Brian MacWhinney
Morphosyntactic Analysis for CHILDES
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:Language development researchers are interested in comparing the process of language learning across languages. Unfortunately, it has been difficult to construct a consistent quantitative framework for such comparisons. However, recent advances in AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning) are providing new methods for ASR (automatic speech recognition) and NLP (natural language processing) that can be brought to bear on this problem. Using the Batchalign2 program (Liu et al., 2023), we have been transcribing and linking data for the CHILDES database and have applied the UD (Universal Dependencies) framework to provide a consistent and comparable morphosyntactic analysis for 27 languages. These new resources open possibilities for deeper crosslinguistic study of language learning.
Connected Speech-Based Cognitive Assessment in Chinese and English
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:We present a novel benchmark dataset and prediction tasks for investigating approaches to assess cognitive function through analysis of connected speech. The dataset consists of speech samples and clinical information for speakers of Mandarin Chinese and English with different levels of cognitive impairment as well as individuals with normal cognition. These data have been carefully matched by age and sex by propensity score analysis to ensure balance and representativity in model training. The prediction tasks encompass mild cognitive impairment diagnosis and cognitive test score prediction. This framework was designed to encourage the development of approaches to speech-based cognitive assessment which generalise across languages. We illustrate it by presenting baseline prediction models that employ language-agnostic and comparable features for diagnosis and cognitive test score prediction. The models achieved unweighted average recall was 59.2% in diagnosis, and root mean squared error of 2.89 in score prediction.
Evaluating Picture Description Speech for Dementia Detection using Image-text Alignment
Aug 11, 2023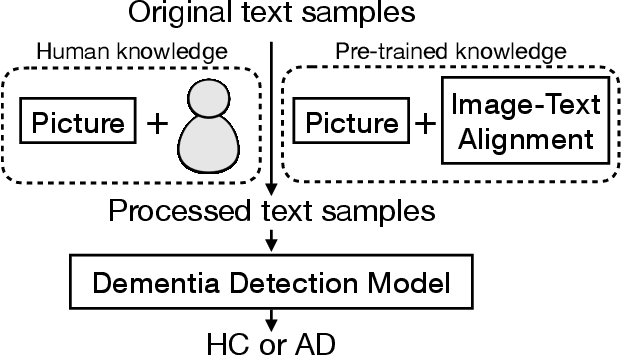
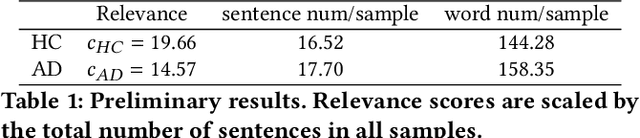

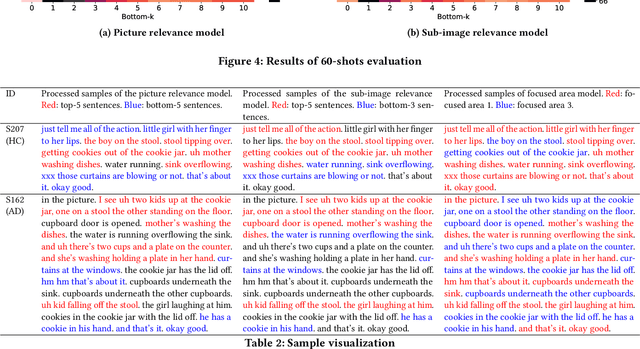
Abstract:Using picture description speech for dementia detection has been studied for 30 years. Despite the long history, previous models focus on identifying the differences in speech patterns between healthy subjects and patients with dementia but do not utilize the picture information directly. In this paper, we propose the first dementia detection models that take both the picture and the description texts as inputs and incorporate knowledge from large pre-trained image-text alignment models. We observe the difference between dementia and healthy samples in terms of the text's relevance to the picture and the focused area of the picture. We thus consider such a difference could be used to enhance dementia detection accuracy. Specifically, we use the text's relevance to the picture to rank and filter the sentences of the samples. We also identified focused areas of the picture as topics and categorized the sentences according to the focused areas. We propose three advanced models that pre-processed the samples based on their relevance to the picture, sub-image, and focused areas. The evaluation results show that our advanced models, with knowledge of the picture and large image-text alignment models, achieve state-of-the-art performance with the best detection accuracy at 83.44%, which is higher than the text-only baseline model at 79.91%. Lastly, we visualize the sample and picture results to explain the advantages of our models.
A New Benchmark of Aphasia Speech Recognition and Detection Based on E-Branchformer and Multi-task Learning
May 19, 2023



Abstract:Aphasia is a language disorder that affects the speaking ability of millions of patients. This paper presents a new benchmark for Aphasia speech recognition and detection tasks using state-of-the-art speech recognition techniques with the AphsiaBank dataset. Specifically, we introduce two multi-task learning methods based on the CTC/Attention architecture to perform both tasks simultaneously. Our system achieves state-of-the-art speaker-level detection accuracy (97.3%), and a relative WER reduction of 11% for moderate Aphasia patients. In addition, we demonstrate the generalizability of our approach by applying it to another disordered speech database, the DementiaBank Pitt corpus. We will make our all-in-one recipes and pre-trained model publicly available to facilitate reproducibility. Our standardized data preprocessing pipeline and open-source recipes enable researchers to compare results directly, promoting progress in disordered speech processing.
Multilingual Alzheimer's Dementia Recognition through Spontaneous Speech: a Signal Processing Grand Challenge
Jan 13, 2023Abstract:This Signal Processing Grand Challenge (SPGC) targets a difficult automatic prediction problem of societal and medical relevance, namely, the detection of Alzheimer's Dementia (AD). Participants were invited to employ signal processing and machine learning methods to create predictive models based on spontaneous speech data. The Challenge has been designed to assess the extent to which predictive models built based on speech in one language (English) generalise to another language (Greek). To the best of our knowledge no work has investigated acoustic features of the speech signal in multilingual AD detection. Our baseline system used conventional machine learning algorithms with Active Data Representation of acoustic features, achieving accuracy of 73.91% on AD detection, and 4.95 root mean squared error on cognitive score prediction.
Detecting cognitive decline using speech only: The ADReSSo Challenge
Mar 23, 2021Abstract:Building on the success of the ADReSS Challenge at Interspeech 2020, which attracted the participation of 34 teams from across the world, the ADReSSo Challenge targets three difficult automatic prediction problems of societal and medical relevance, namely: detection of Alzheimer's Dementia, inference of cognitive testing scores, and prediction of cognitive decline. This paper presents these prediction tasks in detail, describes the datasets used, and reports the results of the baseline classification and regression models we developed for each task. A combination of acoustic and linguistic features extracted directly from audio recordings, without human intervention, yielded a baseline accuracy of 78.87% for the AD classification task, an MMSE prediction root mean squared (RMSE) error of 5.28, and 68.75% accuracy for the cognitive decline prediction task.
Alzheimer's Dementia Recognition through Spontaneous Speech: The ADReSS Challenge
Apr 30, 2020
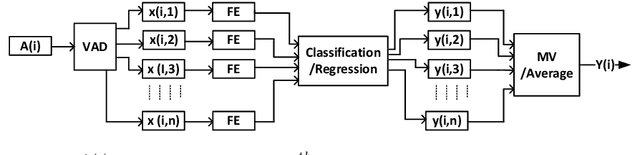
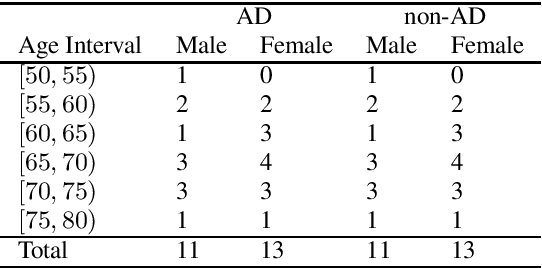
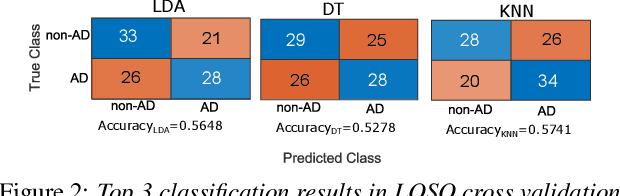
Abstract:The ADReSS Challenge at INTERSPEECH 2020 defines a shared task through which different approaches to the automated recognition of Alzheimer's dementia based on spontaneous speech can be compared. ADReSS provides researchers with a benchmark speech dataset which has been acoustically pre-processed and balanced in terms of age and gender, defining two cognitive assessment tasks, namely: the Alzheimer's speech classification task and the neuropsychological score regression task. In the Alzheimer's speech classification task, ADReSS challenge participants create models for classifying speech as dementia or healthy control speech. In the the neuropsychological score regression task, participants create models to predict mini-mental state examination scores. This paper describes the ADReSS Challenge in detail and presents a baseline for both tasks, including a feature extraction procedure and results for a classification and a regression model. ADReSS aims to provide the speech and language Alzheimer's research community with a platform for comprehensive methodological comparisons. This will contribute to addressing the lack of standardisation that currently affects the field and shed light on avenues for future research and clinical applicability.
Learning the Curriculum with Bayesian Optimization for Task-Specific Word Representation Learning
Jun 21, 2016



Abstract:We use Bayesian optimization to learn curricula for word representation learning, optimizing performance on downstream tasks that depend on the learned representations as features. The curricula are modeled by a linear ranking function which is the scalar product of a learned weight vector and an engineered feature vector that characterizes the different aspects of the complexity of each instance in the training corpus. We show that learning the curriculum improves performance on a variety of downstream tasks over random orders and in comparison to the natural corpus order.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge