Chia-Ju Chou
Connected Speech-Based Cognitive Assessment in Chinese and English
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:We present a novel benchmark dataset and prediction tasks for investigating approaches to assess cognitive function through analysis of connected speech. The dataset consists of speech samples and clinical information for speakers of Mandarin Chinese and English with different levels of cognitive impairment as well as individuals with normal cognition. These data have been carefully matched by age and sex by propensity score analysis to ensure balance and representativity in model training. The prediction tasks encompass mild cognitive impairment diagnosis and cognitive test score prediction. This framework was designed to encourage the development of approaches to speech-based cognitive assessment which generalise across languages. We illustrate it by presenting baseline prediction models that employ language-agnostic and comparable features for diagnosis and cognitive test score prediction. The models achieved unweighted average recall was 59.2% in diagnosis, and root mean squared error of 2.89 in score prediction.
Using ResNet to Utilize 4-class T2-FLAIR Slice Classification Based on the Cholinergic Pathways Hyperintensities Scale for Pathological Aging
Nov 09, 2023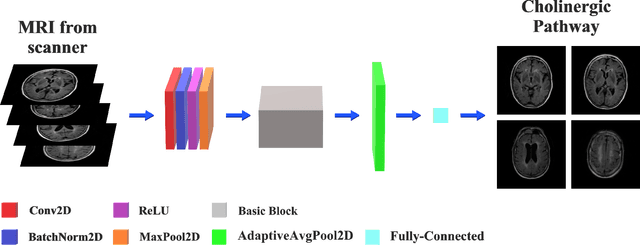
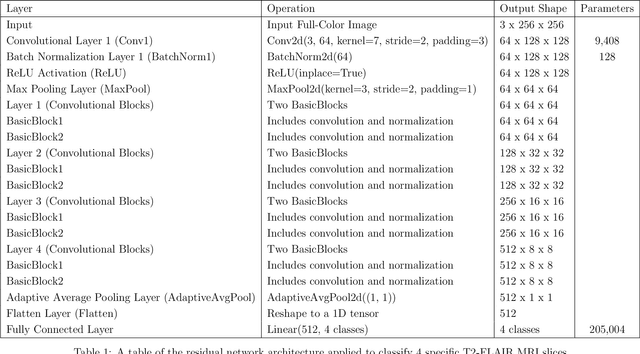
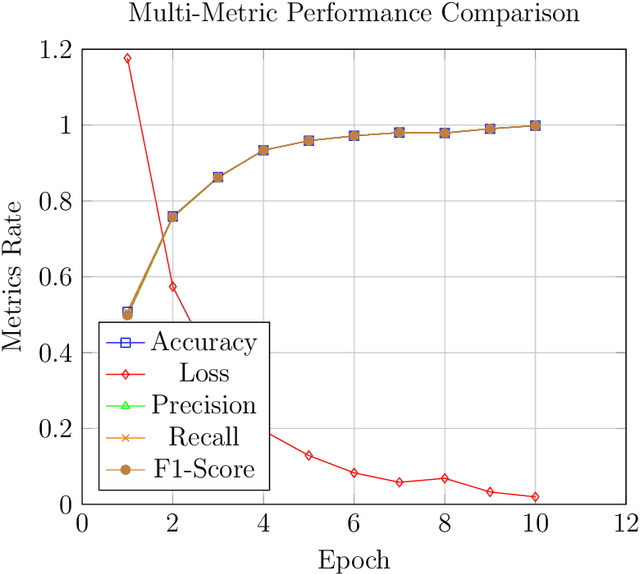
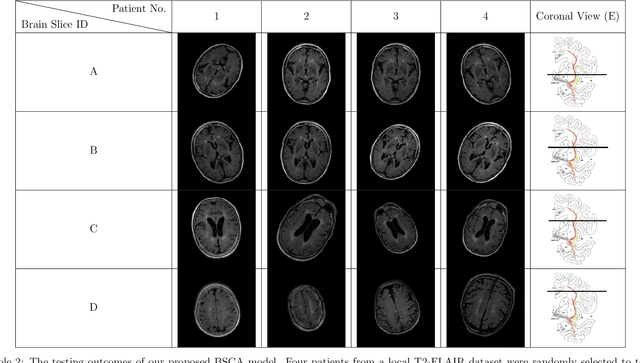
Abstract:The Cholinergic Pathways Hyperintensities Scale (CHIPS) is a visual rating scale used to assess the extent of cholinergic white matter hyperintensities in T2-FLAIR images, serving as an indicator of dementia severity. However, the manual selection of four specific slices for rating throughout the entire brain is a time-consuming process. Our goal was to develop a deep learning-based model capable of automatically identifying the four slices relevant to CHIPS. To achieve this, we trained a 4-class slice classification model (BSCA) using the ADNI T2-FLAIR dataset (N=150) with the assistance of ResNet. Subsequently, we tested the model's performance on a local dataset (N=30). The results demonstrated the efficacy of our model, with an accuracy of 99.82% and an F1-score of 99.83%. This achievement highlights the potential impact of BSCA as an automatic screening tool, streamlining the selection of four specific T2-FLAIR slices that encompass white matter landmarks along the cholinergic pathways. Clinicians can leverage this tool to assess the risk of clinical dementia development efficiently.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge