Bart Goethals
What Data is Really Necessary? A Feasibility Study of Inference Data Minimization for Recommender Systems
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Data minimization is a legal principle requiring personal data processing to be limited to what is necessary for a specified purpose. Operationalizing this principle for recommender systems, which rely on extensive personal data, remains a significant challenge. This paper conducts a feasibility study on minimizing implicit feedback inference data for such systems. We propose a novel problem formulation, analyze various minimization techniques, and investigate key factors influencing their effectiveness. We demonstrate that substantial inference data reduction is technically feasible without significant performance loss. However, its practicality is critically determined by two factors: the technical setting (e.g., performance targets, choice of model) and user characteristics (e.g., history size, preference complexity). Thus, while we establish its technical feasibility, we conclude that data minimization remains practically challenging and its dependence on the technical and user context makes a universal standard for data `necessity' difficult to implement.
APS Explorer: Navigating Algorithm Performance Spaces for Informed Dataset Selection
Aug 26, 2025Abstract:Dataset selection is crucial for offline recommender system experiments, as mismatched data (e.g., sparse interaction scenarios require datasets with low user-item density) can lead to unreliable results. Yet, 86\% of ACM RecSys 2024 papers provide no justification for their dataset choices, with most relying on just four datasets: Amazon (38\%), MovieLens (34\%), Yelp (15\%), and Gowalla (12\%). While Algorithm Performance Spaces (APS) were proposed to guide dataset selection, their adoption has been limited due to the absence of an intuitive, interactive tool for APS exploration. Therefore, we introduce the APS Explorer, a web-based visualization tool for interactive APS exploration, enabling data-driven dataset selection. The APS Explorer provides three interactive features: (1) an interactive PCA plot showing dataset similarity via performance patterns, (2) a dynamic meta-feature table for dataset comparisons, and (3) a specialized visualization for pairwise algorithm performance.
Discrete-event Tensor Factorization: Learning a Smooth Embedding for Continuous Domains
Aug 06, 2025


Abstract:Recommender systems learn from past user behavior to predict future user preferences. Intuitively, it has been established that the most recent interactions are more indicative of future preferences than older interactions. Many recommendation algorithms use this notion to either drop older interactions or to assign them a lower weight, so the model can focus on the more informative, recent information. However, very few approaches model the flow of time explicitly. This paper analyzes how time can be encoded in factorization-style recommendation models. By including absolute time as a feature, our models can learn varying user preferences and changing item perception over time. In addition to simple binning approaches, we also propose a novel, fully continuous time encoding mechanism. Through the use of a polynomial fit inside the loss function, our models completely avoid the need for discretization, and they are able to capture the time dimension in arbitrary resolution. We perform a comparative study on three real-world datasets that span multiple years, where long user histories are present, and items stay relevant for a longer time. Empirical results show that, by explicitly modeling time, our models are very effective at capturing temporal signals, such as varying item popularities over time. Despite this however, our experiments also indicate that a simple post-hoc popularity adjustment is often sufficient to achieve the best performance on the unseen test set. This teaches us that, for the recommendation task, predicting the future is more important than capturing past trends. As such, we argue that specialized mechanisms are needed for extrapolation to future data.
Weighted Tensor Decompositions for Context-aware Collaborative Filtering
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Over recent years it has become well accepted that user interest is not static or immutable. There are a variety of contextual factors, such as time of day, the weather or the user's mood, that influence the current interests of the user. Modelling approaches need to take these factors into account if they want to succeed at finding the most relevant content to recommend given the situation. A popular method for context-aware recommendation is to encode context attributes as extra dimensions of the classic user-item interaction matrix, effectively turning it into a tensor, followed by applying the appropriate tensor decomposition methods to learn missing values. However, unlike with matrix factorization, where all decompositions are essentially a product of matrices, there exist many more options for decomposing tensors by combining vector, matrix and tensor products. We study the most successful decomposition methods that use weighted square loss and categorize them based on their tensor structure and regularization strategy. Additionally, we further extend the pool of methods by filling in the missing combinations. In this paper we provide an overview of the properties of the different decomposition methods, such as their complexity, scalability, and modelling capacity. These benefits are then contrasted with the performances achieved in offline experiments to gain more insight into which method to choose depending on a specific situation and constraints.
Efficient pattern-based anomaly detection in a network of multivariate devices
May 07, 2023



Abstract:Many organisations manage service quality and monitor a large set devices and servers where each entity is associated with telemetry or physical sensor data series. Recently, various methods have been proposed to detect behavioural anomalies, however existing approaches focus on multivariate time series and ignore communication between entities. Moreover, we aim to support end-users in not only in locating entities and sensors causing an anomaly at a certain period, but also explain this decision. We propose a scalable approach to detect anomalies using a two-step approach. First, we recover relations between entities in the network, since relations are often dynamic in nature and caused by an unknown underlying process. Next, we report anomalies based on an embedding of sequential patterns. Pattern mining is efficient and supports interpretation, i.e. patterns represent frequent occurring behaviour in time series. We extend pattern mining to filter sequential patterns based on frequency, temporal constraints and minimum description length. We collect and release two public datasets for international broadcasting and X from an Internet company. \textit{BAD} achieves an overall F1-Score of 0.78 on 9 benchmark datasets, significantly outperforming the best baseline by 3\%. Additionally, \textit{BAD} is also an order-of-magnitude faster than state-of-the-art anomaly detection methods.
Modelling Users with Item Metadata for Explainable and Interactive Recommendation
Jul 08, 2022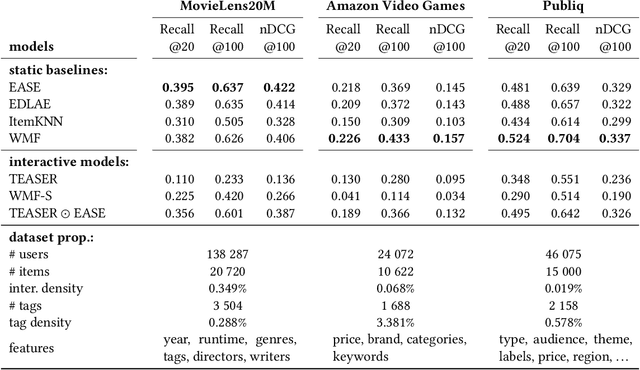
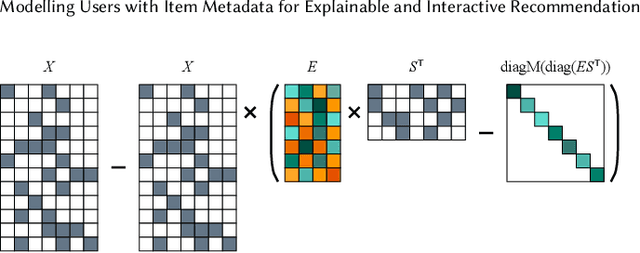
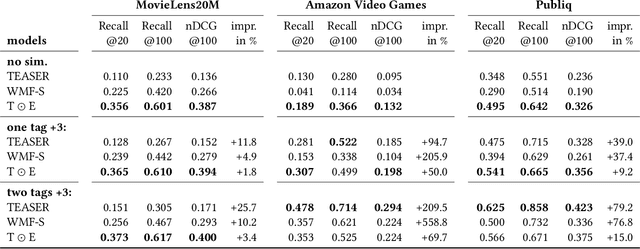
Abstract:Recommender systems are used in many different applications and contexts, however their main goal can always be summarised as "connecting relevant content to interested users". Personalized recommendation algorithms achieve this goal by first building a profile of the user, either implicitly or explicitly, and then matching items with this profile to find relevant content. The more interpretable the profile and this "matching function" are, the easier it is to provide users with accurate and intuitive explanations, and also to let them interact with the system. Indeed, for a user to see what the system has already learned about her interests is of key importance for her to provide feedback to the system and to guide it towards better understanding her preferences. To this end, we propose a linear collaborative filtering recommendation model that builds user profiles within the domain of item metadata, which is arguably the most interpretable domain for end users. Our method is hence inherently transparent and explainable. Moreover, since recommendations are computed as a linear function of item metadata and the interpretable user profile, our method seamlessly supports interactive recommendation. In other words, users can directly tweak the weights of the learned profile for more fine-grained browsing and discovery of content based on their current interests. We demonstrate the interactive aspect of this model in an online application for discovering cultural events in Belgium. Additionally, the performance of the model is evaluated with offline experiments, both static and with simulated feedback, and compared to several state-of-the-art and state-of-practice baselines.
Proximity Forest: An effective and scalable distance-based classifier for time series
Aug 31, 2018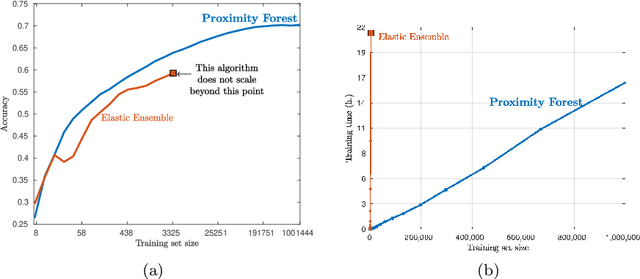
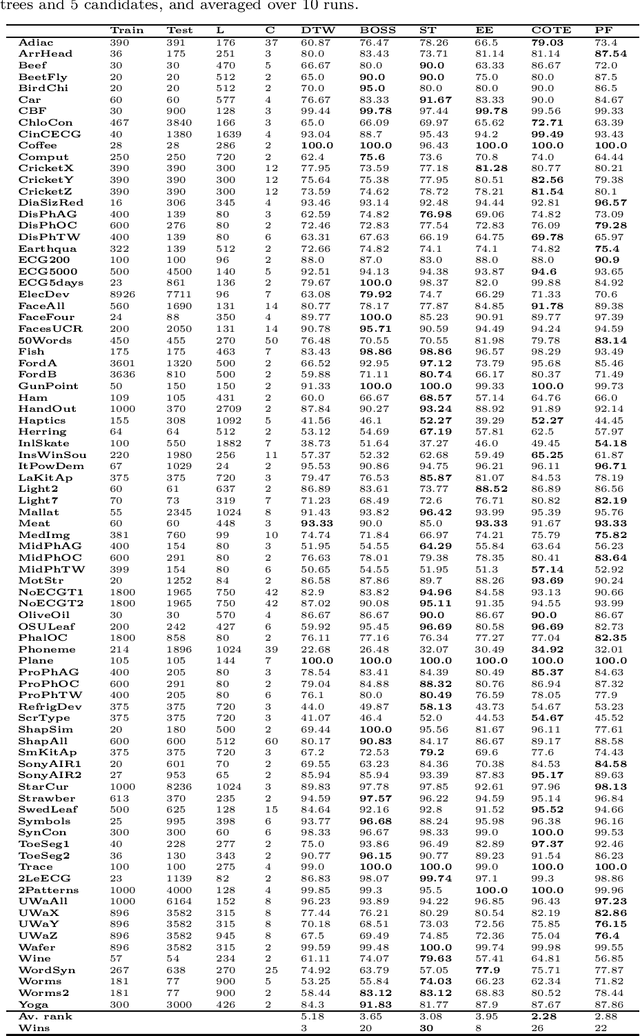
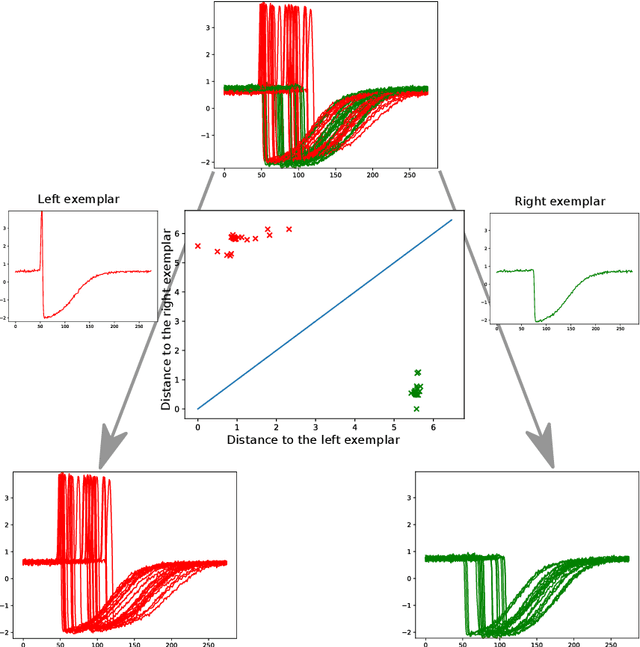
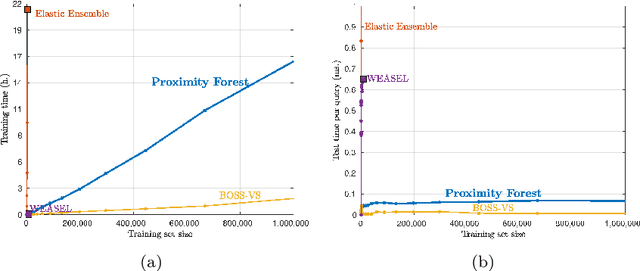
Abstract:Research into the classification of time series has made enormous progress in the last decade. The UCR time series archive has played a significant role in challenging and guiding the development of new learners for time series classification. The largest dataset in the UCR archive holds 10 thousand time series only; which may explain why the primary research focus has been in creating algorithms that have high accuracy on relatively small datasets. This paper introduces Proximity Forest, an algorithm that learns accurate models from datasets with millions of time series, and classifies a time series in milliseconds. The models are ensembles of highly randomized Proximity Trees. Whereas conventional decision trees branch on attribute values (and usually perform poorly on time series), Proximity Trees branch on the proximity of time series to one exemplar time series or another; allowing us to leverage the decades of work into developing relevant measures for time series. Proximity Forest gains both efficiency and accuracy by stochastic selection of both exemplars and similarity measures. Our work is motivated by recent time series applications that provide orders of magnitude more time series than the UCR benchmarks. Our experiments demonstrate that Proximity Forest is highly competitive on the UCR archive: it ranks among the most accurate classifiers while being significantly faster. We demonstrate on a 1M time series Earth observation dataset that Proximity Forest retains this accuracy on datasets that are many orders of magnitude greater than those in the UCR repository, while learning its models at least 100,000 times faster than current state of the art models Elastic Ensemble and COTE.
Understanding Concept Drift
Apr 02, 2017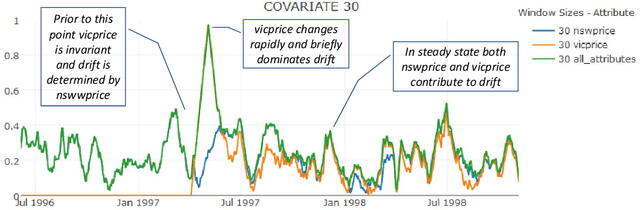
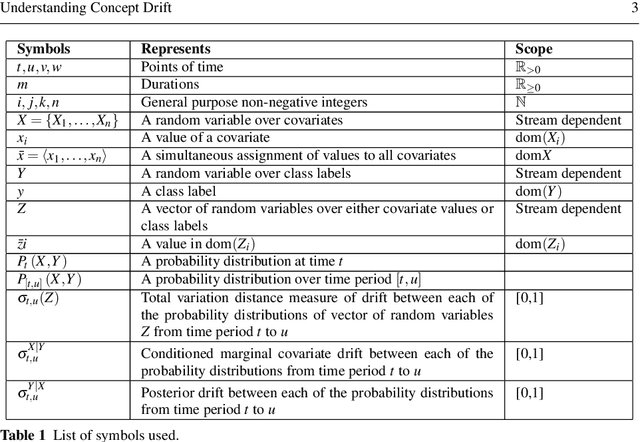
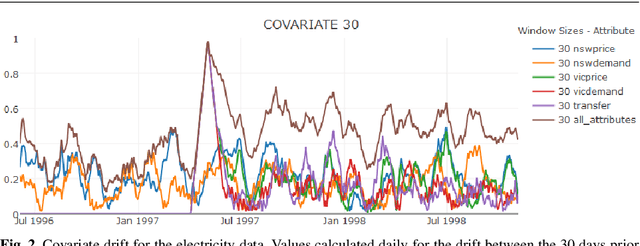
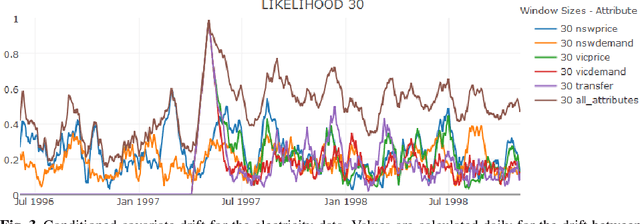
Abstract:Concept drift is a major issue that greatly affects the accuracy and reliability of many real-world applications of machine learning. We argue that to tackle concept drift it is important to develop the capacity to describe and analyze it. We propose tools for this purpose, arguing for the importance of quantitative descriptions of drift in marginal distributions. We present quantitative drift analysis techniques along with methods for communicating their results. We demonstrate their effectiveness by application to three real-world learning tasks.
Interactive Constrained Association Rule Mining
Feb 05, 2003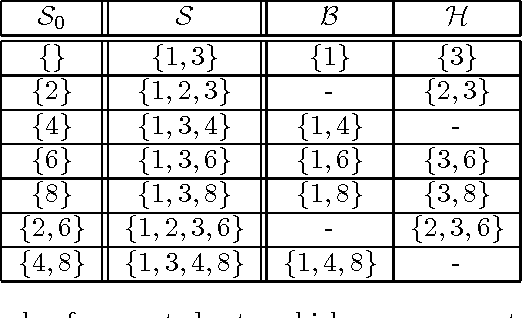
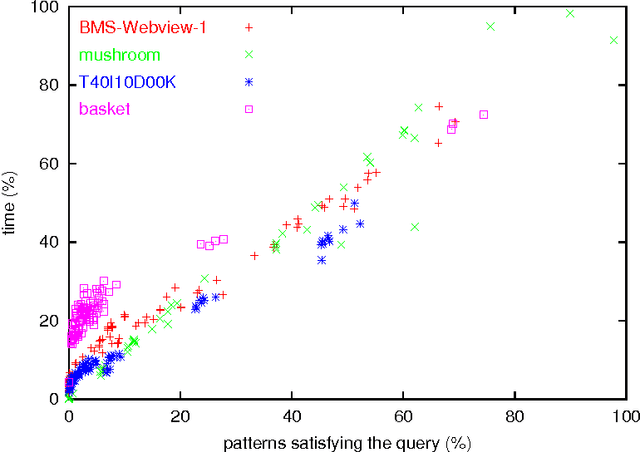
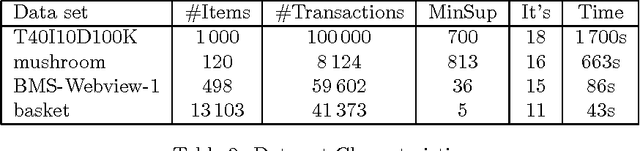
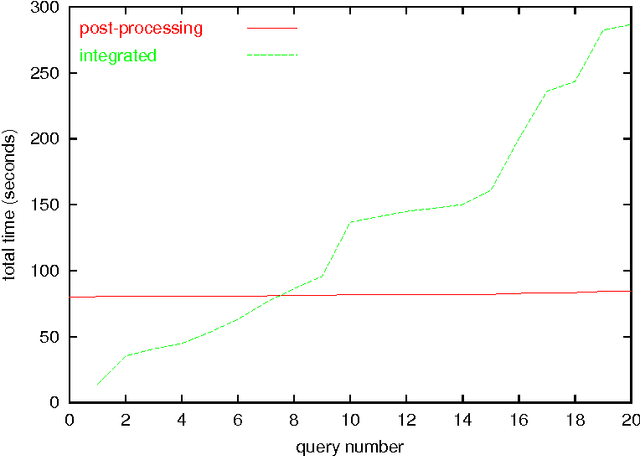
Abstract:We investigate ways to support interactive mining sessions, in the setting of association rule mining. In such sessions, users specify conditions (queries) on the associations to be generated. Our approach is a combination of the integration of querying conditions inside the mining phase, and the incremental querying of already generated associations. We present several concrete algorithms and compare their performance.
A Tight Upper Bound on the Number of Candidate Patterns
Nov 30, 2002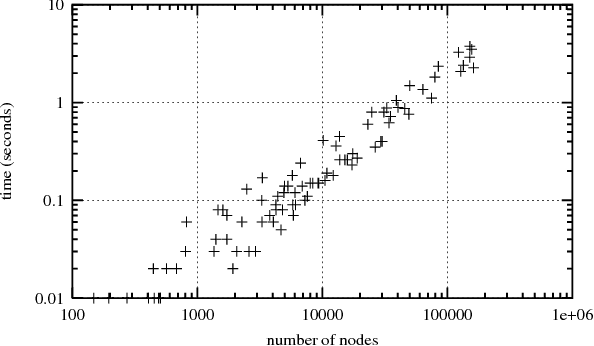
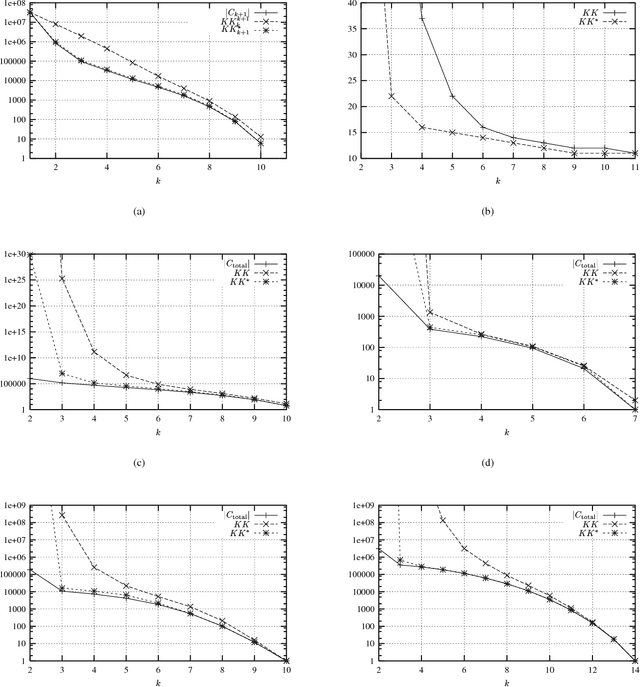
Abstract:In the context of mining for frequent patterns using the standard levelwise algorithm, the following question arises: given the current level and the current set of frequent patterns, what is the maximal number of candidate patterns that can be generated on the next level? We answer this question by providing a tight upper bound, derived from a combinatorial result from the sixties by Kruskal and Katona. Our result is useful to reduce the number of database scans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge