Cassio F. Dantas
EVERGREEN, INRAE
Inherently Faithful Attention Maps for Vision Transformers
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:We introduce an attention-based method that uses learned binary attention masks to ensure that only attended image regions influence the prediction. Context can strongly affect object perception, sometimes leading to biased representations, particularly when objects appear in out-of-distribution backgrounds. At the same time, many image-level object-centric tasks require identifying relevant regions, often requiring context. To address this conundrum, we propose a two-stage framework: stage 1 processes the full image to discover object parts and identify task-relevant regions, while stage 2 leverages input attention masking to restrict its receptive field to these regions, enabling a focused analysis while filtering out potentially spurious information. Both stages are trained jointly, allowing stage 2 to refine stage 1. Extensive experiments across diverse benchmarks demonstrate that our approach significantly improves robustness against spurious correlations and out-of-distribution backgrounds.
PDiscoFormer: Relaxing Part Discovery Constraints with Vision Transformers
Jul 05, 2024Abstract:Computer vision methods that explicitly detect object parts and reason on them are a step towards inherently interpretable models. Existing approaches that perform part discovery driven by a fine-grained classification task make very restrictive assumptions on the geometric properties of the discovered parts; they should be small and compact. Although this prior is useful in some cases, in this paper we show that pre-trained transformer-based vision models, such as self-supervised DINOv2 ViT, enable the relaxation of these constraints. In particular, we find that a total variation (TV) prior, which allows for multiple connected components of any size, substantially outperforms previous work. We test our approach on three fine-grained classification benchmarks: CUB, PartImageNet and Oxford Flowers, and compare our results to previously published methods as well as a re-implementation of the state-of-the-art method PDiscoNet with a transformer-based backbone. We consistently obtain substantial improvements across the board, both on part discovery metrics and the downstream classification task, showing that the strong inductive biases in self-supervised ViT models require to rethink the geometric priors that can be used for unsupervised part discovery.
Semi Supervised Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation via Disentanglement and Pseudo-Labelling
Jun 20, 2024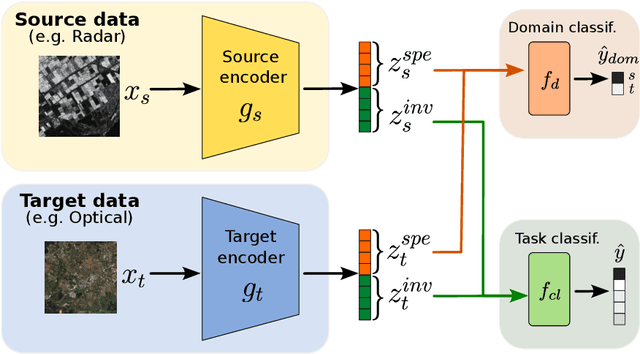
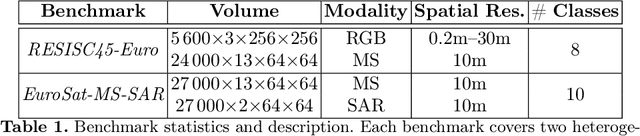
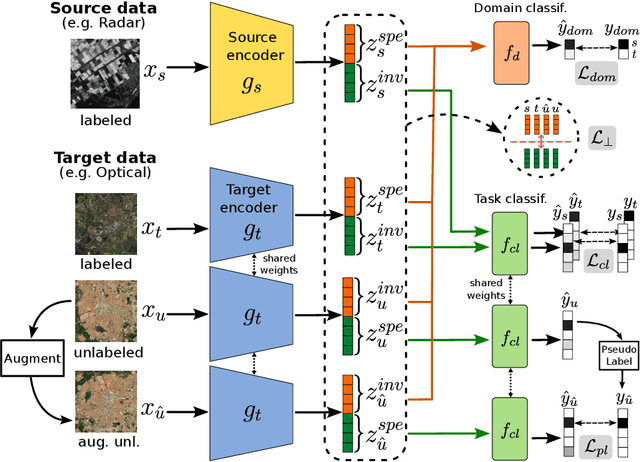
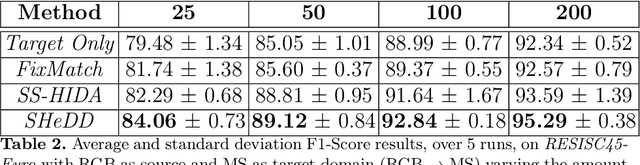
Abstract:Semi-supervised domain adaptation methods leverage information from a source labelled domain with the goal of generalizing over a scarcely labelled target domain. While this setting already poses challenges due to potential distribution shifts between domains, an even more complex scenario arises when source and target data differs in modality representation (e.g. they are acquired by sensors with different characteristics). For instance, in remote sensing, images may be collected via various acquisition modes (e.g. optical or radar), different spectral characteristics (e.g. RGB or multi-spectral) and spatial resolutions. Such a setting is denoted as Semi-Supervised Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation (SSHDA) and it exhibits an even more severe distribution shift due to modality heterogeneity across domains.To cope with the challenging SSHDA setting, here we introduce SHeDD (Semi-supervised Heterogeneous Domain Adaptation via Disentanglement) an end-to-end neural framework tailored to learning a target domain classifier by leveraging both labelled and unlabelled data from heterogeneous data sources. SHeDD is designed to effectively disentangle domain-invariant representations, relevant for the downstream task, from domain-specific information, that can hinder the cross-modality transfer. Additionally, SHeDD adopts an augmentation-based consistency regularization mechanism that takes advantages of reliable pseudo-labels on the unlabelled target samples to further boost its generalization ability on the target domain. Empirical evaluations on two remote sensing benchmarks, encompassing heterogeneous data in terms of acquisition modes and spectral/spatial resolutions, demonstrate the quality of SHeDD compared to both baseline and state-of-the-art competing approaches. Our code is publicly available here: https://github.com/tanodino/SSHDA/
Reuse out-of-year data to enhance land cover mappingvia feature disentanglement and contrastive learning
Apr 17, 2024


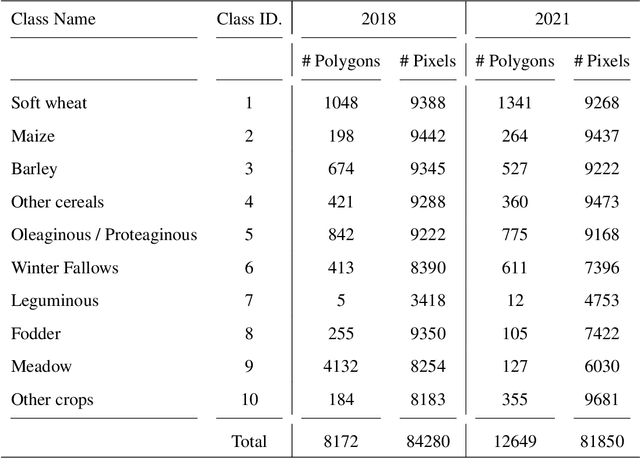
Abstract:Timely up-to-date land use/land cover (LULC) maps play a pivotal role in supporting agricultural territory management, environmental monitoring and facilitating well-informed and sustainable decision-making. Typically, when creating a land cover (LC) map, precise ground truth data is collected through time-consuming and expensive field campaigns. This data is then utilized in conjunction with satellite image time series (SITS) through advanced machine learning algorithms to get the final map. Unfortunately, each time this process is repeated (e.g., annually over a region to estimate agricultural production or potential biodiversity loss), new ground truth data must be collected, leading to the complete disregard of previously gathered reference data despite the substantial financial and time investment they have required. How to make value of historical data, from the same or similar study sites, to enhance the current LULC mapping process constitutes a significant challenge that could enable the financial and human-resource efforts invested in previous data campaigns to be valued again. Aiming to tackle this important challenge, we here propose a deep learning framework based on recent advances in domain adaptation and generalization to combine remote sensing and reference data coming from two different domains (e.g. historical data and fresh ones) to ameliorate the current LC mapping process. Our approach, namely REFeD (data Reuse with Effective Feature Disentanglement for land cover mapping), leverages a disentanglement strategy, based on contrastive learning, where invariant and specific per-domain features are derived to recover the intrinsic information related to the downstream LC mapping task and alleviate possible distribution shifts between domains. Additionally, REFeD is equipped with an effective supervision scheme where feature disentanglement is further enforced via multiple levels of supervision at different granularities. The experimental assessment over two study areas covering extremely diverse and contrasted landscapes, namely Koumbia (located in the West-Africa region, in Burkina Faso) and Centre Val de Loire (located in centre Europe, France), underlines the quality of our framework and the obtained findings demonstrate that out-of-year information coming from the same (or similar) study site, at different periods of time, can constitute a valuable additional source of information to enhance the LC mapping process.
PDiscoNet: Semantically consistent part discovery for fine-grained recognition
Sep 06, 2023



Abstract:Fine-grained classification often requires recognizing specific object parts, such as beak shape and wing patterns for birds. Encouraging a fine-grained classification model to first detect such parts and then using them to infer the class could help us gauge whether the model is indeed looking at the right details better than with interpretability methods that provide a single attribution map. We propose PDiscoNet to discover object parts by using only image-level class labels along with priors encouraging the parts to be: discriminative, compact, distinct from each other, equivariant to rigid transforms, and active in at least some of the images. In addition to using the appropriate losses to encode these priors, we propose to use part-dropout, where full part feature vectors are dropped at once to prevent a single part from dominating in the classification, and part feature vector modulation, which makes the information coming from each part distinct from the perspective of the classifier. Our results on CUB, CelebA, and PartImageNet show that the proposed method provides substantially better part discovery performance than previous methods while not requiring any additional hyper-parameter tuning and without penalizing the classification performance. The code is available at https://github.com/robertdvdk/part_detection.
Masking Strategies for Background Bias Removal in Computer Vision Models
Aug 23, 2023Abstract:Models for fine-grained image classification tasks, where the difference between some classes can be extremely subtle and the number of samples per class tends to be low, are particularly prone to picking up background-related biases and demand robust methods to handle potential examples with out-of-distribution (OOD) backgrounds. To gain deeper insights into this critical problem, our research investigates the impact of background-induced bias on fine-grained image classification, evaluating standard backbone models such as Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Vision Transformers (ViT). We explore two masking strategies to mitigate background-induced bias: Early masking, which removes background information at the (input) image level, and late masking, which selectively masks high-level spatial features corresponding to the background. Extensive experiments assess the behavior of CNN and ViT models under different masking strategies, with a focus on their generalization to OOD backgrounds. The obtained findings demonstrate that both proposed strategies enhance OOD performance compared to the baseline models, with early masking consistently exhibiting the best OOD performance. Notably, a ViT variant employing GAP-Pooled Patch token-based classification combined with early masking achieves the highest OOD robustness.
Counterfactual Explanations for Land Cover Mapping in a Multi-class Setting
Jan 04, 2023Abstract:Counterfactual explanations are an emerging tool to enhance interpretability of deep learning models. Given a sample, these methods seek to find and display to the user similar samples across the decision boundary. In this paper, we propose a generative adversarial counterfactual approach for satellite image time series in a multi-class setting for the land cover classification task. One of the distinctive features of the proposed approach is the lack of prior assumption on the targeted class for a given counterfactual explanation. This inherent flexibility allows for the discovery of interesting information on the relationship between land cover classes. The other feature consists of encouraging the counterfactual to differ from the original sample only in a small and compact temporal segment. These time-contiguous perturbations allow for a much sparser and, thus, interpretable solution. Furthermore, plausibility/realism of the generated counterfactual explanations is enforced via the proposed adversarial learning strategy.
Benchopt: Reproducible, efficient and collaborative optimization benchmarks
Jun 28, 2022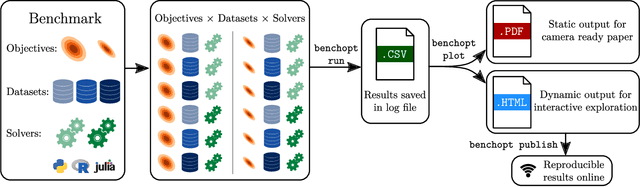
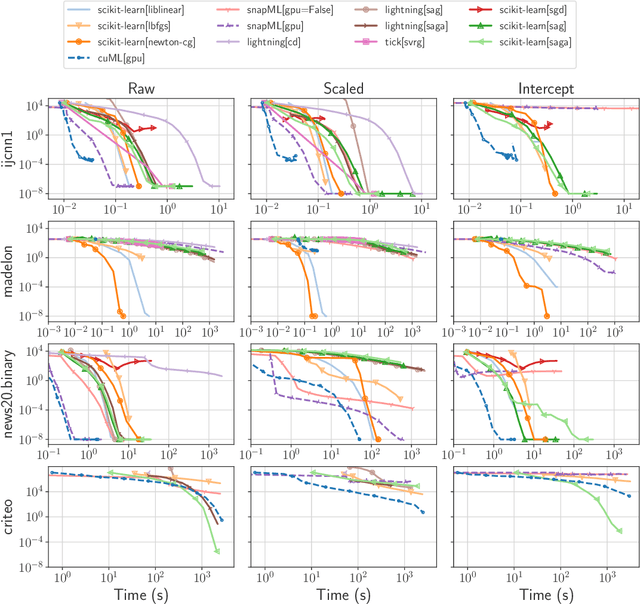
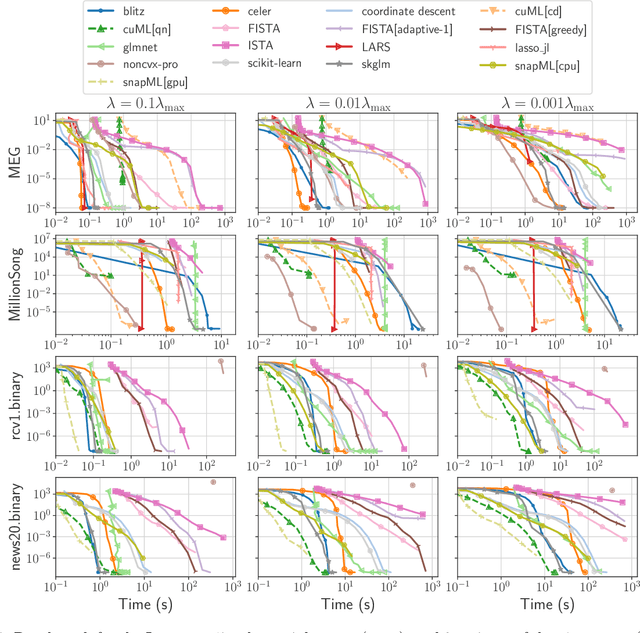
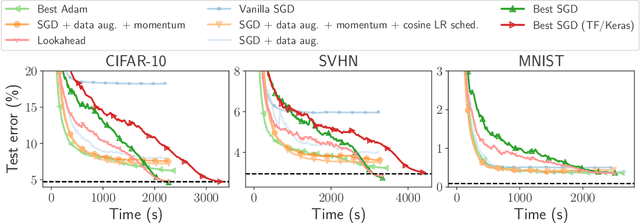
Abstract:Numerical validation is at the core of machine learning research as it allows to assess the actual impact of new methods, and to confirm the agreement between theory and practice. Yet, the rapid development of the field poses several challenges: researchers are confronted with a profusion of methods to compare, limited transparency and consensus on best practices, as well as tedious re-implementation work. As a result, validation is often very partial, which can lead to wrong conclusions that slow down the progress of research. We propose Benchopt, a collaborative framework to automate, reproduce and publish optimization benchmarks in machine learning across programming languages and hardware architectures. Benchopt simplifies benchmarking for the community by providing an off-the-shelf tool for running, sharing and extending experiments. To demonstrate its broad usability, we showcase benchmarks on three standard learning tasks: $\ell_2$-regularized logistic regression, Lasso, and ResNet18 training for image classification. These benchmarks highlight key practical findings that give a more nuanced view of the state-of-the-art for these problems, showing that for practical evaluation, the devil is in the details. We hope that Benchopt will foster collaborative work in the community hence improving the reproducibility of research findings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge