Chandranath Adak
Agentic Multi-Persona Framework for Evidence-Aware Fake News Detection
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:The rapid proliferation of online misinformation poses significant risks to public trust, policy, and safety, necessitating reliable automated fake news detection. Existing methods often struggle with multimodal content, domain generalization, and explainability. We propose AMPEND-LS, an agentic multi-persona evidence-grounded framework with LLM-SLM synergy for multimodal fake news detection. AMPEND-LS integrates textual, visual, and contextual signals through a structured reasoning pipeline powered by LLMs, augmented with reverse image search, knowledge graph paths, and persuasion strategy analysis. To improve reliability, we introduce a credibility fusion mechanism combining semantic similarity, domain trustworthiness, and temporal context, and a complementary SLM classifier to mitigate LLM uncertainty and hallucinations. Extensive experiments across three benchmark datasets demonstrate that AMPEND-LS consistently outperformed state-of-the-art baselines in accuracy, F1 score, and robustness. Qualitative case studies further highlight its transparent reasoning and resilience against evolving misinformation. This work advances the development of adaptive, explainable, and evidence-aware systems for safeguarding online information integrity.
Blurb-Refined Inference from Crowdsourced Book Reviews using Hierarchical Genre Mining with Dual-Path Graph Convolutions
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Accurate book genre classification is fundamental to digital library organization, content discovery, and personalized recommendation. Existing approaches typically model genre prediction as a flat, single-label task, ignoring hierarchical genre structure and relying heavily on noisy, subjective user reviews, which often degrade classification reliability. We propose HiGeMine, a two-phase hierarchical genre mining framework that robustly integrates user reviews with authoritative book blurbs. In the first phase, HiGeMine employs a zero-shot semantic alignment strategy to filter reviews, retaining only those semantically consistent with the corresponding blurb, thereby mitigating noise, bias, and irrelevance. In the second phase, we introduce a dual-path, two-level graph-based classification architecture: a coarse-grained Level-1 binary classifier distinguishes fiction from non-fiction, followed by Level-2 multi-label classifiers for fine-grained genre prediction. Inter-genre dependencies are explicitly modeled using a label co-occurrence graph, while contextual representations are derived from pretrained language models applied to the filtered textual content. To facilitate systematic evaluation, we curate a new hierarchical book genre dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HiGeMine consistently outperformed strong baselines across hierarchical genre classification tasks. The proposed framework offers a principled and effective solution for leveraging both structured and unstructured textual data in hierarchical book genre analysis.
ProtoSiTex: Learning Semi-Interpretable Prototypes for Multi-label Text Classification
Oct 14, 2025



Abstract:The surge in user-generated reviews has amplified the need for interpretable models that can provide fine-grained insights. Existing prototype-based models offer intuitive explanations but typically operate at coarse granularity (sentence or document level) and fail to address the multi-label nature of real-world text classification. We propose ProtoSiTex, a semi-interpretable framework designed for fine-grained multi-label text classification. ProtoSiTex employs a dual-phase alternating training strategy: an unsupervised prototype discovery phase that learns semantically coherent and diverse prototypes, and a supervised classification phase that maps these prototypes to class labels. A hierarchical loss function enforces consistency across sub-sentence, sentence, and document levels, enhancing interpretability and alignment. Unlike prior approaches, ProtoSiTex captures overlapping and conflicting semantics using adaptive prototypes and multi-head attention. We also introduce a benchmark dataset of hotel reviews annotated at the sub-sentence level with multiple labels. Experiments on this dataset and two public benchmarks (binary and multi-class) show that ProtoSiTex achieves state-of-the-art performance while delivering faithful, human-aligned explanations, establishing it as a robust solution for semi-interpretable multi-label text classification.
An Adaptive Data-Resilient Multi-Modal Framework for Hierarchical Multi-Label Book Genre Identification
May 05, 2025
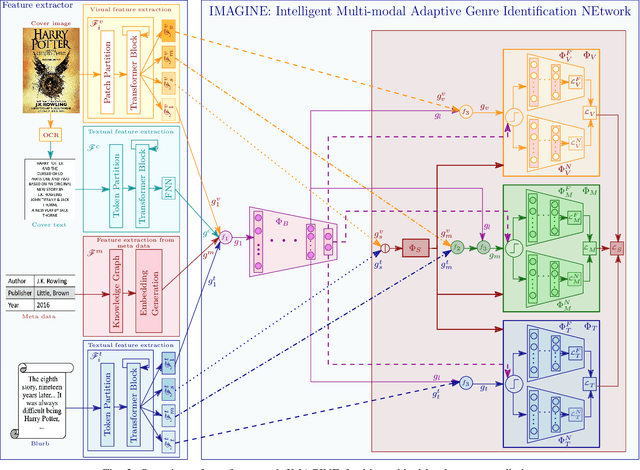


Abstract:Identifying the finer details of a book's genres enhances user experience by enabling efficient book discovery and personalized recommendations, ultimately improving reader engagement and satisfaction. It also provides valuable insights into market trends and consumer preferences, allowing publishers and marketers to make data-driven decisions regarding book production and marketing strategies. While traditional book genre classification methods primarily rely on review data or textual analysis, incorporating additional modalities, such as book covers, blurbs, and metadata, can offer richer context and improve prediction accuracy. However, the presence of incomplete or noisy information across these modalities presents a significant challenge. This paper introduces IMAGINE (Intelligent Multi-modal Adaptive Genre Identification NEtwork), a framework designed to address these complexities. IMAGINE extracts robust feature representations from multiple modalities and dynamically selects the most informative sources based on data availability. It employs a hierarchical classification strategy to capture genre relationships and remains adaptable to varying input conditions. Additionally, we curate a hierarchical genre classification dataset that structures genres into a well-defined taxonomy, accommodating the diverse nature of literary works. IMAGINE integrates information from multiple sources and assigns multiple genre labels to each book, ensuring a more comprehensive classification. A key feature of our framework is its resilience to incomplete data, enabling accurate predictions even when certain modalities, such as text, images, or metadata, are missing or incomplete. Experimental results show that IMAGINE outperformed existing baselines in genre classification accuracy, particularly in scenarios with insufficient modality-specific data.
Reinforcing Competitive Multi-Agents for Playing So Long Sucker
Nov 17, 2024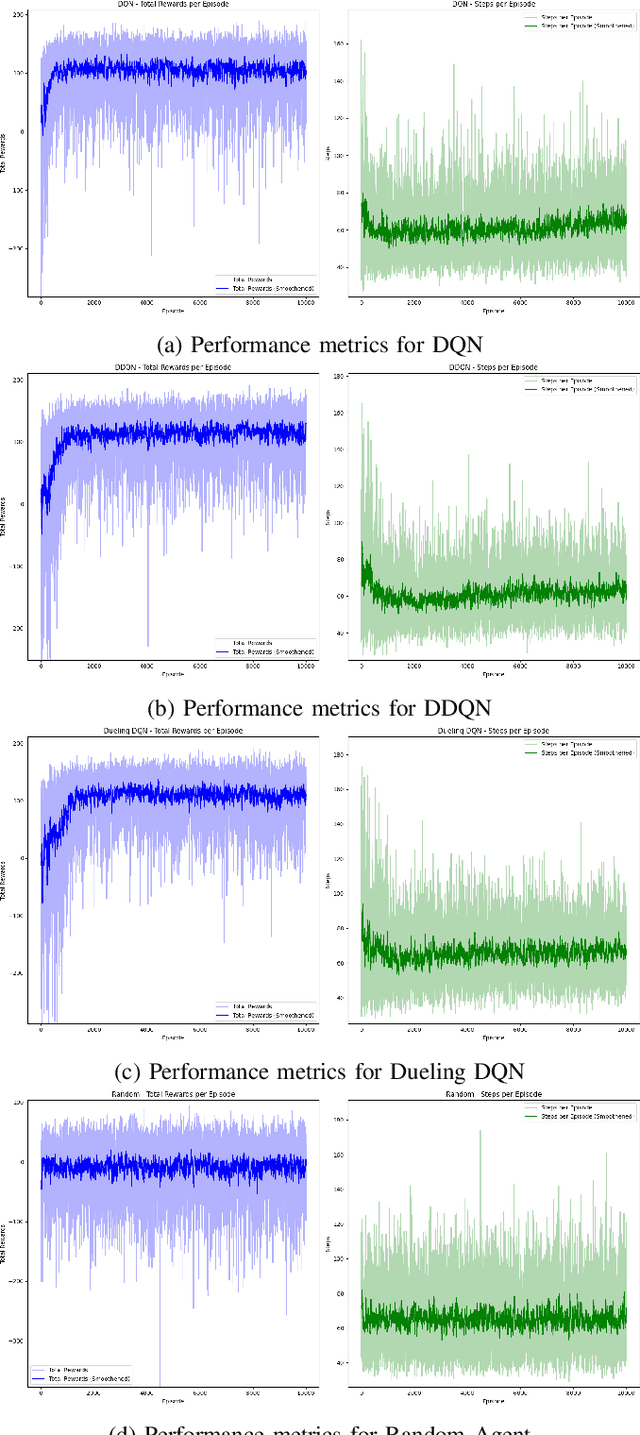
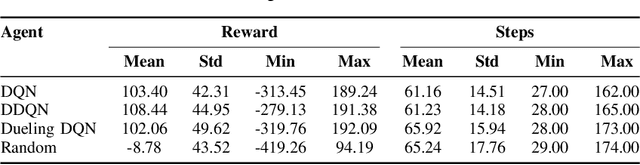
Abstract:This paper examines the use of classical deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithms, DQN, DDQN, and Dueling DQN, in the strategy game So Long Sucker (SLS), a diplomacy-driven game defined by coalition-building and strategic betrayal. SLS poses unique challenges due to its blend of cooperative and adversarial dynamics, making it an ideal platform for studying multi-agent learning and game theory. The study's primary goal is to teach autonomous agents the game's rules and strategies using classical DRL methods. To support this effort, the authors developed a novel, publicly available implementation of SLS, featuring a graphical user interface (GUI) and benchmarking tools for DRL algorithms. Experimental results reveal that while considered basic by modern DRL standards, DQN, DDQN, and Dueling DQN agents achieved roughly 50% of the maximum possible game reward. This suggests a baseline understanding of the game's mechanics, with agents favoring legal moves over illegal ones. However, a significant limitation was the extensive training required, around 2000 games, for agents to reach peak performance, compared to human players who grasp the game within a few rounds. Even after prolonged training, agents occasionally made illegal moves, highlighting both the potential and limitations of these classical DRL methods in semi-complex, socially driven games. The findings establish a foundational benchmark for training agents in SLS and similar negotiation-based environments while underscoring the need for advanced or hybrid DRL approaches to improve learning efficiency and adaptability. Future research could incorporate game-theoretic strategies to enhance agent decision-making in dynamic multi-agent contexts.
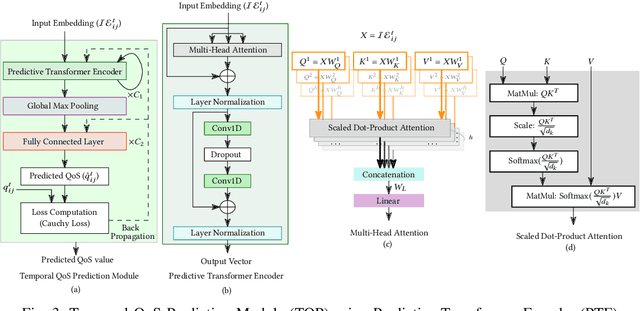
Anomaly Resilient Temporal QoS Prediction using Hypergraph Convoluted Transformer Network
Oct 23, 2024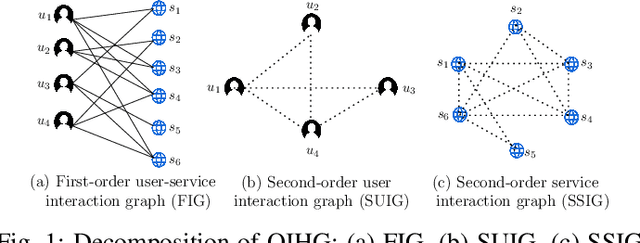
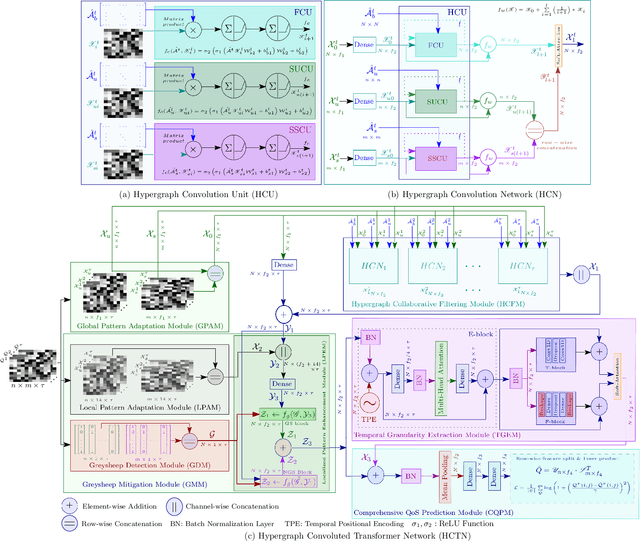
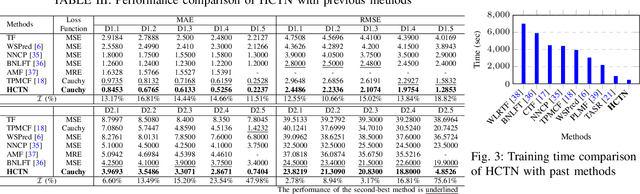
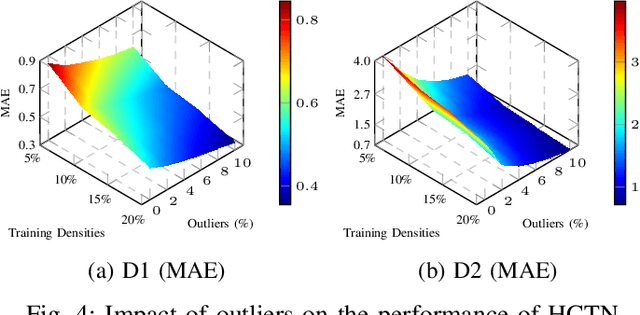
Abstract:Quality-of-Service (QoS) prediction is a critical task in the service lifecycle, enabling precise and adaptive service recommendations by anticipating performance variations over time in response to evolving network uncertainties and user preferences. However, contemporary QoS prediction methods frequently encounter data sparsity and cold-start issues, which hinder accurate QoS predictions and limit the ability to capture diverse user preferences. Additionally, these methods often assume QoS data reliability, neglecting potential credibility issues such as outliers and the presence of greysheep users and services with atypical invocation patterns. Furthermore, traditional approaches fail to leverage diverse features, including domain-specific knowledge and complex higher-order patterns, essential for accurate QoS predictions. In this paper, we introduce a real-time, trust-aware framework for temporal QoS prediction to address the aforementioned challenges, featuring an end-to-end deep architecture called the Hypergraph Convoluted Transformer Network (HCTN). HCTN combines a hypergraph structure with graph convolution over hyper-edges to effectively address high-sparsity issues by capturing complex, high-order correlations. Complementing this, the transformer network utilizes multi-head attention along with parallel 1D convolutional layers and fully connected dense blocks to capture both fine-grained and coarse-grained dynamic patterns. Additionally, our approach includes a sparsity-resilient solution for detecting greysheep users and services, incorporating their unique characteristics to improve prediction accuracy. Trained with a robust loss function resistant to outliers, HCTN demonstrated state-of-the-art performance on the large-scale WSDREAM-2 datasets for response time and throughput.
Demystifying Visual Features of Movie Posters for Multi-Label Genre Identification
Sep 21, 2023

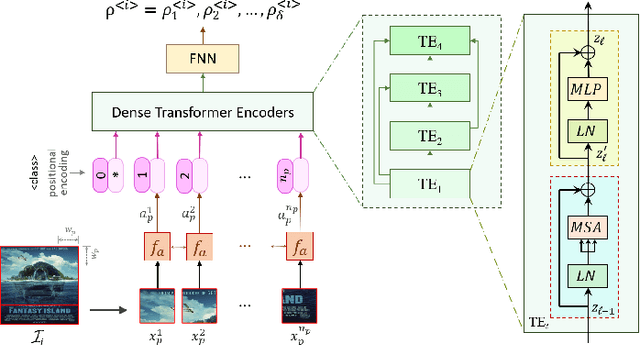
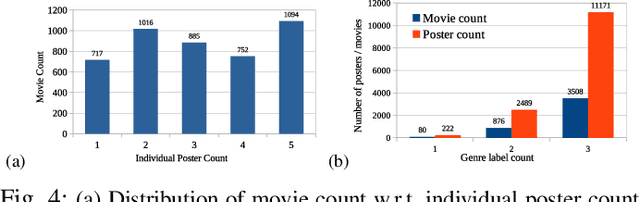
Abstract:In the film industry, movie posters have been an essential part of advertising and marketing for many decades, and continue to play a vital role even today in the form of digital posters through online, social media and OTT platforms. Typically, movie posters can effectively promote and communicate the essence of a film, such as its genre, visual style/ tone, vibe and storyline cue/ theme, which are essential to attract potential viewers. Identifying the genres of a movie often has significant practical applications in recommending the film to target audiences. Previous studies on movie genre identification are limited to subtitles, plot synopses, and movie scenes that are mostly accessible after the movie release. Posters usually contain pre-release implicit information to generate mass interest. In this paper, we work for automated multi-label genre identification only from movie poster images, without any aid of additional textual/meta-data information about movies, which is one of the earliest attempts of its kind. Here, we present a deep transformer network with a probabilistic module to identify the movie genres exclusively from the poster. For experimental analysis, we procured 13882 number of posters of 13 genres from the Internet Movie Database (IMDb), where our model performances were encouraging and even outperformed some major contemporary architectures.
Impact of Visual Context on Noisy Multimodal NMT: An Empirical Study for English to Indian Languages
Aug 30, 2023Abstract:The study investigates the effectiveness of utilizing multimodal information in Neural Machine Translation (NMT). While prior research focused on using multimodal data in low-resource scenarios, this study examines how image features impact translation when added to a large-scale, pre-trained unimodal NMT system. Surprisingly, the study finds that images might be redundant in this context. Additionally, the research introduces synthetic noise to assess whether images help the model deal with textual noise. Multimodal models slightly outperform text-only models in noisy settings, even with random images. The study's experiments translate from English to Hindi, Bengali, and Malayalam, outperforming state-of-the-art benchmarks significantly. Interestingly, the effect of visual context varies with source text noise: no visual context works best for non-noisy translations, cropped image features are optimal for low noise, and full image features work better in high-noise scenarios. This sheds light on the role of visual context, especially in noisy settings, opening up a new research direction for Noisy Neural Machine Translation in multimodal setups. The research emphasizes the importance of combining visual and textual information for improved translation in various environments.
Metal Oxide-based Gas Sensor Array for the VOCs Analysis in Complex Mixtures using Machine Learning
Jul 13, 2023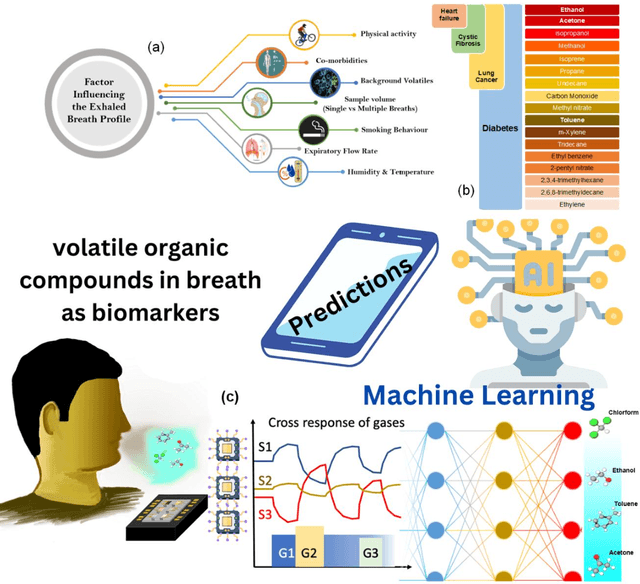
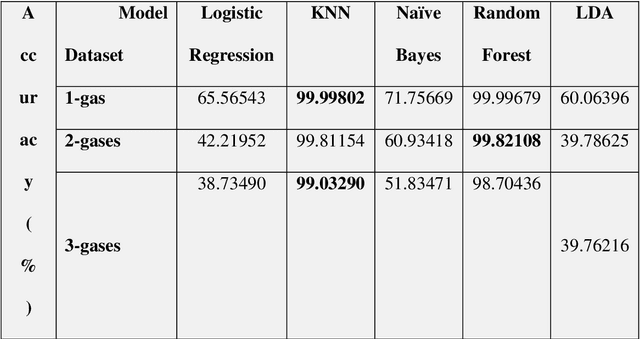
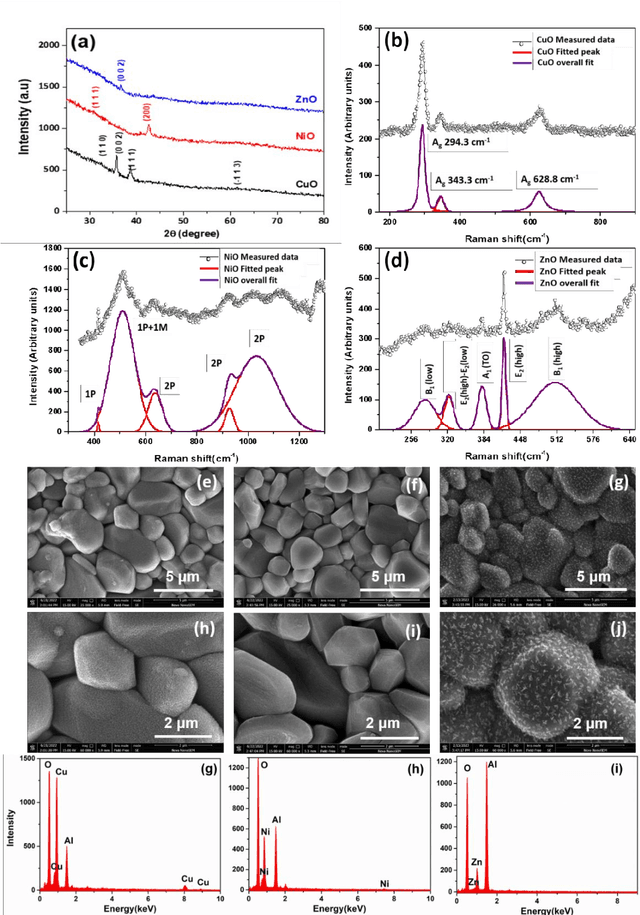
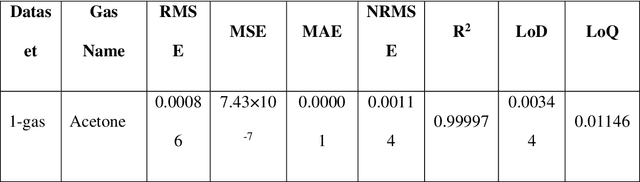
Abstract:Detection of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) from the breath is becoming a viable route for the early detection of diseases non-invasively. This paper presents a sensor array with three metal oxide electrodes that can use machine learning methods to identify four distinct VOCs in a mixture. The metal oxide sensor array was subjected to various VOC concentrations, including ethanol, acetone, toluene and chloroform. The dataset obtained from individual gases and their mixtures were analyzed using multiple machine learning algorithms, such as Random Forest (RF), K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Decision Tree, Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, Naive Bayes, Linear Discriminant Analysis, Artificial Neural Network, and Support Vector Machine. KNN and RF have shown more than 99% accuracy in classifying different varying chemicals in the gas mixtures. In regression analysis, KNN has delivered the best results with R2 value of more than 0.99 and LOD of 0.012, 0.015, 0.014 and 0.025 PPM for predicting the concentrations of varying chemicals Acetone, Toluene, Ethanol, and Chloroform, respectively in complex mixtures. Therefore, it is demonstrated that the array utilizing the provided algorithms can classify and predict the concentrations of the four gases simultaneously for disease diagnosis and treatment monitoring.
TPMCF: Temporal QoS Prediction using Multi-Source Collaborative Features
Mar 30, 2023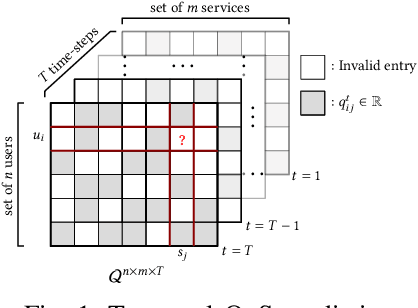
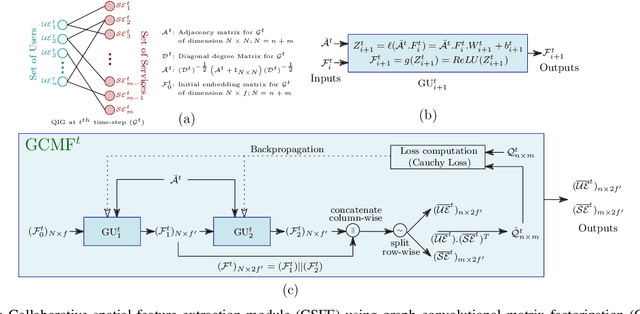
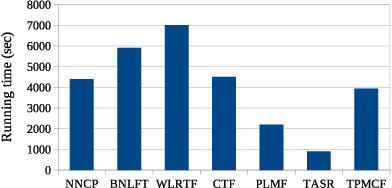
Abstract:Recently, with the rapid deployment of service APIs, personalized service recommendations have played a paramount role in the growth of the e-commerce industry. Quality-of-Service (QoS) parameters determining the service performance, often used for recommendation, fluctuate over time. Thus, the QoS prediction is essential to identify a suitable service among functionally equivalent services over time. The contemporary temporal QoS prediction methods hardly achieved the desired accuracy due to various limitations, such as the inability to handle data sparsity and outliers and capture higher-order temporal relationships among user-service interactions. Even though some recent recurrent neural-network-based architectures can model temporal relationships among QoS data, prediction accuracy degrades due to the absence of other features (e.g., collaborative features) to comprehend the relationship among the user-service interactions. This paper addresses the above challenges and proposes a scalable strategy for Temporal QoS Prediction using Multi-source Collaborative-Features (TPMCF), achieving high prediction accuracy and faster responsiveness. TPMCF combines the collaborative-features of users/services by exploiting user-service relationship with the spatio-temporal auto-extracted features by employing graph convolution and transformer encoder with multi-head self-attention. We validated our proposed method on WS-DREAM-2 datasets. Extensive experiments showed TPMCF outperformed major state-of-the-art approaches regarding prediction accuracy while ensuring high scalability and reasonably faster responsiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge