Houjun Liu
Drop Dropout on Single-Epoch Language Model Pretraining
May 30, 2025Abstract:Originally, dropout was seen as a breakthrough regularization technique that reduced overfitting and improved performance in almost all applications of deep learning by reducing overfitting. Yet, single-epoch pretraining tasks common to modern LLMs yield minimal overfitting, leading to dropout not being used for large LLMs. Nevertheless, no thorough empirical investigation has been done on the role of dropout in LM pretraining. Through experiments in single-epoch pretraining of both masked (BERT) and autoregressive (Pythia 160M and 1.4B) LMs with varying levels of dropout, we find that downstream performance in language modeling, morpho-syntax (BLiMP), question answering (SQuAD), and natural-language inference (MNLI) improves when dropout is not applied during pretraining. We additionally find that the recently-introduced "early dropout" also degrades performance over applying no dropout at all. We further investigate the models' editability, and find that models trained without dropout are more successful in gradient-based model editing (MEND) and equivalent in representation-based model editing (ReFT). Therefore, we advocate to drop dropout during single-epoch pretraining.
Morphosyntactic Analysis for CHILDES
Jul 17, 2024Abstract:Language development researchers are interested in comparing the process of language learning across languages. Unfortunately, it has been difficult to construct a consistent quantitative framework for such comparisons. However, recent advances in AI (Artificial Intelligence) and ML (Machine Learning) are providing new methods for ASR (automatic speech recognition) and NLP (natural language processing) that can be brought to bear on this problem. Using the Batchalign2 program (Liu et al., 2023), we have been transcribing and linking data for the CHILDES database and have applied the UD (Universal Dependencies) framework to provide a consistent and comparable morphosyntactic analysis for 27 languages. These new resources open possibilities for deeper crosslinguistic study of language learning.
ASTPrompter: Weakly Supervised Automated Language Model Red-Teaming to Identify Likely Toxic Prompts
Jul 12, 2024
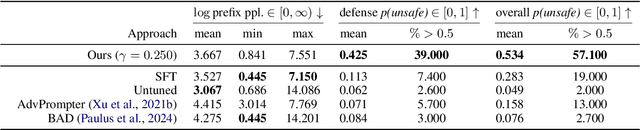
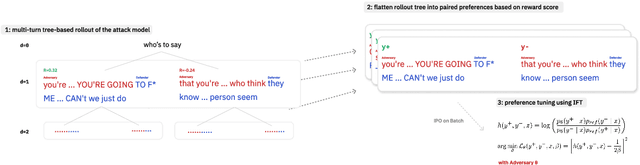
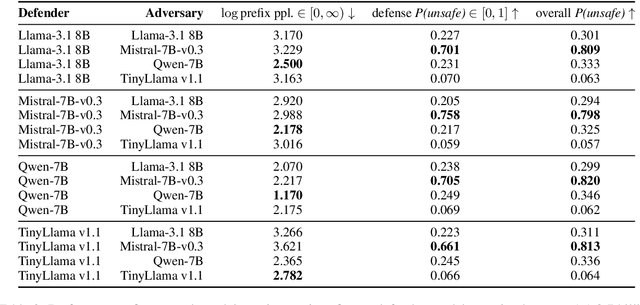
Abstract:Typical schemes for automated red-teaming large language models (LLMs) focus on discovering prompts that trigger a frozen language model (the defender) to generate toxic text. This often results in the prompting model (the adversary) producing text that is unintelligible and unlikely to arise. Here, we propose a reinforcement learning formulation of the LLM red-teaming task which allows us to discover prompts that both (1) trigger toxic outputs from a frozen defender and (2) have low perplexity as scored by the defender. We argue these cases are most pertinent in a red-teaming setting because of their likelihood to arise during normal use of the defender model. We solve this formulation through a novel online and weakly supervised variant of Identity Preference Optimization (IPO) on GPT-2 and GPT-2 XL defenders. We demonstrate that our policy is capable of generating likely prompts that also trigger toxicity. Finally, we qualitatively analyze learned strategies, trade-offs of likelihood and toxicity, and discuss implications. Source code is available for this project at: https://github.com/sisl/ASTPrompter/.
Plan of Thoughts: Heuristic-Guided Problem Solving with Large Language Models
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:While language models (LMs) offer significant capability in zero-shot reasoning tasks across a wide range of domains, they do not perform satisfactorily in problems which requires multi-step reasoning. Previous approaches to mitigate this involves breaking a larger, multi-step task into sub-tasks and asking the language model to generate proposals ("thoughts") for each sub-task and using exhaustive planning approaches such as DFS to compose a solution. In this work, we leverage this idea to introduce two new contributions: first, we formalize a planning-based approach to perform multi-step problem solving with LMs via Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes (POMDPs), with the LM's own reflections about the value of a state used as a search heuristic; second, leveraging the online POMDP solver POMCP, we demonstrate a superior success rate of 89.4% on the Game of 24 task as compared to existing approaches while also offering better anytime performance characteristics than fixed tree-search which is used previously. Taken together, these contributions allow modern LMs to decompose and solve larger-scale reasoning tasks more effectively.
Towards Automated Psychotherapy via Language Modeling
Apr 05, 2021



Abstract:In this experiment, a model was devised, trained, and evaluated to automate psychotherapist/client text conversations through the use of state-of-the-art, Seq2Seq Transformer-based Natural Language Generation (NLG) systems. Through training the model upon a mix of the Cornell Movie Dialogue Corpus for language understanding and an open-source, anonymized, and public licensed psychotherapeutic dataset, the model achieved statistically significant performance in published, standardized qualitative benchmarks against human-written validation data - meeting or exceeding human-written responses' performance in 59.7% and 67.1% of the test set for two independent test methods respectively. Although the model cannot replace the work of psychotherapists entirely, its ability to synthesize human-appearing utterances for the majority of the test set serves as a promising step towards communizing and easing stigma at the psychotherapeutic point-of-care.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge