Augustin Toma
Exploring the Design Space of 3D MLLMs for CT Report Generation
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have emerged as a promising way to automate Radiology Report Generation (RRG). In this work, we systematically investigate the design space of 3D MLLMs, including visual input representation, projectors, Large Language Models (LLMs), and fine-tuning techniques for 3D CT report generation. We also introduce two knowledge-based report augmentation methods that improve performance on the GREEN score by up to 10\%, achieving the 2nd place on the MICCAI 2024 AMOS-MM challenge. Our results on the 1,687 cases from the AMOS-MM dataset show that RRG is largely independent of the size of LLM under the same training protocol. We also show that larger volume size does not always improve performance if the original ViT was pre-trained on a smaller volume size. Lastly, we show that using a segmentation mask along with the CT volume improves performance. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/bowang-lab/AMOS-MM-Solution
ECG-FM: An Open Electrocardiogram Foundation Model
Aug 09, 2024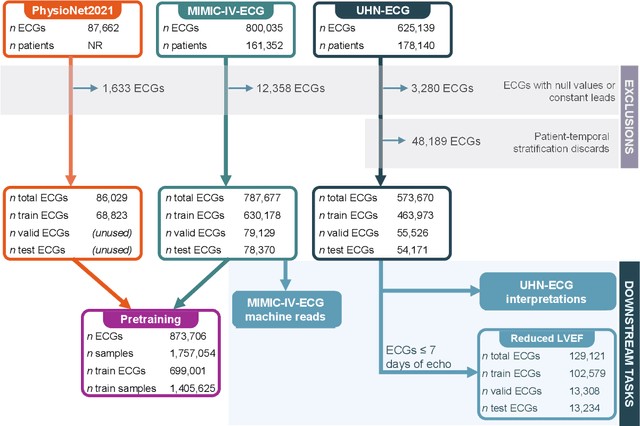
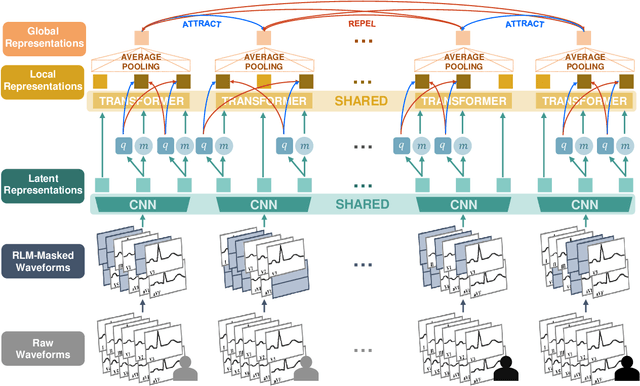
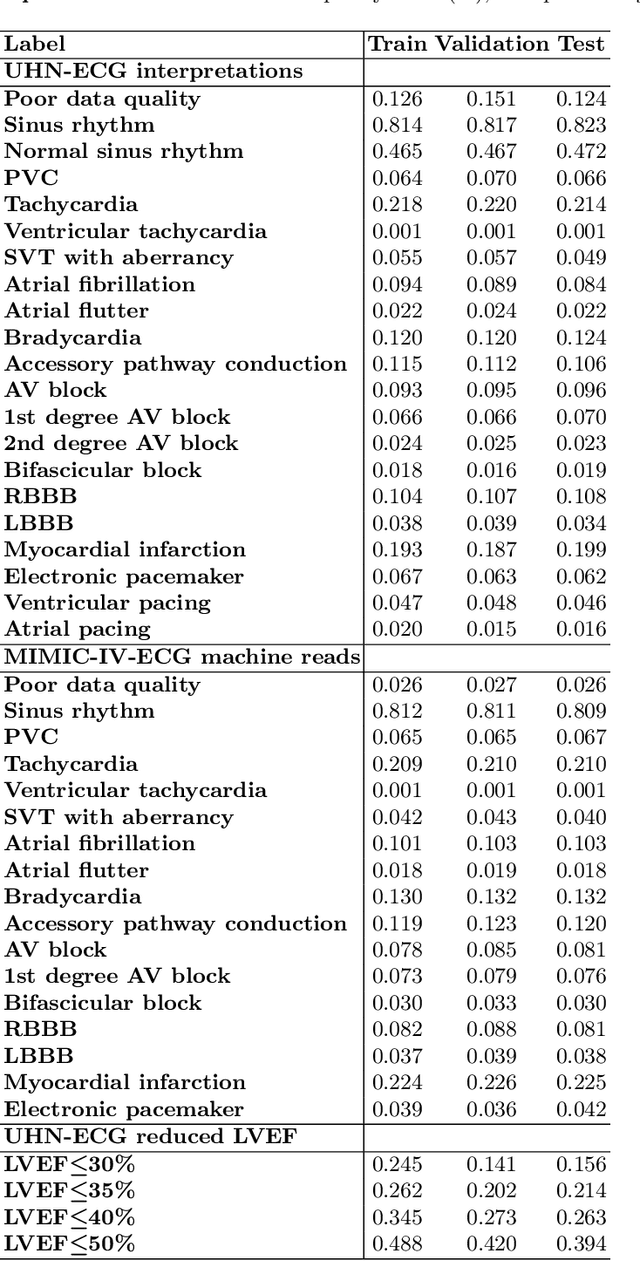
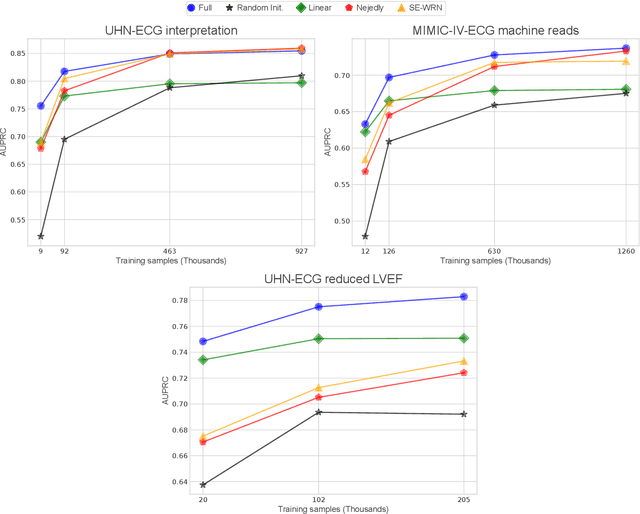
Abstract:The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a ubiquitous diagnostic test. Conventional task-specific ECG analysis models require large numbers of expensive ECG annotations or associated labels to train. Transfer learning techniques have been shown to improve generalization and reduce reliance on labeled data. We present ECG-FM, an open foundation model for ECG analysis, and conduct a comprehensive study performed on a dataset of 1.66 million ECGs sourced from both publicly available and private institutional sources. ECG-FM adopts a transformer-based architecture and is pretrained on 2.5 million samples using ECG-specific augmentations and contrastive learning, as well as a continuous signal masking objective. Our transparent evaluation includes a diverse range of downstream tasks, where we predict ECG interpretation labels, reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, and abnormal cardiac troponin. Affirming ECG-FM's effectiveness as a foundation model, we demonstrate how its command of contextual information results in strong performance, rich pretrained embeddings, and reliable interpretability. Due to a lack of open-weight practices, we highlight how ECG analysis is lagging behind other medical machine learning subfields in terms of foundation model adoption. Our code is available at https://github.com/bowang-lab/ECG-FM/.
WangLab at MEDIQA-M3G 2024: Multimodal Medical Answer Generation using Large Language Models
Apr 22, 2024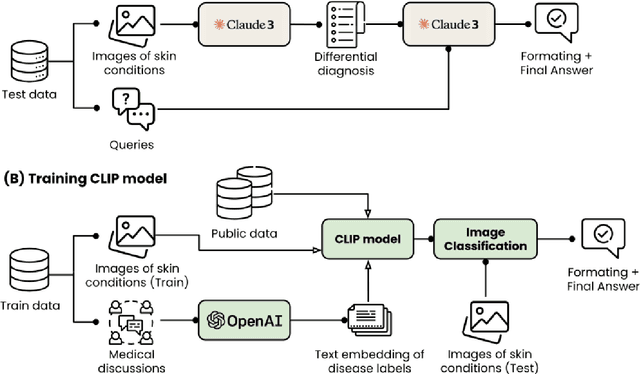
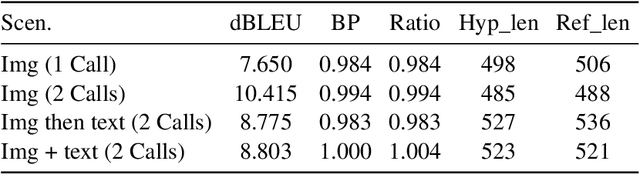
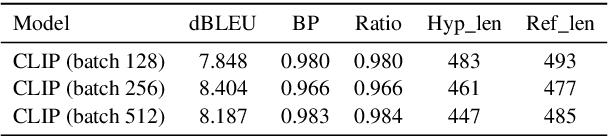
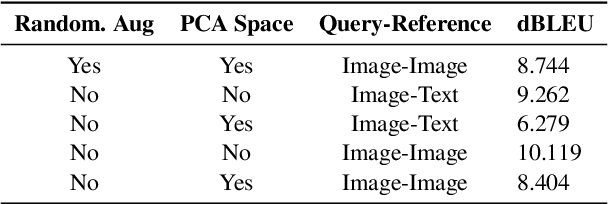
Abstract:This paper outlines our submission to the MEDIQA2024 Multilingual and Multimodal Medical Answer Generation (M3G) shared task. We report results for two standalone solutions under the English category of the task, the first involving two consecutive API calls to the Claude 3 Opus API and the second involving training an image-disease label joint embedding in the style of CLIP for image classification. These two solutions scored 1st and 2nd place respectively on the competition leaderboard, substantially outperforming the next best solution. Additionally, we discuss insights gained from post-competition experiments. While the performance of these two solutions have significant room for improvement due to the difficulty of the shared task and the challenging nature of medical visual question answering in general, we identify the multi-stage LLM approach and the CLIP image classification approach as promising avenues for further investigation.
WangLab at MEDIQA-CORR 2024: Optimized LLM-based Programs for Medical Error Detection and Correction
Apr 22, 2024



Abstract:Medical errors in clinical text pose significant risks to patient safety. The MEDIQA-CORR 2024 shared task focuses on detecting and correcting these errors across three subtasks: identifying the presence of an error, extracting the erroneous sentence, and generating a corrected sentence. In this paper, we present our approach that achieved top performance in all three subtasks. For the MS dataset, which contains subtle errors, we developed a retrieval-based system leveraging external medical question-answering datasets. For the UW dataset, reflecting more realistic clinical notes, we created a pipeline of modules to detect, localize, and correct errors. Both approaches utilized the DSPy framework for optimizing prompts and few-shot examples in large language model (LLM) based programs. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of LLM based programs for medical error correction. However, our approach has limitations in addressing the full diversity of potential errors in medical documentation. We discuss the implications of our work and highlight future research directions to advance the robustness and applicability of medical error detection and correction systems.
Clinical Camel: An Open-Source Expert-Level Medical Language Model with Dialogue-Based Knowledge Encoding
May 19, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) present immense potential in the medical field, yet concerns over data privacy, regulatory compliance, and model stability restrict their widespread adoption. Although the distillation of high-performing closed-source LLMs has proven effective for general tasks, their application in healthcare is limited due to reduced domain knowledge and remnants of alignment behavior hindering clinical tasks. To address these challenges, we propose Dialogue-Based Knowledge Encoding (DBKE). DBKE enhances models' implicit knowledge base and primes them for conversational recall, augmenting their conversational capabilities and enabling a soft alignment for subsequent use cases. By transforming dense academic source text into synthetic dialogue, DBKE broadens the model's knowledge base and enables a soft alignment that guides downstream behaviours. We present Clinical Camel, an open-source, healthcare-focused conversational model, to showcase the effectiveness of DBKE. Clinical Camel outperforms GPT-3.5 on the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE) Step 1 and Step 3 with scores of 53.2 % and 58.2 %, respectively, compared to GPT-3.5's scores of 36.1 % and 55.7 %. Clinical Camel adeptly handles multi-stage clinical case problems, provides adaptive counseling, and generates clinical notes. However, it is prone to hallucinations, which pose a significant obstacle in safety-critical settings. The performance of Clinical Camel underscores the importance of continued research and development of open-source models for the safe and effective integration of LLMs in healthcare settings.
Clinical Note Generation from Doctor-Patient Conversations using Large Language Models: Insights from MEDIQA-Chat
May 03, 2023



Abstract:This paper describes our submission to the MEDIQA-Chat 2023 shared task for automatic clinical note generation from doctor-patient conversations. We report results for two approaches: the first fine-tunes a pre-trained language model (PLM) on the shared task data, and the second uses few-shot in-context learning (ICL) with a large language model (LLM). Both achieve high performance as measured by automatic metrics (e.g. ROUGE, BERTScore) and ranked second and first, respectively, of all submissions to the shared task. Expert human scrutiny indicates that notes generated via the ICL-based approach with GPT-4 are preferred about as often as human-written notes, making it a promising path toward automated note generation from doctor-patient conversations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge