Cheng-Yen Hsieh
Andy
Protein Autoregressive Modeling via Multiscale Structure Generation
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:We present protein autoregressive modeling (PAR), the first multi-scale autoregressive framework for protein backbone generation via coarse-to-fine next-scale prediction. Using the hierarchical nature of proteins, PAR generates structures that mimic sculpting a statue, forming a coarse topology and refining structural details over scales. To achieve this, PAR consists of three key components: (i) multi-scale downsampling operations that represent protein structures across multiple scales during training; (ii) an autoregressive transformer that encodes multi-scale information and produces conditional embeddings to guide structure generation; (iii) a flow-based backbone decoder that generates backbone atoms conditioned on these embeddings. Moreover, autoregressive models suffer from exposure bias, caused by the training and the generation procedure mismatch, and substantially degrades structure generation quality. We effectively alleviate this issue by adopting noisy context learning and scheduled sampling, enabling robust backbone generation. Notably, PAR exhibits strong zero-shot generalization, supporting flexible human-prompted conditional generation and motif scaffolding without requiring fine-tuning. On the unconditional generation benchmark, PAR effectively learns protein distributions and produces backbones of high design quality, and exhibits favorable scaling behavior. Together, these properties establish PAR as a promising framework for protein structure generation.
Elucidating the Design Space of Multimodal Protein Language Models
Apr 16, 2025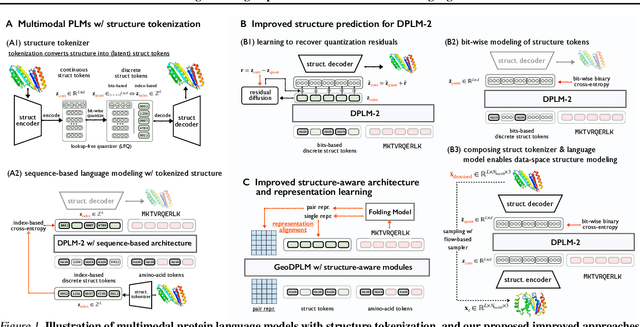
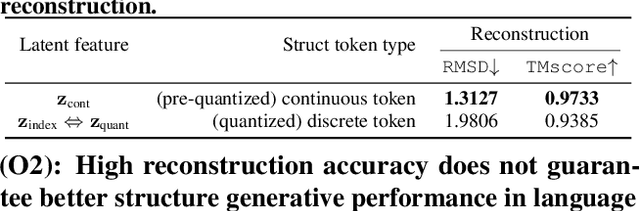
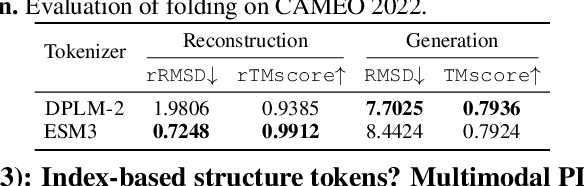
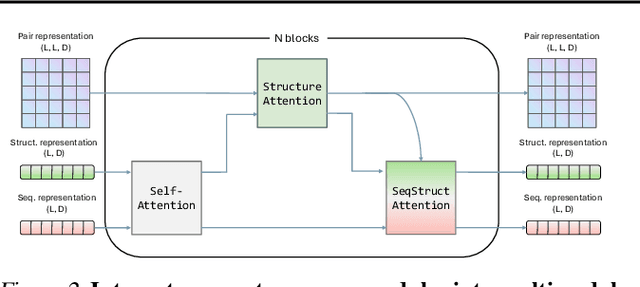
Abstract:Multimodal protein language models (PLMs) integrate sequence and token-based structural information, serving as a powerful foundation for protein modeling, generation, and design. However, the reliance on tokenizing 3D structures into discrete tokens causes substantial loss of fidelity about fine-grained structural details and correlations. In this paper, we systematically elucidate the design space of multimodal PLMs to overcome their limitations. We identify tokenization loss and inaccurate structure token predictions by the PLMs as major bottlenecks. To address these, our proposed design space covers improved generative modeling, structure-aware architectures and representation learning, and data exploration. Our advancements approach finer-grained supervision, demonstrating that token-based multimodal PLMs can achieve robust structural modeling. The effective design methods dramatically improve the structure generation diversity, and notably, folding abilities of our 650M model by reducing the RMSD from 5.52 to 2.36 on PDB testset, even outperforming 3B baselines and on par with the specialized folding models.
Tracking Any Object Amodally
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:Amodal perception, the ability to comprehend complete object structures from partial visibility, is a fundamental skill, even for infants. Its significance extends to applications like autonomous driving, where a clear understanding of heavily occluded objects is essential. However, modern detection and tracking algorithms often overlook this critical capability, perhaps due to the prevalence of modal annotations in most datasets. To address the scarcity of amodal data, we introduce the TAO-Amodal benchmark, featuring 880 diverse categories in thousands of video sequences. Our dataset includes amodal and modal bounding boxes for visible and occluded objects, including objects that are partially out-of-frame. To enhance amodal tracking with object permanence, we leverage a lightweight plug-in module, the amodal expander, to transform standard, modal trackers into amodal ones through fine-tuning on a few hundred video sequences with data augmentation. We achieve a 3.3\% and 1.6\% improvement on the detection and tracking of occluded objects on TAO-Amodal. When evaluated on people, our method produces dramatic improvements of 2x compared to state-of-the-art modal baselines.
Self-Supervised Pyramid Representation Learning for Multi-Label Visual Analysis and Beyond
Aug 30, 2022



Abstract:While self-supervised learning has been shown to benefit a number of vision tasks, existing techniques mainly focus on image-level manipulation, which may not generalize well to downstream tasks at patch or pixel levels. Moreover, existing SSL methods might not sufficiently describe and associate the above representations within and across image scales. In this paper, we propose a Self-Supervised Pyramid Representation Learning (SS-PRL) framework. The proposed SS-PRL is designed to derive pyramid representations at patch levels via learning proper prototypes, with additional learners to observe and relate inherent semantic information within an image. In particular, we present a cross-scale patch-level correlation learning in SS-PRL, which allows the model to aggregate and associate information learned across patch scales. We show that, with our proposed SS-PRL for model pre-training, one can easily adapt and fine-tune the models for a variety of applications including multi-label classification, object detection, and instance segmentation.
C3-SL: Circular Convolution-Based Batch-Wise Compression for Communication-Efficient Split Learning
Jul 25, 2022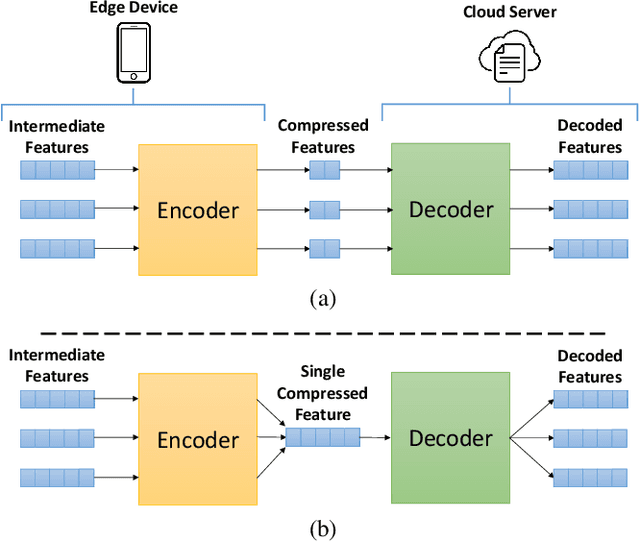


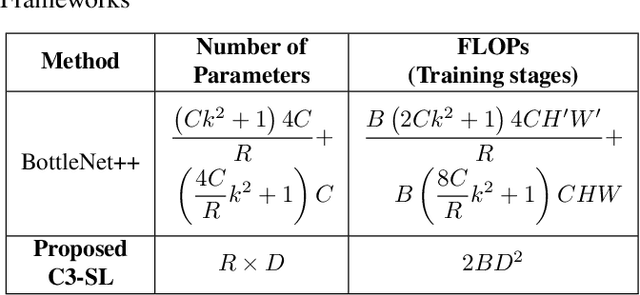
Abstract:Most existing studies improve the efficiency of Split learning (SL) by compressing the transmitted features. However, most works focus on dimension-wise compression that transforms high-dimensional features into a low-dimensional space. In this paper, we propose circular convolution-based batch-wise compression for SL (C3-SL) to compress multiple features into one single feature. To avoid information loss while merging multiple features, we exploit the quasi-orthogonality of features in high-dimensional space with circular convolution and superposition. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to explore the potential of batch-wise compression under the SL scenario. Based on the simulation results on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100, our method achieves a 16x compression ratio with negligible accuracy drops compared with the vanilla SL. Moreover, C3-SL significantly reduces 1152x memory and 2.25x computation overhead compared to the state-of-the-art dimension-wise compression method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge