Bashar Talafha
CS-FLEURS: A Massively Multilingual and Code-Switched Speech Dataset
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:We present CS-FLEURS, a new dataset for developing and evaluating code-switched speech recognition and translation systems beyond high-resourced languages. CS-FLEURS consists of 4 test sets which cover in total 113 unique code-switched language pairs across 52 languages: 1) a 14 X-English language pair set with real voices reading synthetically generated code-switched sentences, 2) a 16 X-English language pair set with generative text-to-speech 3) a 60 {Arabic, Mandarin, Hindi, Spanish}-X language pair set with the generative text-to-speech, and 4) a 45 X-English lower-resourced language pair test set with concatenative text-to-speech. Besides the four test sets, CS-FLEURS also provides a training set with 128 hours of generative text-to-speech data across 16 X-English language pairs. Our hope is that CS-FLEURS helps to broaden the scope of future code-switched speech research. Dataset link: https://huggingface.co/datasets/byan/cs-fleurs.
Casablanca: Data and Models for Multidialectal Arabic Speech Recognition
Oct 06, 2024



Abstract:In spite of the recent progress in speech processing, the majority of world languages and dialects remain uncovered. This situation only furthers an already wide technological divide, thereby hindering technological and socioeconomic inclusion. This challenge is largely due to the absence of datasets that can empower diverse speech systems. In this paper, we seek to mitigate this obstacle for a number of Arabic dialects by presenting Casablanca, a large-scale community-driven effort to collect and transcribe a multi-dialectal Arabic dataset. The dataset covers eight dialects: Algerian, Egyptian, Emirati, Jordanian, Mauritanian, Moroccan, Palestinian, and Yemeni, and includes annotations for transcription, gender, dialect, and code-switching. We also develop a number of strong baselines exploiting Casablanca. The project page for Casablanca is accessible at: www.dlnlp.ai/speech/casablanca.
WojoodNER 2024: The Second Arabic Named Entity Recognition Shared Task
Jul 13, 2024Abstract:We present WojoodNER-2024, the second Arabic Named Entity Recognition (NER) Shared Task. In WojoodNER-2024, we focus on fine-grained Arabic NER. We provided participants with a new Arabic fine-grained NER dataset called wojoodfine, annotated with subtypes of entities. WojoodNER-2024 encompassed three subtasks: (i) Closed-Track Flat Fine-Grained NER, (ii) Closed-Track Nested Fine-Grained NER, and (iii) an Open-Track NER for the Israeli War on Gaza. A total of 43 unique teams registered for this shared task. Five teams participated in the Flat Fine-Grained Subtask, among which two teams tackled the Nested Fine-Grained Subtask and one team participated in the Open-Track NER Subtask. The winning teams achieved F-1 scores of 91% and 92% in the Flat Fine-Grained and Nested Fine-Grained Subtasks, respectively. The sole team in the Open-Track Subtask achieved an F-1 score of 73.7%.
VoxArabica: A Robust Dialect-Aware Arabic Speech Recognition System
Oct 27, 2023



Abstract:Arabic is a complex language with many varieties and dialects spoken by over 450 millions all around the world. Due to the linguistic diversity and variations, it is challenging to build a robust and generalized ASR system for Arabic. In this work, we address this gap by developing and demoing a system, dubbed VoxArabica, for dialect identification (DID) as well as automatic speech recognition (ASR) of Arabic. We train a wide range of models such as HuBERT (DID), Whisper, and XLS-R (ASR) in a supervised setting for Arabic DID and ASR tasks. Our DID models are trained to identify 17 different dialects in addition to MSA. We finetune our ASR models on MSA, Egyptian, Moroccan, and mixed data. Additionally, for the remaining dialects in ASR, we provide the option to choose various models such as Whisper and MMS in a zero-shot setting. We integrate these models into a single web interface with diverse features such as audio recording, file upload, model selection, and the option to raise flags for incorrect outputs. Overall, we believe VoxArabica will be useful for a wide range of audiences concerned with Arabic research. Our system is currently running at https://cdce-206-12-100-168.ngrok.io/.
WojoodNER 2023: The First Arabic Named Entity Recognition Shared Task
Oct 24, 2023



Abstract:We present WojoodNER-2023, the first Arabic Named Entity Recognition (NER) Shared Task. The primary focus of WojoodNER-2023 is on Arabic NER, offering novel NER datasets (i.e., Wojood) and the definition of subtasks designed to facilitate meaningful comparisons between different NER approaches. WojoodNER-2023 encompassed two Subtasks: FlatNER and NestedNER. A total of 45 unique teams registered for this shared task, with 11 of them actively participating in the test phase. Specifically, 11 teams participated in FlatNER, while $8$ teams tackled NestedNER. The winning teams achieved F1 scores of 91.96 and 93.73 in FlatNER and NestedNER, respectively.
N-Shot Benchmarking of Whisper on Diverse Arabic Speech Recognition
Jun 05, 2023
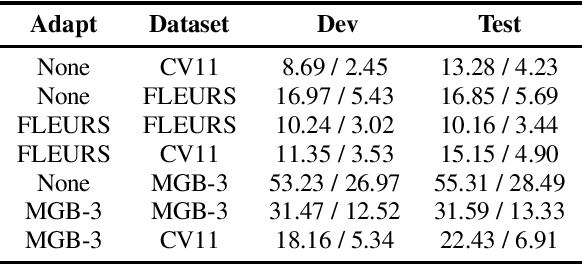
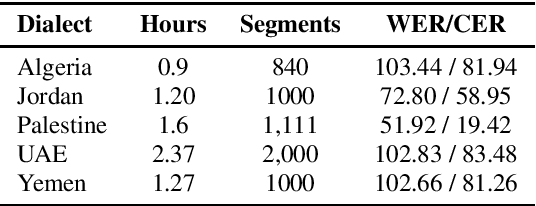
Abstract:Whisper, the recently developed multilingual weakly supervised model, is reported to perform well on multiple speech recognition benchmarks in both monolingual and multilingual settings. However, it is not clear how Whisper would fare under diverse conditions even on languages it was evaluated on such as Arabic. In this work, we address this gap by comprehensively evaluating Whisper on several varieties of Arabic speech for the ASR task. Our evaluation covers most publicly available Arabic speech data and is performed under n-shot (zero-, few-, and full) finetuning. We also investigate the robustness of Whisper under completely novel conditions, such as in dialect-accented standard Arabic and in unseen dialects for which we develop evaluation data. Our experiments show that although Whisper zero-shot outperforms fully finetuned XLS-R models on all datasets, its performance deteriorates significantly in the zero-shot setting for five unseen dialects (i.e., Algeria, Jordan, Palestine, UAE, and Yemen).
sarcasm detection and quantification in arabic tweets
Aug 03, 2021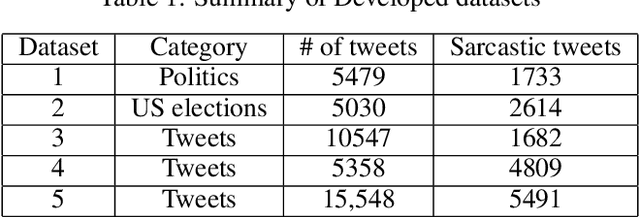
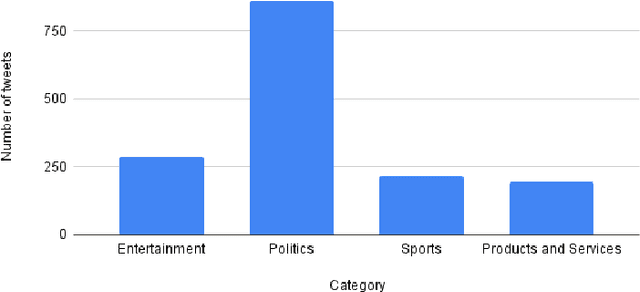
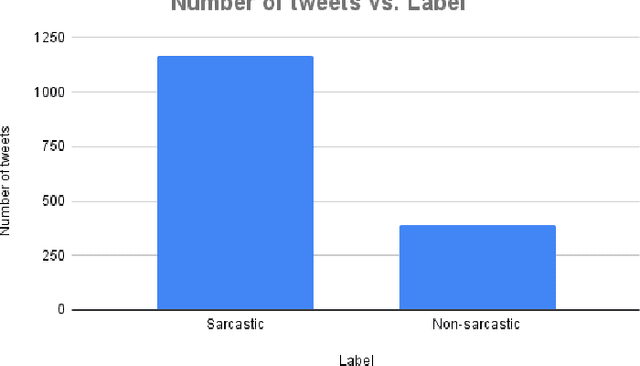

Abstract:The role of predicting sarcasm in the text is known as automatic sarcasm detection. Given the prevalence and challenges of sarcasm in sentiment-bearing text, this is a critical phase in most sentiment analysis tasks. With the increasing popularity and usage of different social media platforms among users around the world, people are using sarcasm more and more in their day-to-day conversations, social media posts and tweets, and it is considered as a way for people to express their sentiment about some certain topics or issues. As a result of the increasing popularity, researchers started to focus their research endeavors on detecting sarcasm from a text in different languages especially the English language. However, the task of sarcasm detection is a challenging task due to the nature of sarcastic texts; which can be relative and significantly differs from one person to another depending on the topic, region, the user's mentality and other factors. In addition to these challenges, sarcasm detection in the Arabic language has its own challenges due to the complexity of the Arabic language, such as being morphologically rich, with many dialects that significantly vary between each other, while also being lowly resourced. In recent years, only few research attempts started tackling the task of sarcasm detection in Arabic, including creating and collecting corpora, organizing workshops and establishing baseline models. This paper intends to create a new humanly annotated Arabic corpus for sarcasm detection collected from tweets, and implementing a new approach for sarcasm detection and quantification in Arabic tweets. The annotation technique followed in this paper is unique in sarcasm detection and the proposed approach tackles the problem as a regression problem instead of classification; i.e., the model attempts to predict the level of sarcasm instead of binary classification.
Multi-Dialect Arabic BERT for Country-Level Dialect Identification
Jul 10, 2020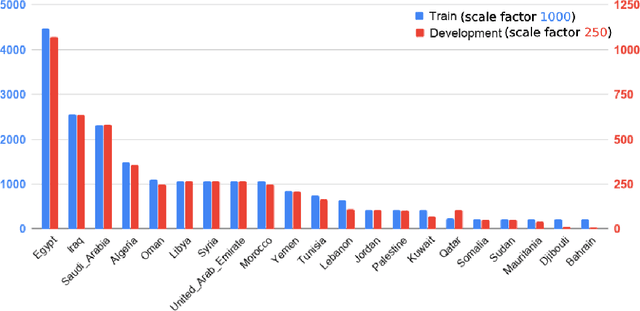
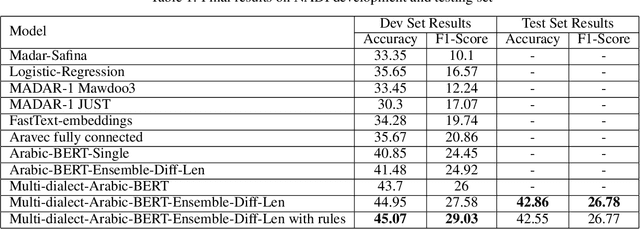
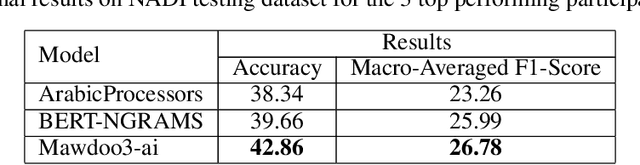
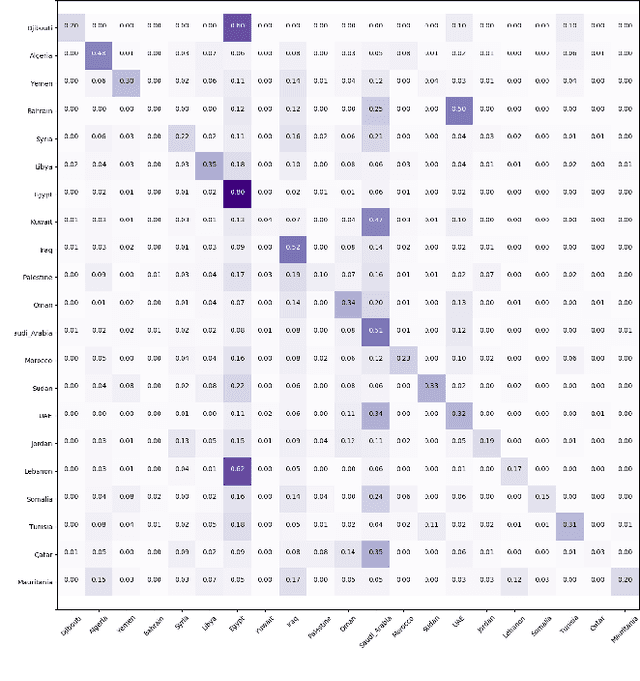
Abstract:Arabic dialect identification is a complex problem for a number of inherent properties of the language itself. In this paper, we present the experiments conducted, and the models developed by our competing team, Mawdoo3 AI, along the way to achieving our winning solution to subtask 1 of the Nuanced Arabic Dialect Identification (NADI) shared task. The dialect identification subtask provides 21,000 country-level labeled tweets covering all 21 Arab countries. An unlabeled corpus of 10M tweets from the same domain is also presented by the competition organizers for optional use. Our winning solution itself came in the form of an ensemble of different training iterations of our pre-trained BERT model, which achieved a micro-averaged F1-score of 26.78% on the subtask at hand. We publicly release the pre-trained language model component of our winning solution under the name of Multi-dialect-Arabic-BERT model, for any interested researcher out there.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge