Changyuan Wen
NTIRE 2020 Challenge on Real Image Denoising: Dataset, Methods and Results
May 08, 2020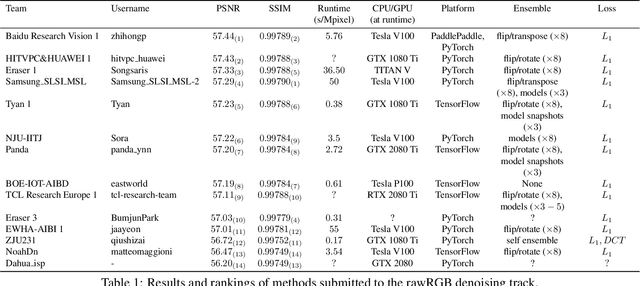
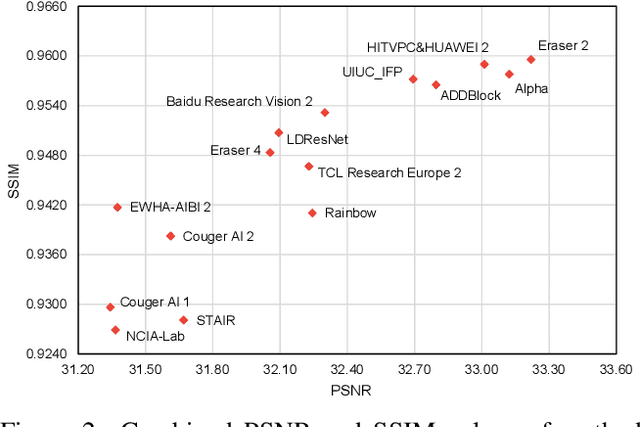
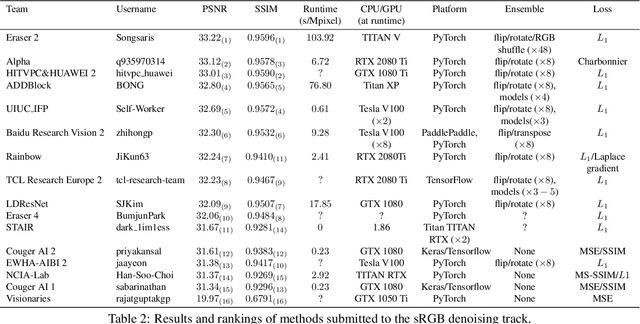
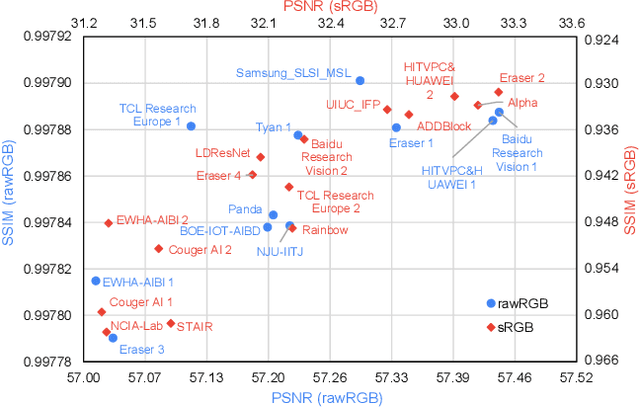
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2020 challenge on real image denoising with focus on the newly introduced dataset, the proposed methods and their results. The challenge is a new version of the previous NTIRE 2019 challenge on real image denoising that was based on the SIDD benchmark. This challenge is based on a newly collected validation and testing image datasets, and hence, named SIDD+. This challenge has two tracks for quantitatively evaluating image denoising performance in (1) the Bayer-pattern rawRGB and (2) the standard RGB (sRGB) color spaces. Each track ~250 registered participants. A total of 22 teams, proposing 24 methods, competed in the final phase of the challenge. The proposed methods by the participating teams represent the current state-of-the-art performance in image denoising targeting real noisy images. The newly collected SIDD+ datasets are publicly available at: https://bit.ly/siddplus_data.
Distilling portable Generative Adversarial Networks for Image Translation
Mar 07, 2020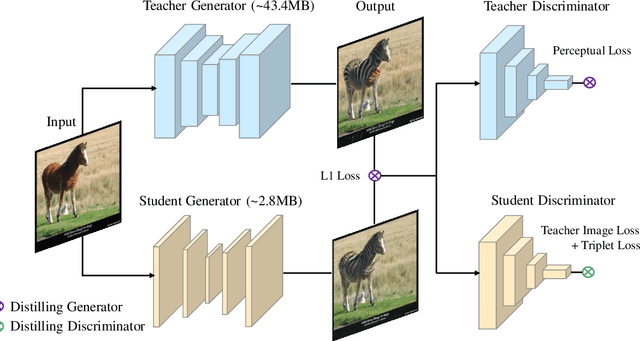
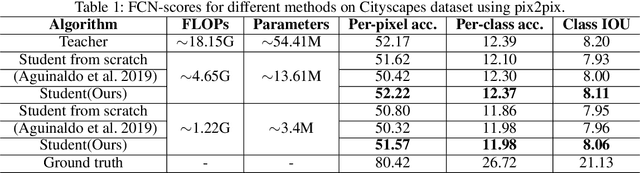

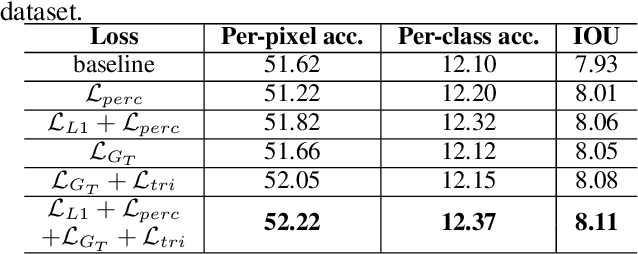
Abstract:Despite Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have been widely used in various image-to-image translation tasks, they can be hardly applied on mobile devices due to their heavy computation and storage cost. Traditional network compression methods focus on visually recognition tasks, but never deal with generation tasks. Inspired by knowledge distillation, a student generator of fewer parameters is trained by inheriting the low-level and high-level information from the original heavy teacher generator. To promote the capability of student generator, we include a student discriminator to measure the distances between real images, and images generated by student and teacher generators. An adversarial learning process is therefore established to optimize student generator and student discriminator. Qualitative and quantitative analysis by conducting experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method can learn portable generative models with strong performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge