSR, RealSet65, DIV2K-Val, and ImageNet datasets. Furthermore, the experimental results in several datasets demonstrate that our high-frequency perceptual loss yields better SR image quality than LPIPS and VGG-based perceptual losses. Our code will be released at https://github.com/shoaib-sami/HF-Diff.
UFQA: Utility guided Fingerphoto Quality Assessment
Jul 15, 2024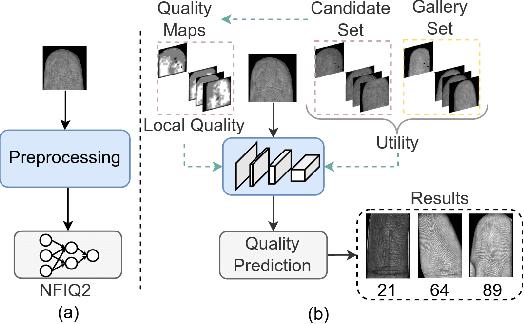
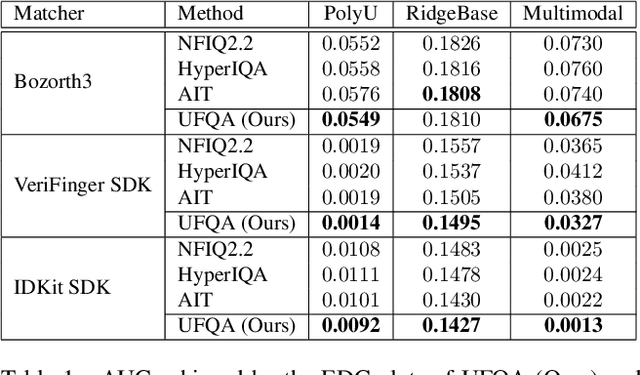
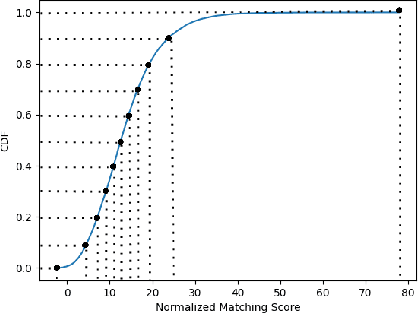
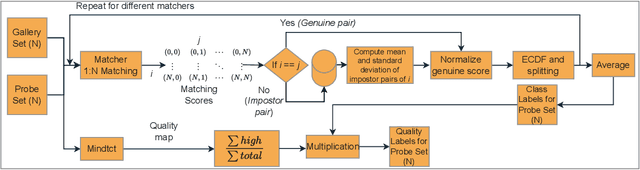
Abstract:Quality assessment of fingerprints captured using digital cameras and smartphones, also called fingerphotos, is a challenging problem in biometric recognition systems. As contactless biometric modalities are gaining more attention, their reliability should also be improved. Many factors, such as illumination, image contrast, camera angle, etc., in fingerphoto acquisition introduce various types of distortion that may render the samples useless. Current quality estimation methods developed for fingerprints collected using contact-based sensors are inadequate for fingerphotos. We propose Utility guided Fingerphoto Quality Assessment (UFQA), a self-supervised dual encoder framework to learn meaningful feature representations to assess fingerphoto quality. A quality prediction model is trained to assess fingerphoto quality with additional supervision of quality maps. The quality metric is a predictor of the utility of fingerphotos in matching scenarios. Therefore, we use a holistic approach by including fingerphoto utility and local quality when labeling the training data. Experimental results verify that our approach performs better than the widely used fingerprint quality metric NFIQ2.2 and state-of-the-art image quality assessment algorithms on multiple publicly available fingerphoto datasets.
Text-Guided Face Recognition using Multi-Granularity Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning
Dec 14, 2023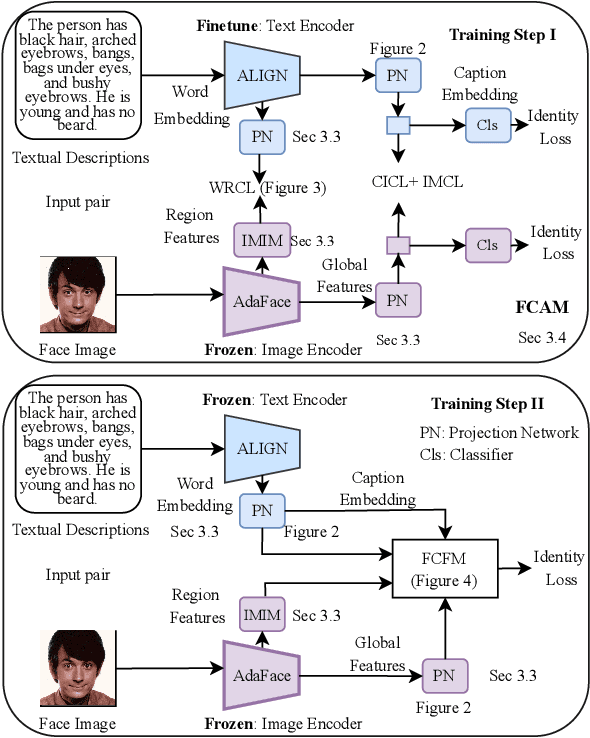
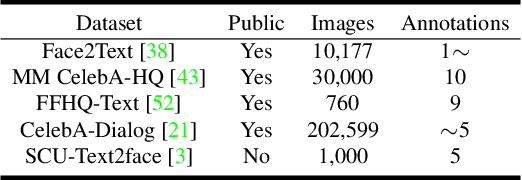
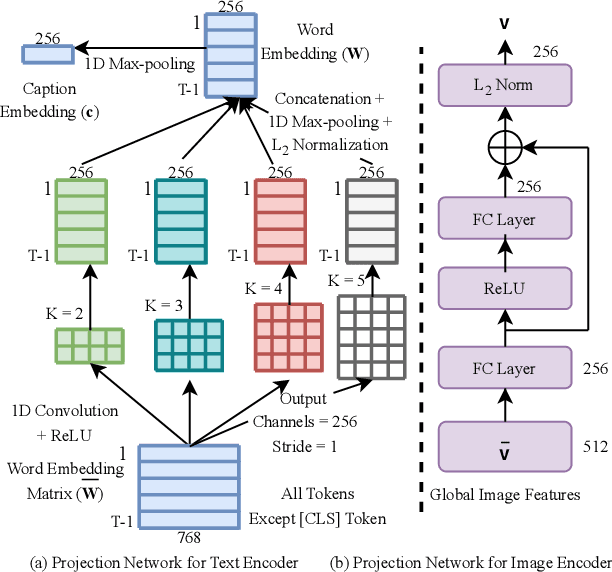
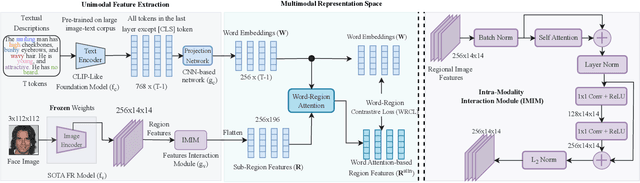
Abstract:State-of-the-art face recognition (FR) models often experience a significant performance drop when dealing with facial images in surveillance scenarios where images are in low quality and often corrupted with noise. Leveraging facial characteristics, such as freckles, scars, gender, and ethnicity, becomes highly beneficial in improving FR performance in such scenarios. In this paper, we introduce text-guided face recognition (TGFR) to analyze the impact of integrating facial attributes in the form of natural language descriptions. We hypothesize that adding semantic information into the loop can significantly improve the image understanding capability of an FR algorithm compared to other soft biometrics. However, learning a discriminative joint embedding within the multimodal space poses a considerable challenge due to the semantic gap in the unaligned image-text representations, along with the complexities arising from ambiguous and incoherent textual descriptions of the face. To address these challenges, we introduce a face-caption alignment module (FCAM), which incorporates cross-modal contrastive losses across multiple granularities to maximize the mutual information between local and global features of the face-caption pair. Within FCAM, we refine both facial and textual features for learning aligned and discriminative features. We also design a face-caption fusion module (FCFM) that applies fine-grained interactions and coarse-grained associations among cross-modal features. Through extensive experiments conducted on three face-caption datasets, proposed TGFR demonstrates remarkable improvements, particularly on low-quality images, over existing FR models and outperforms other related methods and benchmarks.
A Universal Anti-Spoofing Approach for Contactless Fingerprint Biometric Systems
Oct 23, 2023
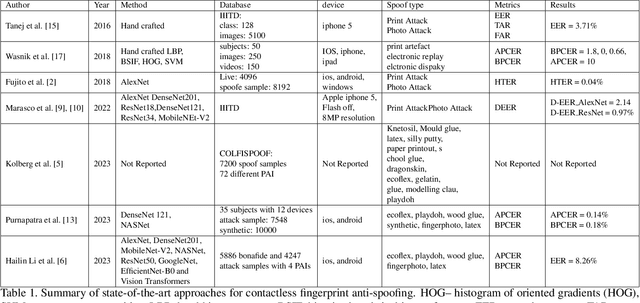
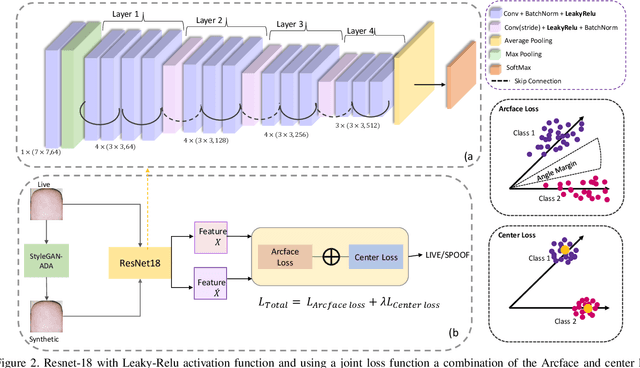
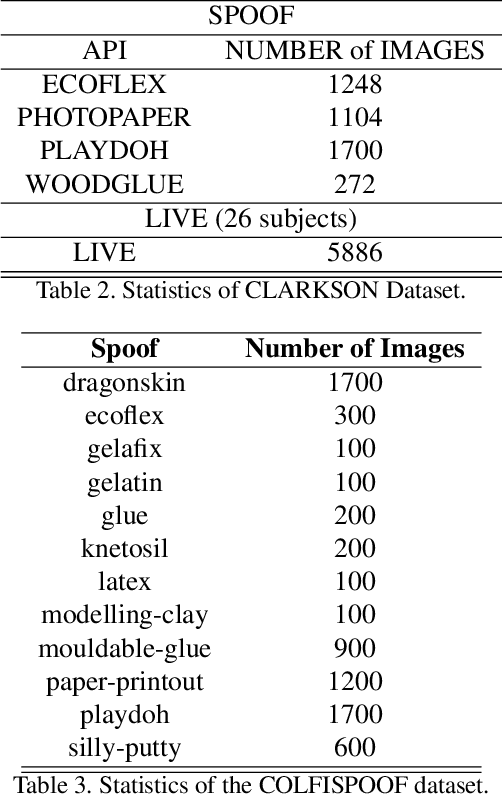
Abstract:With the increasing integration of smartphones into our daily lives, fingerphotos are becoming a potential contactless authentication method. While it offers convenience, it is also more vulnerable to spoofing using various presentation attack instruments (PAI). The contactless fingerprint is an emerging biometric authentication but has not yet been heavily investigated for anti-spoofing. While existing anti-spoofing approaches demonstrated fair results, they have encountered challenges in terms of universality and scalability to detect any unseen/unknown spoofed samples. To address this issue, we propose a universal presentation attack detection method for contactless fingerprints, despite having limited knowledge of presentation attack samples. We generated synthetic contactless fingerprints using StyleGAN from live finger photos and integrating them to train a semi-supervised ResNet-18 model. A novel joint loss function, combining the Arcface and Center loss, is introduced with a regularization to balance between the two loss functions and minimize the variations within the live samples while enhancing the inter-class variations between the deepfake and live samples. We also conducted a comprehensive comparison of different regularizations' impact on the joint loss function for presentation attack detection (PAD) and explored the performance of a modified ResNet-18 architecture with different activation functions (i.e., leaky ReLU and RelU) in conjunction with Arcface and center loss. Finally, we evaluate the performance of the model using unseen types of spoof attacks and live data. Our proposed method achieves a Bona Fide Classification Error Rate (BPCER) of 0.12\%, an Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate (APCER) of 0.63\%, and an Average Classification Error Rate (ACER) of 0.37\%.
Synthetic Latent Fingerprint Generation Using Style Transfer
Sep 27, 2023
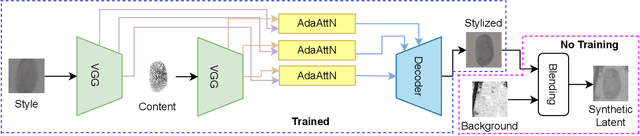
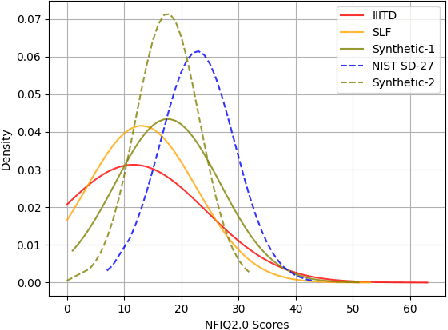
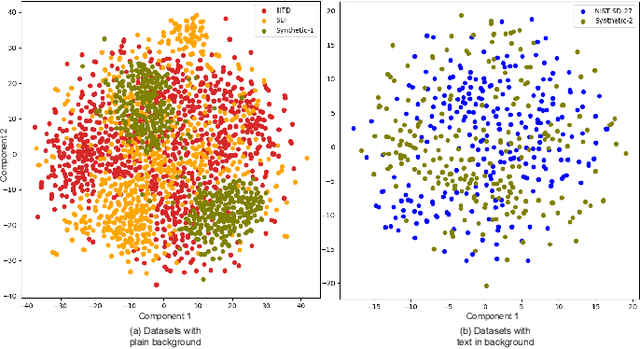
Abstract:Limited data availability is a challenging problem in the latent fingerprint domain. Synthetically generated fingerprints are vital for training data-hungry neural network-based algorithms. Conventional methods distort clean fingerprints to generate synthetic latent fingerprints. We propose a simple and effective approach using style transfer and image blending to synthesize realistic latent fingerprints. Our evaluation criteria and experiments demonstrate that the generated synthetic latent fingerprints preserve the identity information from the input contact-based fingerprints while possessing similar characteristics as real latent fingerprints. Additionally, we show that the generated fingerprints exhibit several qualities and styles, suggesting that the proposed method can generate multiple samples from a single fingerprint.
Improving Face Recognition from Caption Supervision with Multi-Granular Contextual Feature Aggregation
Aug 13, 2023
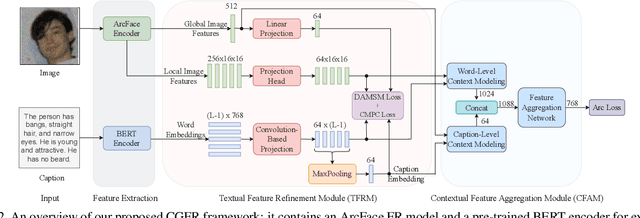

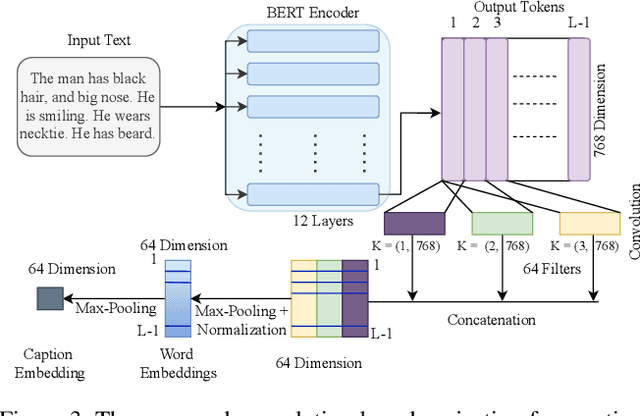
Abstract:We introduce caption-guided face recognition (CGFR) as a new framework to improve the performance of commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) face recognition (FR) systems. In contrast to combining soft biometrics (eg., facial marks, gender, and age) with face images, in this work, we use facial descriptions provided by face examiners as a piece of auxiliary information. However, due to the heterogeneity of the modalities, improving the performance by directly fusing the textual and facial features is very challenging, as both lie in different embedding spaces. In this paper, we propose a contextual feature aggregation module (CFAM) that addresses this issue by effectively exploiting the fine-grained word-region interaction and global image-caption association. Specifically, CFAM adopts a self-attention and a cross-attention scheme for improving the intra-modality and inter-modality relationship between the image and textual features, respectively. Additionally, we design a textual feature refinement module (TFRM) that refines the textual features of the pre-trained BERT encoder by updating the contextual embeddings. This module enhances the discriminative power of textual features with a cross-modal projection loss and realigns the word and caption embeddings with visual features by incorporating a visual-semantic alignment loss. We implemented the proposed CGFR framework on two face recognition models (ArcFace and AdaFace) and evaluated its performance on the Multi-Modal CelebA-HQ dataset. Our framework significantly improves the performance of ArcFace in both 1:1 verification and 1:N identification protocol.
Benchmarking Human Face Similarity Using Identical Twins
Aug 25, 2022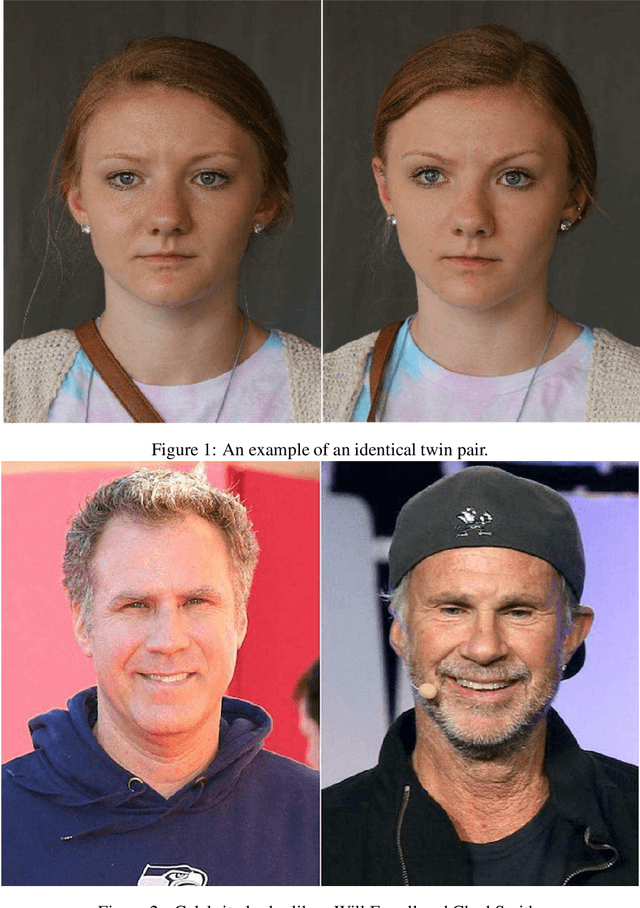
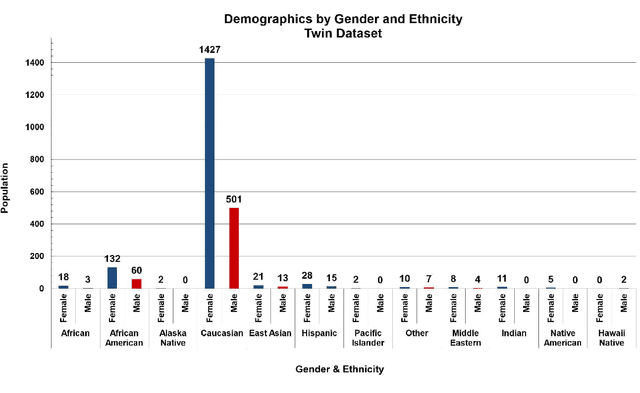
Abstract:The problem of distinguishing identical twins and non-twin look-alikes in automated facial recognition (FR) applications has become increasingly important with the widespread adoption of facial biometrics. Due to the high facial similarity of both identical twins and look-alikes, these face pairs represent the hardest cases presented to facial recognition tools. This work presents an application of one of the largest twin datasets compiled to date to address two FR challenges: 1) determining a baseline measure of facial similarity between identical twins and 2) applying this similarity measure to determine the impact of doppelgangers, or look-alikes, on FR performance for large face datasets. The facial similarity measure is determined via a deep convolutional neural network. This network is trained on a tailored verification task designed to encourage the network to group together highly similar face pairs in the embedding space and achieves a test AUC of 0.9799. The proposed network provides a quantitative similarity score for any two given faces and has been applied to large-scale face datasets to identify similar face pairs. An additional analysis which correlates the comparison score returned by a facial recognition tool and the similarity score returned by the proposed network has also been performed.
Synthesis-Guided Feature Learning for Cross-Spectral Periocular Recognition
Nov 16, 2021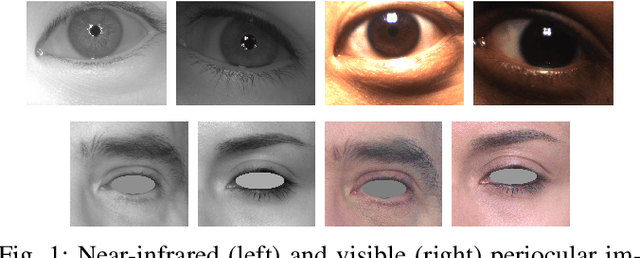
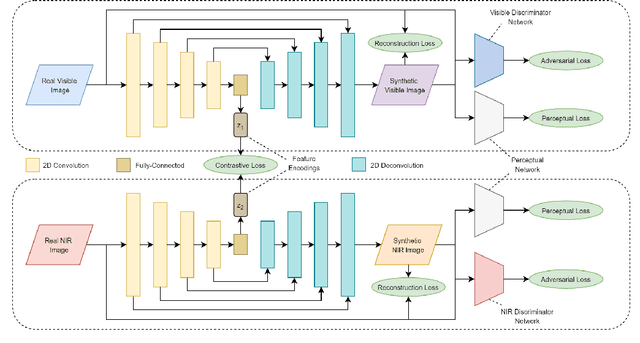
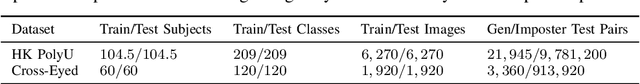
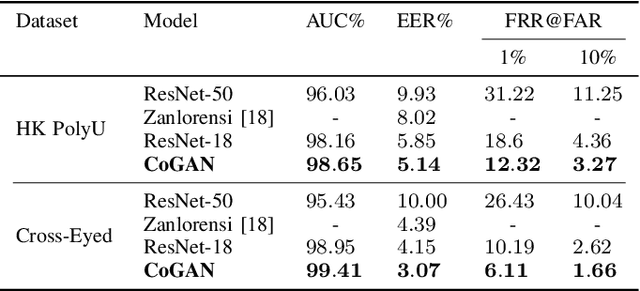
Abstract:A common yet challenging scenario in periocular biometrics is cross-spectral matching - in particular, the matching of visible wavelength against near-infrared (NIR) periocular images. We propose a novel approach to cross-spectral periocular verification that primarily focuses on learning a mapping from visible and NIR periocular images to a shared latent representational subspace, and supports this effort by simultaneously learning intra-spectral image reconstruction. We show the auxiliary image reconstruction task (and in particular the reconstruction of high-level, semantic features) results in learning a more discriminative, domain-invariant subspace compared to the baseline while incurring no additional computational or memory costs at test-time. The proposed Coupled Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (CoGAN) architecture uses paired generator networks (one operating on visible images and the other on NIR) composed of U-Nets with ResNet-18 encoders trained for feature learning via contrastive loss and for intra-spectral image reconstruction with adversarial, pixel-based, and perceptual reconstruction losses. Moreover, the proposed CoGAN model beats the current state-of-art (SotA) in cross-spectral periocular recognition. On the Hong Kong PolyU benchmark dataset, we achieve 98.65% AUC and 5.14% EER compared to the SotA EER of 8.02%. On the Cross-Eyed dataset, we achieve 99.31% AUC and 3.99% EER versus SotA EER of 4.39%.
Deep Hashing for Secure Multimodal Biometrics
Dec 29, 2020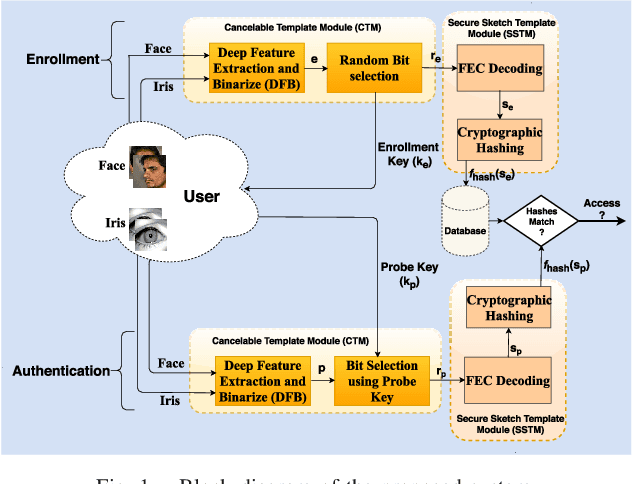
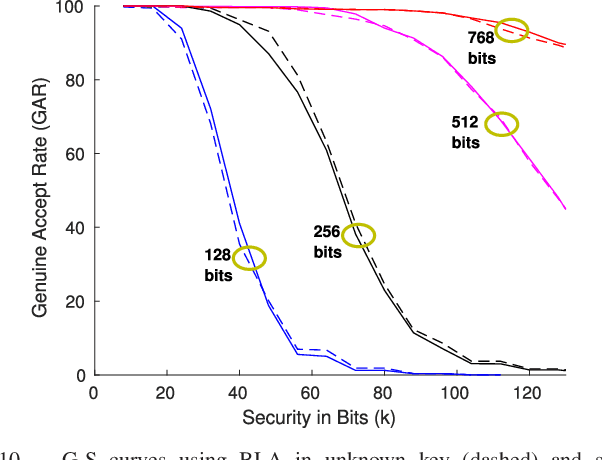
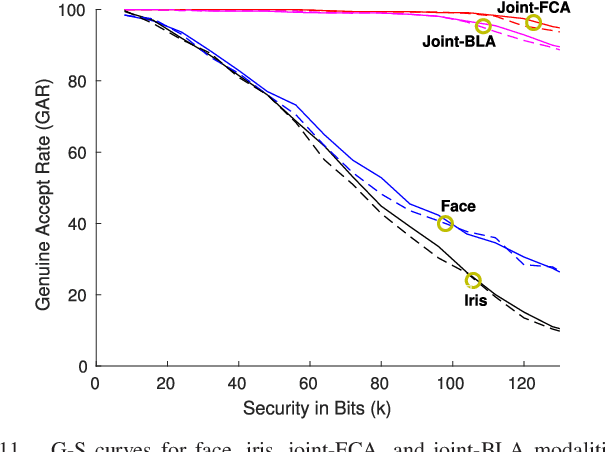
Abstract:When compared to unimodal systems, multimodal biometric systems have several advantages, including lower error rate, higher accuracy, and larger population coverage. However, multimodal systems have an increased demand for integrity and privacy because they must store multiple biometric traits associated with each user. In this paper, we present a deep learning framework for feature-level fusion that generates a secure multimodal template from each user's face and iris biometrics. We integrate a deep hashing (binarization) technique into the fusion architecture to generate a robust binary multimodal shared latent representation. Further, we employ a hybrid secure architecture by combining cancelable biometrics with secure sketch techniques and integrate it with a deep hashing framework, which makes it computationally prohibitive to forge a combination of multiple biometrics that pass the authentication. The efficacy of the proposed approach is shown using a multimodal database of face and iris and it is observed that the matching performance is improved due to the fusion of multiple biometrics. Furthermore, the proposed approach also provides cancelability and unlinkability of the templates along with improved privacy of the biometric data. Additionally, we also test the proposed hashing function for an image retrieval application using a benchmark dataset. The main goal of this paper is to develop a method for integrating multimodal fusion, deep hashing, and biometric security, with an emphasis on structural data from modalities like face and iris. The proposed approach is in no way a general biometric security framework that can be applied to all biometric modalities, as further research is needed to extend the proposed framework to other unconstrained biometric modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge