Bharadwaj Veeravalli
DART-ing Through the Drift: Dynamic Tracing of Knowledge Neurons for Adaptive Inference-Time Pruning
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit substantial parameter redundancy, particularly in Feed-Forward Networks (FFNs). Existing pruning methods suffer from two primary limitations. First, reliance on dataset-specific calibration introduces significant data dependency and computational overhead. Second, being predominantly static, they fail to account for the evolving subset of knowledge neurons in LLMs during autoregressive generation as the context evolves. To address this, we introduce DART, i.e., Dynamic Attention-Guided Runtime Tracing), a lightweight, training-free method that performs on-the-fly context-based pruning. DART monitors shifts in attention score distributions to infer context changes, dynamically updating neuron-level masks to retain salient parameters. Across ten benchmarks, DART outperforms prior dynamic baseline, achieving accuracy gains of up to 14.5% on LLAMA-3.1-8B at 70% FFN sparsity. Furthermore, DART achieves up to 3x better ROUGE-L scores with respect to static-masked pruning on summarization tasks, with its performance comparable to the original dense models. We conclusively demonstrate that the proposed framework effectively adapts to diverse semantic contexts, preserves model capabilities across both general and domain-specific tasks while running at less than 10MBs of memory for LLAMA-3.1-8B(16GBs) with 0.1% FLOPs overhead. The code is available at https://github.com/seeder-research/DART.
Integrating SAM Supervision for 3D Weakly Supervised Point Cloud Segmentation
Aug 27, 2025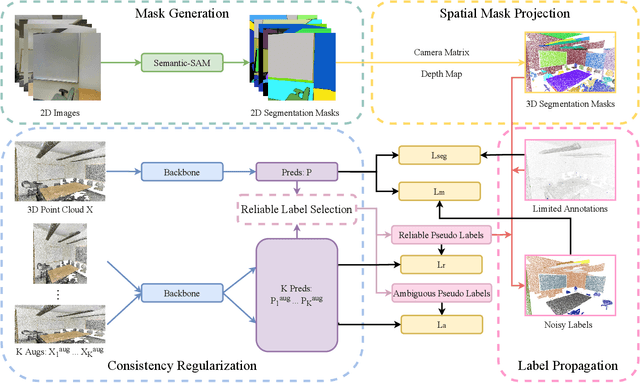
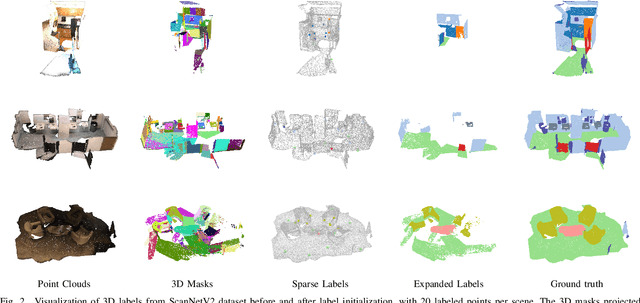
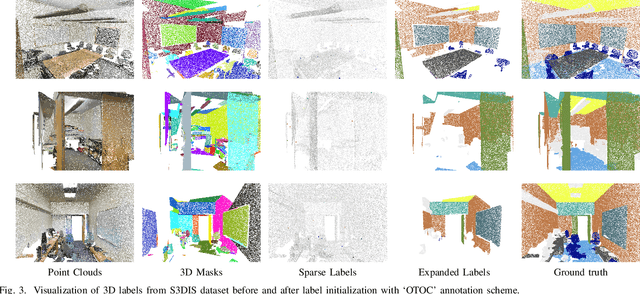

Abstract:Current methods for 3D semantic segmentation propose training models with limited annotations to address the difficulty of annotating large, irregular, and unordered 3D point cloud data. They usually focus on the 3D domain only, without leveraging the complementary nature of 2D and 3D data. Besides, some methods extend original labels or generate pseudo labels to guide the training, but they often fail to fully use these labels or address the noise within them. Meanwhile, the emergence of comprehensive and adaptable foundation models has offered effective solutions for segmenting 2D data. Leveraging this advancement, we present a novel approach that maximizes the utility of sparsely available 3D annotations by incorporating segmentation masks generated by 2D foundation models. We further propagate the 2D segmentation masks into the 3D space by establishing geometric correspondences between 3D scenes and 2D views. We extend the highly sparse annotations to encompass the areas delineated by 3D masks, thereby substantially augmenting the pool of available labels. Furthermore, we apply confidence- and uncertainty-based consistency regularization on augmentations of the 3D point cloud and select the reliable pseudo labels, which are further spread on the 3D masks to generate more labels. This innovative strategy bridges the gap between limited 3D annotations and the powerful capabilities of 2D foundation models, ultimately improving the performance of 3D weakly supervised segmentation.
SusGen-GPT: A Data-Centric LLM for Financial NLP and Sustainability Report Generation
Dec 14, 2024Abstract:The rapid growth of the financial sector and the rising focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations highlight the need for advanced NLP tools. However, open-source LLMs proficient in both finance and ESG domains remain scarce. To address this gap, we introduce SusGen-30K, a category-balanced dataset comprising seven financial NLP tasks and ESG report generation, and propose TCFD-Bench, a benchmark for evaluating sustainability report generation. Leveraging this dataset, we developed SusGen-GPT, a suite of models achieving state-of-the-art performance across six adapted and two off-the-shelf tasks, trailing GPT-4 by only 2% despite using 7-8B parameters compared to GPT-4's 1,700B. Based on this, we propose the SusGen system, integrated with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), to assist in sustainability report generation. This work demonstrates the efficiency of our approach, advancing research in finance and ESG.
A Timely Survey on Vision Transformer for Deepfake Detection
May 14, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, the rapid advancement of deepfake technology has revolutionized content creation, lowering forgery costs while elevating quality. However, this progress brings forth pressing concerns such as infringements on individual rights, national security threats, and risks to public safety. To counter these challenges, various detection methodologies have emerged, with Vision Transformer (ViT)-based approaches showcasing superior performance in generality and efficiency. This survey presents a timely overview of ViT-based deepfake detection models, categorized into standalone, sequential, and parallel architectures. Furthermore, it succinctly delineates the structure and characteristics of each model. By analyzing existing research and addressing future directions, this survey aims to equip researchers with a nuanced understanding of ViT's pivotal role in deepfake detection, serving as a valuable reference for both academic and practical pursuits in this domain.
CAT: Exploiting Inter-Class Dynamics for Domain Adaptive Object Detection
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:Domain adaptive object detection aims to adapt detection models to domains where annotated data is unavailable. Existing methods have been proposed to address the domain gap using the semi-supervised student-teacher framework. However, a fundamental issue arises from the class imbalance in the labelled training set, which can result in inaccurate pseudo-labels. The relationship between classes, especially where one class is a majority and the other minority, has a large impact on class bias. We propose Class-Aware Teacher (CAT) to address the class bias issue in the domain adaptation setting. In our work, we approximate the class relationships with our Inter-Class Relation module (ICRm) and exploit it to reduce the bias within the model. In this way, we are able to apply augmentations to highly related classes, both inter- and intra-domain, to boost the performance of minority classes while having minimal impact on majority classes. We further reduce the bias by implementing a class-relation weight to our classification loss. Experiments conducted on various datasets and ablation studies show that our method is able to address the class bias in the domain adaptation setting. On the Cityscapes to Foggy Cityscapes dataset, we attained a 52.5 mAP, a substantial improvement over the 51.2 mAP achieved by the state-of-the-art method.
Fus-MAE: A cross-attention-based data fusion approach for Masked Autoencoders in remote sensing
Jan 05, 2024


Abstract:Self-supervised frameworks for representation learning have recently stirred up interest among the remote sensing community, given their potential to mitigate the high labeling costs associated with curating large satellite image datasets. In the realm of multimodal data fusion, while the often used contrastive learning methods can help bridging the domain gap between different sensor types, they rely on data augmentations techniques that require expertise and careful design, especially for multispectral remote sensing data. A possible but rather scarcely studied way to circumvent these limitations is to use a masked image modelling based pretraining strategy. In this paper, we introduce Fus-MAE, a self-supervised learning framework based on masked autoencoders that uses cross-attention to perform early and feature-level data fusion between synthetic aperture radar and multispectral optical data - two modalities with a significant domain gap. Our empirical findings demonstrate that Fus-MAE can effectively compete with contrastive learning strategies tailored for SAR-optical data fusion and outperforms other masked-autoencoders frameworks trained on a larger corpus.
2PCNet: Two-Phase Consistency Training for Day-to-Night Unsupervised Domain Adaptive Object Detection
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:Object detection at night is a challenging problem due to the absence of night image annotations. Despite several domain adaptation methods, achieving high-precision results remains an issue. False-positive error propagation is still observed in methods using the well-established student-teacher framework, particularly for small-scale and low-light objects. This paper proposes a two-phase consistency unsupervised domain adaptation network, 2PCNet, to address these issues. The network employs high-confidence bounding-box predictions from the teacher in the first phase and appends them to the student's region proposals for the teacher to re-evaluate in the second phase, resulting in a combination of high and low confidence pseudo-labels. The night images and pseudo-labels are scaled-down before being used as input to the student, providing stronger small-scale pseudo-labels. To address errors that arise from low-light regions and other night-related attributes in images, we propose a night-specific augmentation pipeline called NightAug. This pipeline involves applying random augmentations, such as glare, blur, and noise, to daytime images. Experiments on publicly available datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior results to state-of-the-art methods by 20\%, and to supervised models trained directly on the target data.
ACT-Net: Asymmetric Co-Teacher Network for Semi-supervised Memory-efficient Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 05, 2022



Abstract:While deep models have shown promising performance in medical image segmentation, they heavily rely on a large amount of well-annotated data, which is difficult to access, especially in clinical practice. On the other hand, high-accuracy deep models usually come in large model sizes, limiting their employment in real scenarios. In this work, we propose a novel asymmetric co-teacher framework, ACT-Net, to alleviate the burden on both expensive annotations and computational costs for semi-supervised knowledge distillation. We advance teacher-student learning with a co-teacher network to facilitate asymmetric knowledge distillation from large models to small ones by alternating student and teacher roles, obtaining tiny but accurate models for clinical employment. To verify the effectiveness of our ACT-Net, we employ the ACDC dataset for cardiac substructure segmentation in our experiments. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that ACT-Net outperforms other knowledge distillation methods and achieves lossless segmentation performance with 250x fewer parameters.
MMGL: Multi-Scale Multi-View Global-Local Contrastive learning for Semi-supervised Cardiac Image Segmentation
Jul 05, 2022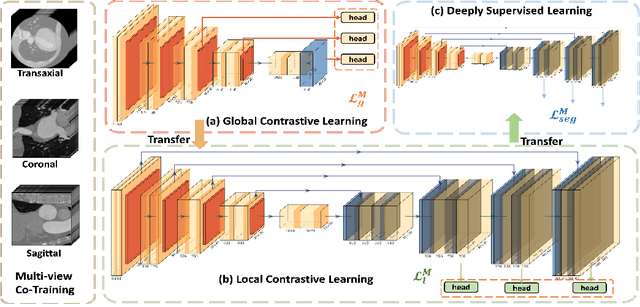

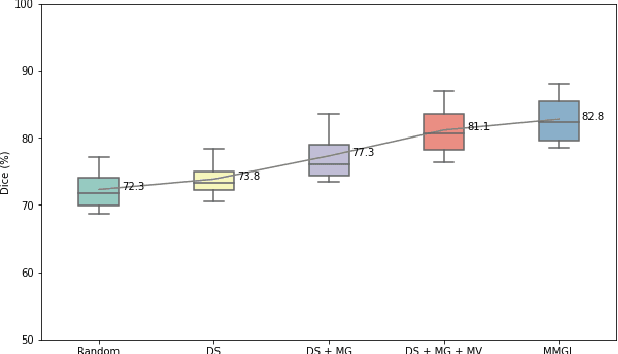
Abstract:With large-scale well-labeled datasets, deep learning has shown significant success in medical image segmentation. However, it is challenging to acquire abundant annotations in clinical practice due to extensive expertise requirements and costly labeling efforts. Recently, contrastive learning has shown a strong capacity for visual representation learning on unlabeled data, achieving impressive performance rivaling supervised learning in many domains. In this work, we propose a novel multi-scale multi-view global-local contrastive learning (MMGL) framework to thoroughly explore global and local features from different scales and views for robust contrastive learning performance, thereby improving segmentation performance with limited annotations. Extensive experiments on the MM-WHS dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of MMGL framework on semi-supervised cardiac image segmentation, outperforming the state-of-the-art contrastive learning methods by a large margin.
Object-Aware Self-supervised Multi-Label Learning
May 14, 2022
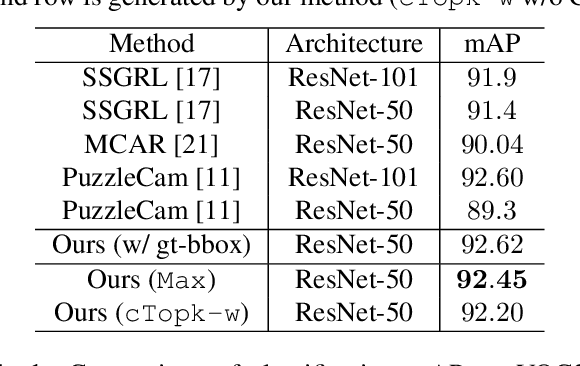

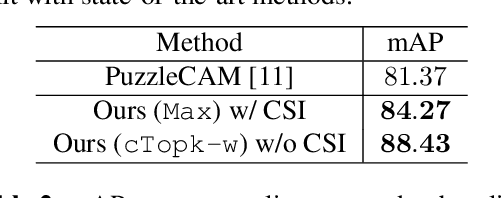
Abstract:Multi-label Learning on Image data has been widely exploited with deep learning models. However, supervised training on deep CNN models often cannot discover sufficient discriminative features for classification. As a result, numerous self-supervision methods are proposed to learn more robust image representations. However, most self-supervised approaches focus on single-instance single-label data and fall short on more complex images with multiple objects. Therefore, we propose an Object-Aware Self-Supervision (OASS) method to obtain more fine-grained representations for multi-label learning, dynamically generating auxiliary tasks based on object locations. Secondly, the robust representation learned by OASS can be leveraged to efficiently generate Class-Specific Instances (CSI) in a proposal-free fashion to better guide multi-label supervision signal transfer to instances. Extensive experiments on the VOC2012 dataset for multi-label classification demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method against the state-of-the-art counterparts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge