Anna V. Kononova
Multi-Agent Influence Diagrams to Hybrid Threat Modeling
Mar 03, 2026Abstract:Western governments have adopted an assortment of counter-hybrid threat measures to defend against hostile actions below the conventional military threshold. The impact of these measures is unclear because of the ambiguity of hybrid threats, their cross-domain nature, and uncertainty about how countermeasures shape adversarial behavior. This paper offers a novel approach to clarifying this impact by unifying previously bifurcating hybrid threat modeling methods through a (multi-agent) influence diagram framework. The model balances the costs of countermeasures, their ability to dissuade the adversary from executing hybrid threats, and their potential to mitigate the impact of hybrid threats. We run 1000 semi-synthetic variants of a real-world-inspired scenario simulating the strategic interaction between attacking agent A and defending agent B over a cyber attack on critical infrastructure to explore the effectiveness of a set of five different counter-hybrid threat measures. Counter-hybrid measures range from strengthening resilience and denial of the adversary's ability to execute a hybrid threat to dissuasion through the threat of punishment. Our analysis primarily evaluates the overarching characteristics of counter-hybrid threat measures. This approach allows us to generalize the effectiveness of these measures and examine parameter impact sensitivity. In addition, we discuss policy relevance and outline future research avenues.
Structural bias in multi-objective optimisation
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Structural bias (SB) refers to systematic preferences of an optimisation algorithm for particular regions of the search space that arise independently of the objective function. While SB has been studied extensively in single-objective optimisation, its role in multi-objective optimisation remains largely unexplored. This is problematic, as dominance relations, diversity preservation and Pareto-based selection mechanisms may introduce or amplify structural effects. In this paper, we extend the concept of structural bias to the multi-objective setting and propose a methodology to study it in isolation from fitness-driven guidance. We introduce a suite of synthetic multi-objective test problems with analytically controlled Pareto fronts and deliberately uninformative objective values. These problems are designed to decouple algorithmic behaviour from problem structure, allowing bias induced purely by algorithmic operators and design choices to be observed. The test suite covers a range of Pareto front shapes, densities and noise levels, enabling systematic analysis of different manifestations of structural bias. We discuss methodological challenges specific to the multi-objective case and outline how existing SB detection approaches can be adapted. This work provides a first step towards behaviour-based benchmarking of multi-objective optimisers, complementing performance-based evaluation and informing more robust algorithm design.
Landscape-aware Automated Algorithm Design: An Efficient Framework for Real-world Optimization
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened new frontiers in automated algorithm design, giving rise to numerous powerful methods. However, these approaches retain critical limitations: they require extensive evaluation of the target problem to guide the search process, making them impractical for real-world optimization tasks, where each evaluation consumes substantial computational resources. This research proposes an innovative and efficient framework that decouples algorithm discovery from high-cost evaluation. Our core innovation lies in combining a Genetic Programming (GP) function generator with an LLM-driven evolutionary algorithm designer. The evolutionary direction of the GP-based function generator is guided by the similarity between the landscape characteristics of generated proxy functions and those of real-world problems, ensuring that algorithms discovered via proxy functions exhibit comparable performance on real-world problems. Our method enables deep exploration of the algorithmic space before final validation while avoiding costly real-world evaluations. We validated the framework's efficacy across multiple real-world problems, demonstrating its ability to discover high-performance algorithms while substantially reducing expensive evaluations. This approach shows a path to apply LLM-based automated algorithm design to computationally intensive real-world optimization challenges.
LLaMEA-SAGE: Guiding Automated Algorithm Design with Structural Feedback from Explainable AI
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models have enabled automated algorithm design (AAD) by generating optimization algorithms directly from natural-language prompts. While evolutionary frameworks such as LLaMEA demonstrate strong exploratory capabilities across the algorithm design space, their search dynamics are entirely driven by fitness feedback, leaving substantial information about the generated code unused. We propose a mechanism for guiding AAD using feedback constructed from graph-theoretic and complexity features extracted from the abstract syntax trees of the generated algorithms, based on a surrogate model learned over an archive of evaluated solutions. Using explainable AI techniques, we identify features that substantially affect performance and translate them into natural-language mutation instructions that steer subsequent LLM-based code generation without restricting expressivity. We propose LLaMEA-SAGE, which integrates this feature-driven guidance into LLaMEA, and evaluate it across several benchmarks. We show that the proposed structured guidance achieves the same performance faster than vanilla LLaMEA in a small controlled experiment. In a larger-scale experiment using the MA-BBOB suite from the GECCO-MA-BBOB competition, our guided approach achieves superior performance compared to state-of-the-art AAD methods. These results demonstrate that signals derived from code can effectively bias LLM-driven algorithm evolution, bridging the gap between code structure and human-understandable performance feedback in automated algorithm design.
Lens-descriptor guided evolutionary algorithm for optimization of complex optical systems with glass choice
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Designing high-performance optical lenses entails exploring a high-dimensional, tightly constrained space of surface curvatures, glass choices, element thicknesses, and spacings. In practice, standard optimizers (e.g., gradient-based local search and evolutionary strategies) often converge to a single local optimum, overlooking many comparably good alternatives that matter for downstream engineering decisions. We propose the Lens Descriptor-Guided Evolutionary Algorithm (LDG-EA), a two-stage framework for multimodal lens optimization. LDG-EA first partitions the design space into behavior descriptors defined by curvature-sign patterns and material indices, then learns a probabilistic model over descriptors to allocate evaluations toward promising regions. Within each descriptor, LDG-EA applies the Hill-Valley Evolutionary Algorithm with covariance-matrix self-adaptation to recover multiple distinct local minima, optionally followed by gradient-based refinement. On a 24-variable (18 continuous and 6 integer), six-element Double-Gauss topology, LDG-EA generates on average around 14500 candidate minima spanning 636 unique descriptors, an order of magnitude more than a CMA-ES baseline, while keeping wall-clock time at one hour scale. Although the best LDG-EA design is slightly worse than a fine-tuned reference lens, it remains in the same performance range. Overall, the proposed LDG-EA produces a diverse set of solutions while maintaining competitive quality within practical computational budgets and wall-clock time.
Benchmarking that Matters: Rethinking Benchmarking for Practical Impact
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Benchmarking has driven scientific progress in Evolutionary Computation, yet current practices fall short of real-world needs. Widely used synthetic suites such as BBOB and CEC isolate algorithmic phenomena but poorly reflect the structure, constraints, and information limitations of continuous and mixed-integer optimization problems in practice. This disconnect leads to the misuse of benchmarking suites for competitions, automated algorithm selection, and industrial decision-making, despite these suites being designed for different purposes. We identify key gaps in current benchmarking practices and tooling, including limited availability of real-world-inspired problems, missing high-level features, and challenges in multi-objective and noisy settings. We propose a vision centered on curated real-world-inspired benchmarks, practitioner-accessible feature spaces and community-maintained performance databases. Real progress requires coordinated effort: A living benchmarking ecosystem that evolves with real-world insights and supports both scientific understanding and industrial use.
From Spikes to Speech: NeuroVoc -- A Biologically Plausible Vocoder Framework for Auditory Perception and Cochlear Implant Simulation
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:We present NeuroVoc, a flexible model-agnostic vocoder framework that reconstructs acoustic waveforms from simulated neural activity patterns using an inverse Fourier transform. The system applies straightforward signal processing to neurogram representations, time-frequency binned outputs from auditory nerve fiber models. Crucially, the model architecture is modular, allowing for easy substitution or modification of the underlying auditory models. This flexibility eliminates the need for speech-coding-strategy-specific vocoder implementations when simulating auditory perception in cochlear implant (CI) users. It also allows direct comparisons between normal hearing (NH) and electrical hearing (EH) models, as demonstrated in this study. The vocoder preserves distinctive features of each model; for example, the NH model retains harmonic structure more faithfully than the EH model. We evaluated perceptual intelligibility in noise using an online Digits-in-Noise (DIN) test, where participants completed three test conditions: one with standard speech, and two with vocoded speech using the NH and EH models. Both the standard DIN test and the EH-vocoded groups were statistically equivalent to clinically reported data for NH and CI listeners. On average, the NH and EH vocoded groups increased SRT compared to the standard test by 2.4 dB and 7.1 dB, respectively. These findings show that, although some degradation occurs, the vocoder can reconstruct intelligible speech under both hearing models and accurately reflects the reduced speech-in-noise performance experienced by CI users.
Towards a Deeper Understanding of Reasoning Capabilities in Large Language Models
May 15, 2025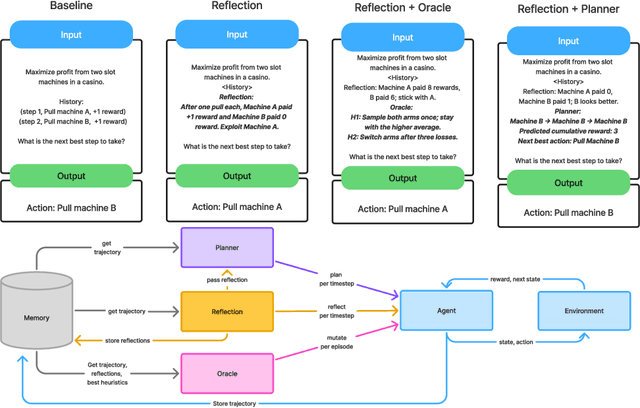
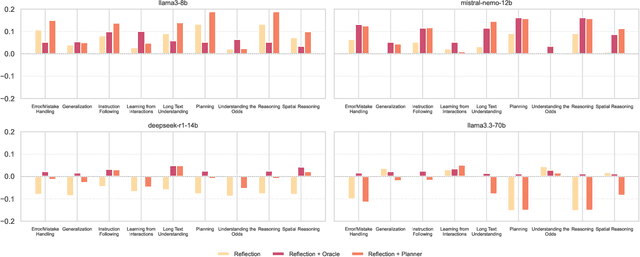
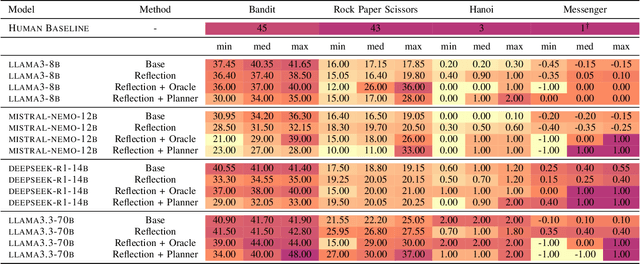
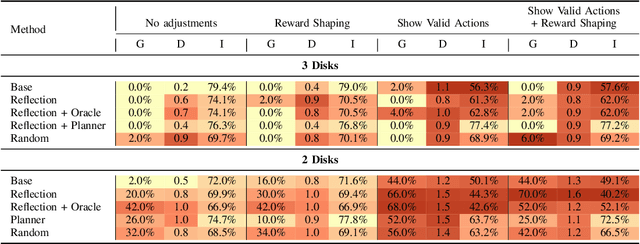
Abstract:While large language models demonstrate impressive performance on static benchmarks, the true potential of large language models as self-learning and reasoning agents in dynamic environments remains unclear. This study systematically evaluates the efficacy of self-reflection, heuristic mutation, and planning as prompting techniques to test the adaptive capabilities of agents. We conduct experiments with various open-source language models in dynamic environments and find that larger models generally outperform smaller ones, but that strategic prompting can close this performance gap. Second, a too-long prompt can negatively impact smaller models on basic reactive tasks, while larger models show more robust behaviour. Third, advanced prompting techniques primarily benefit smaller models on complex games, but offer less improvement for already high-performing large language models. Yet, we find that advanced reasoning methods yield highly variable outcomes: while capable of significantly improving performance when reasoning and decision-making align, they also introduce instability and can lead to big performance drops. Compared to human performance, our findings reveal little evidence of true emergent reasoning. Instead, large language model performance exhibits persistent limitations in crucial areas such as planning, reasoning, and spatial coordination, suggesting that current-generation large language models still suffer fundamental shortcomings that may not be fully overcome through self-reflective prompting alone. Reasoning is a multi-faceted task, and while reasoning methods like Chain of thought improves multi-step reasoning on math word problems, our findings using dynamic benchmarks highlight important shortcomings in general reasoning capabilities, indicating a need to move beyond static benchmarks to capture the complexity of reasoning.
BLADE: Benchmark suite for LLM-driven Automated Design and Evolution of iterative optimisation heuristics
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:The application of Large Language Models (LLMs) for Automated Algorithm Discovery (AAD), particularly for optimisation heuristics, is an emerging field of research. This emergence necessitates robust, standardised benchmarking practices to rigorously evaluate the capabilities and limitations of LLM-driven AAD methods and the resulting generated algorithms, especially given the opacity of their design process and known issues with existing benchmarks. To address this need, we introduce BLADE (Benchmark suite for LLM-driven Automated Design and Evolution), a modular and extensible framework specifically designed for benchmarking LLM-driven AAD methods in a continuous black-box optimisation context. BLADE integrates collections of benchmark problems (including MA-BBOB and SBOX-COST among others) with instance generators and textual descriptions aimed at capability-focused testing, such as generalisation, specialisation and information exploitation. It offers flexible experimental setup options, standardised logging for reproducibility and fair comparison, incorporates methods for analysing the AAD process (e.g., Code Evolution Graphs and various visualisation approaches) and facilitates comparison against human-designed baselines through integration with established tools like IOHanalyser and IOHexplainer. BLADE provides an `out-of-the-box' solution to systematically evaluate LLM-driven AAD approaches. The framework is demonstrated through two distinct use cases exploring mutation prompt strategies and function specialisation.
Graphical Models for Decision-Making: Integrating Causality and Game Theory
Apr 16, 2025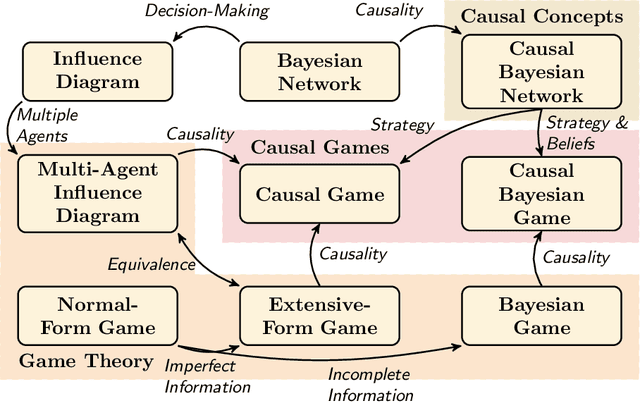
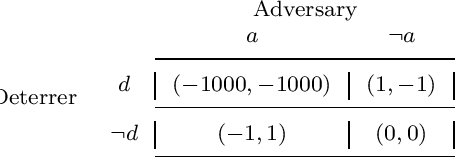
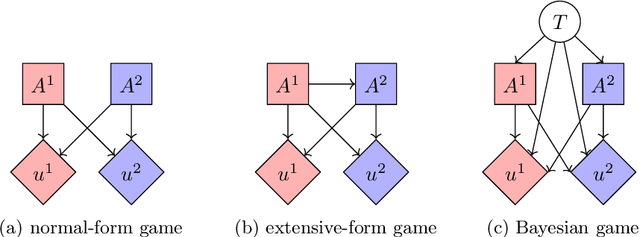
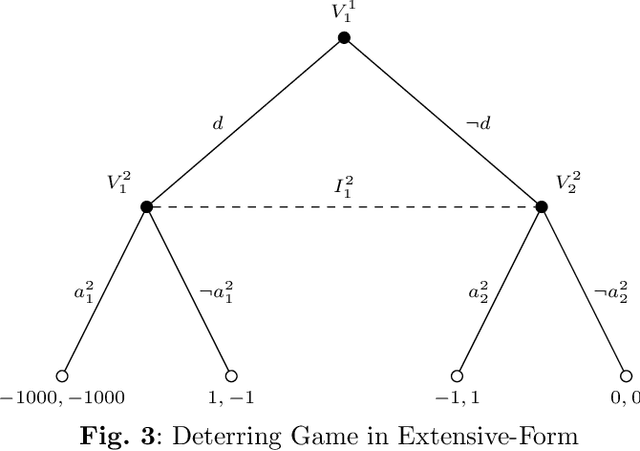
Abstract:Causality and game theory are two influential fields that contribute significantly to decision-making in various domains. Causality defines and models causal relationships in complex policy problems, while game theory provides insights into strategic interactions among stakeholders with competing interests. Integrating these frameworks has led to significant theoretical advancements with the potential to improve decision-making processes. However, practical applications of these developments remain underexplored. To support efforts toward implementation, this paper clarifies key concepts in game theory and causality that are essential to their intersection, particularly within the context of probabilistic graphical models. By rigorously examining these concepts and illustrating them with intuitive, consistent examples, we clarify the required inputs for implementing these models, provide practitioners with insights into their application and selection across different scenarios, and reference existing research that supports their implementation. We hope this work encourages broader adoption of these models in real-world scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge