Changsheng Wang
Downgrade to Upgrade: Optimizer Simplification Enhances Robustness in LLM Unlearning
Oct 02, 2025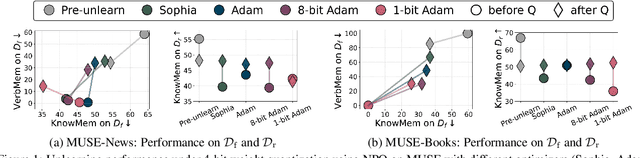
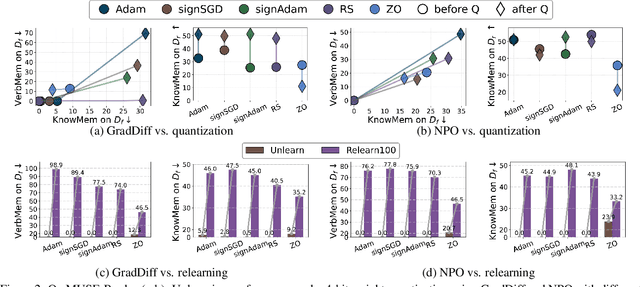
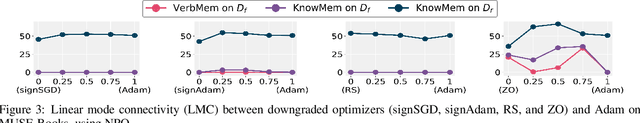
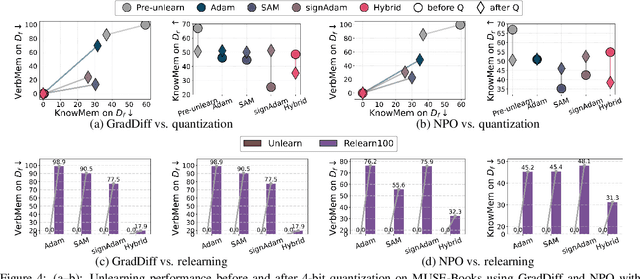
Abstract:Large language model (LLM) unlearning aims to surgically remove the influence of undesired data or knowledge from an existing model while preserving its utility on unrelated tasks. This paradigm has shown promise in addressing privacy and safety concerns. However, recent findings reveal that unlearning effects are often fragile: post-unlearning manipulations such as weight quantization or fine-tuning can quickly neutralize the intended forgetting. Prior efforts to improve robustness primarily reformulate unlearning objectives by explicitly assuming the role of vulnerability sources. In this work, we take a different perspective by investigating the role of the optimizer, independent of unlearning objectives and formulations, in shaping unlearning robustness. We show that the 'grade' of the optimizer, defined by the level of information it exploits, ranging from zeroth-order (gradient-free) to first-order (gradient-based) to second-order (Hessian-based), is tightly linked to the resilience of unlearning. Surprisingly, we find that downgrading the optimizer, such as using zeroth-order methods or compressed-gradient variants (e.g., gradient sign-based optimizers), often leads to stronger robustness. While these optimizers produce noisier and less precise updates, they encourage convergence to harder-to-disturb basins in the loss landscape, thereby resisting post-training perturbations. By connecting zeroth-order methods with randomized smoothing, we further highlight their natural advantage for robust unlearning. Motivated by these insights, we propose a hybrid optimizer that combines first-order and zeroth-order updates, preserving unlearning efficacy while enhancing robustness. Extensive experiments on the MUSE and WMDP benchmarks, across multiple LLM unlearning algorithms, validate that our approach achieves more resilient forgetting without sacrificing unlearning quality.
Reasoning Model Unlearning: Forgetting Traces, Not Just Answers, While Preserving Reasoning Skills
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large reasoning models (LRMs) have enabled strong chain-of-thought (CoT) generation through test-time computation. While these multi-step reasoning capabilities represent a major milestone in language model performance, they also introduce new safety risks. In this work, we present the first systematic study to revisit the problem of machine unlearning in the context of LRMs. Machine unlearning refers to the process of removing the influence of sensitive, harmful, or undesired data or knowledge from a trained model without full retraining. We show that conventional unlearning algorithms, originally designed for non-reasoning models, are inadequate for LRMs. In particular, even when final answers are successfully erased, sensitive information often persists within the intermediate reasoning steps, i.e., CoT trajectories. To address this challenge, we extend conventional unlearning and propose Reasoning-aware Representation Misdirection for Unlearning ($R^2MU$), a novel method that effectively suppresses sensitive reasoning traces and prevents the generation of associated final answers, while preserving the model's reasoning ability. Our experiments demonstrate that $R^2MU$ significantly reduces sensitive information leakage within reasoning traces and achieves strong performance across both safety and reasoning benchmarks, evaluated on state-of-the-art models such as DeepSeek-R1-Distill-LLaMA-8B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-14B.
LLM Unlearning Reveals a Stronger-Than-Expected Coreset Effect in Current Benchmarks
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Large language model unlearning has become a critical challenge in ensuring safety and controlled model behavior by removing undesired data-model influences from the pretrained model while preserving general utility. Significant recent efforts have been dedicated to developing LLM unlearning benchmarks such as WMDP (Weapons of Mass Destruction Proxy) and MUSE (Machine Unlearning Six-way Evaluation), facilitating standardized unlearning performance assessment and method comparison. Despite their usefulness, we uncover for the first time a novel coreset effect within these benchmarks. Specifically, we find that LLM unlearning achieved with the original (full) forget set can be effectively maintained using a significantly smaller subset (functioning as a "coreset"), e.g., as little as 5% of the forget set, even when selected at random. This suggests that LLM unlearning in these benchmarks can be performed surprisingly easily, even in an extremely low-data regime. We demonstrate that this coreset effect remains strong, regardless of the LLM unlearning method used, such as NPO (Negative Preference Optimization) and RMU (Representation Misdirection Unlearning), the popular ones in these benchmarks. The surprisingly strong coreset effect is also robust across various data selection methods, ranging from random selection to more sophisticated heuristic approaches. We explain the coreset effect in LLM unlearning through a keyword-based perspective, showing that keywords extracted from the forget set alone contribute significantly to unlearning effectiveness and indicating that current unlearning is driven by a compact set of high-impact tokens rather than the entire dataset. We further justify the faithfulness of coreset-unlearned models along additional dimensions, such as mode connectivity and robustness to jailbreaking attacks. Codes are available at https://github.com/OPTML-Group/MU-Coreset.
Safeguarding Vision-Language Models Against Patched Visual Prompt Injectors
May 17, 2024



Abstract:Large language models have become increasingly prominent, also signaling a shift towards multimodality as the next frontier in artificial intelligence, where their embeddings are harnessed as prompts to generate textual content. Vision-language models (VLMs) stand at the forefront of this advancement, offering innovative ways to combine visual and textual data for enhanced understanding and interaction. However, this integration also enlarges the attack surface. Patch-based adversarial attack is considered the most realistic threat model in physical vision applications, as demonstrated in many existing literature. In this paper, we propose to address patched visual prompt injection, where adversaries exploit adversarial patches to generate target content in VLMs. Our investigation reveals that patched adversarial prompts exhibit sensitivity to pixel-wise randomization, a trait that remains robust even against adaptive attacks designed to counteract such defenses. Leveraging this insight, we introduce SmoothVLM, a defense mechanism rooted in smoothing techniques, specifically tailored to protect VLMs from the threat of patched visual prompt injectors. Our framework significantly lowers the attack success rate to a range between 0% and 5.0% on two leading VLMs, while achieving around 67.3% to 95.0% context recovery of the benign images, demonstrating a balance between security and usability.
Uplift Modeling for Target User Attacks on Recommender Systems
Mar 05, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems are vulnerable to injective attacks, which inject limited fake users into the platforms to manipulate the exposure of target items to all users. In this work, we identify that conventional injective attackers overlook the fact that each item has its unique potential audience, and meanwhile, the attack difficulty across different users varies. Blindly attacking all users will result in a waste of fake user budgets and inferior attack performance. To address these issues, we focus on an under-explored attack task called target user attacks, aiming at promoting target items to a particular user group. In addition, we formulate the varying attack difficulty as heterogeneous treatment effects through a causal lens and propose an Uplift-guided Budget Allocation (UBA) framework. UBA estimates the treatment effect on each target user and optimizes the allocation of fake user budgets to maximize the attack performance. Theoretical and empirical analysis demonstrates the rationality of treatment effect estimation methods of UBA. By instantiating UBA on multiple attackers, we conduct extensive experiments on three datasets under various settings with different target items, target users, fake user budgets, victim models, and defense models, validating the effectiveness and robustness of UBA.
RecAD: Towards A Unified Library for Recommender Attack and Defense
Sep 09, 2023Abstract:In recent years, recommender systems have become a ubiquitous part of our daily lives, while they suffer from a high risk of being attacked due to the growing commercial and social values. Despite significant research progress in recommender attack and defense, there is a lack of a widely-recognized benchmarking standard in the field, leading to unfair performance comparison and limited credibility of experiments. To address this, we propose RecAD, a unified library aiming at establishing an open benchmark for recommender attack and defense. RecAD takes an initial step to set up a unified benchmarking pipeline for reproducible research by integrating diverse datasets, standard source codes, hyper-parameter settings, running logs, attack knowledge, attack budget, and evaluation results. The benchmark is designed to be comprehensive and sustainable, covering both attack, defense, and evaluation tasks, enabling more researchers to easily follow and contribute to this promising field. RecAD will drive more solid and reproducible research on recommender systems attack and defense, reduce the redundant efforts of researchers, and ultimately increase the credibility and practical value of recommender attack and defense. The project is released at https://github.com/gusye1234/recad.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge