Andrey Gritsenko
Open-World Class Discovery with Kernel Networks
Dec 13, 2020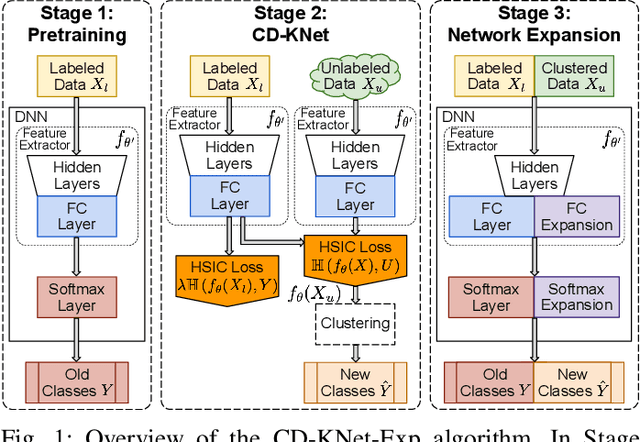



Abstract:We study an Open-World Class Discovery problem in which, given labeled training samples from old classes, we need to discover new classes from unlabeled test samples. There are two critical challenges to addressing this paradigm: (a) transferring knowledge from old to new classes, and (b) incorporating knowledge learned from new classes back to the original model. We propose Class Discovery Kernel Network with Expansion (CD-KNet-Exp), a deep learning framework, which utilizes the Hilbert Schmidt Independence Criterion to bridge supervised and unsupervised information together in a systematic way, such that the learned knowledge from old classes is distilled appropriately for discovering new classes. Compared to competing methods, CD-KNet-Exp shows superior performance on three publicly available benchmark datasets and a challenging real-world radio frequency fingerprinting dataset.
Incremental ELMVIS for unsupervised learning
Dec 18, 2019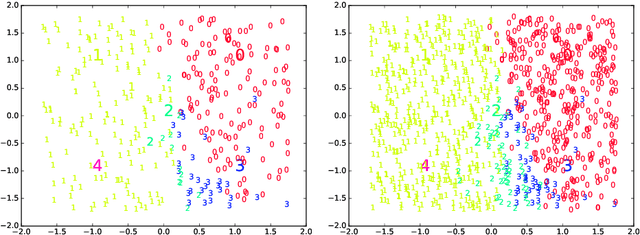
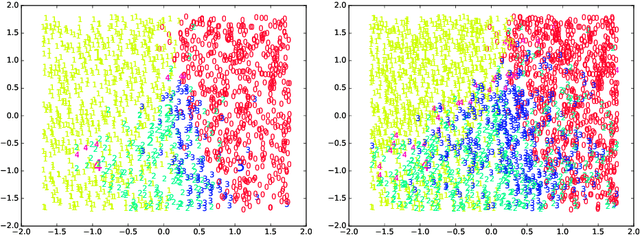
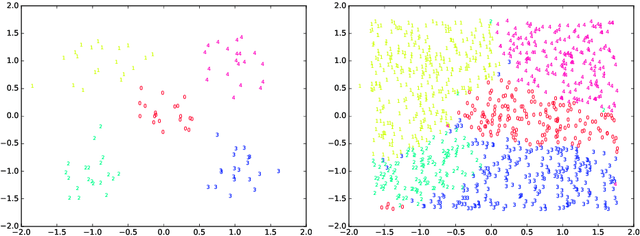
Abstract:An incremental version of the ELMVIS+ method is proposed in this paper. It iteratively selects a few best fitting data samples from a large pool, and adds them to the model. The method keeps high speed of ELMVIS+ while allowing for much larger possible sample pools due to lower memory requirements. The extension is useful for reaching a better local optimum with greedy optimization of ELMVIS, and the data structure can be specified in semi-supervised optimization. The major new application of incremental ELMVIS is not to visualization, but to a general dataset processing. The method is capable of learning dependencies from non-organized unsupervised data -- either reconstructing a shuffled dataset, or learning dependencies in complex high-dimensional space. The results are interesting and promising, although there is space for improvements.
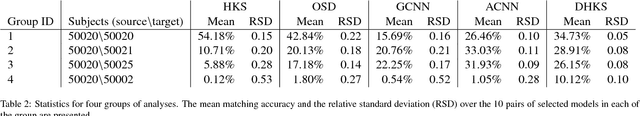
Automatic Identification of Twin Zygosity in Resting-State Functional MRI
Oct 26, 2018



Abstract:A key strength of twin studies arises from the fact that there are two types of twins, monozygotic and dizygotic, that share differing amounts of genetic information. Accurate differentiation of twin types allows efficient inference on genetic influences in a population. However, identification of zygosity is often prone to errors without genotying. In this study, we propose a novel pairwise feature representation to classify the zygosity of twin pairs of resting state functional magnetic resonance images (rs-fMRI). For this, we project an fMRI signal to a set of basis functions and use the projection coefficients as the compact and discriminative feature representation of noisy fMRI. We encode the relationship between twins as the correlation between the new feature representations across brain regions. We employ hill climbing variable selection to identify brain regions that are the most genetically affected. The proposed framework was applied to 208 twin pairs and achieved 94.19% classification accuracy in automatically identifying the zygosity of paired images.
Deep Spectral Descriptors: Learning the point-wise correspondence metric via Siamese deep neural networks
Jun 25, 2018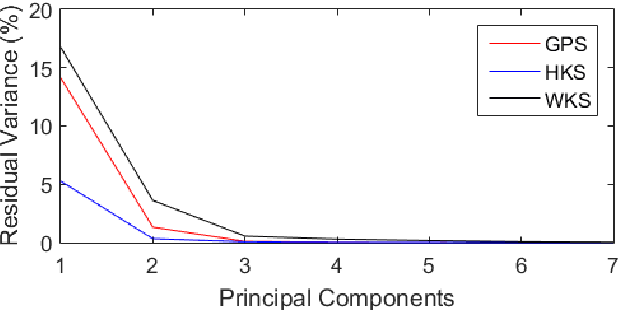
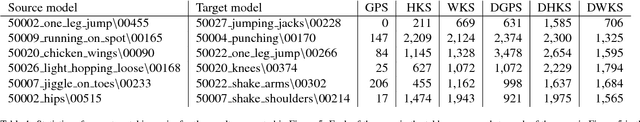
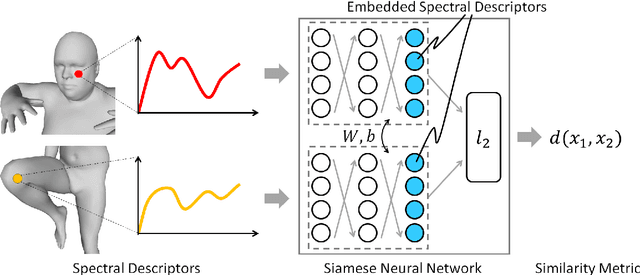
Abstract:A robust and informative local shape descriptor plays an important role in mesh registration. In this regard, spectral descriptors that are based on the spectrum of the Laplace-Beltrami operator have gained a spotlight among the researchers for the last decade due to their desirable properties, such as isometry invariance. Despite such, however, spectral descriptors often fail to give a correct similarity measure for non-isometric cases where the metric distortion between the models is large. Hence, they are in general not suitable for the registration problems, except for the special cases when the models are near-isometry. In this paper, we investigate a way to develop shape descriptors for non-isometric registration tasks by embedding the spectral shape descriptors into a different metric space where the Euclidean distance between the elements directly indicates the geometric dissimilarity. We design and train a Siamese deep neural network to find such an embedding, where the embedded descriptors are promoted to rearrange based on the geometric similarity. We found our approach can significantly enhance the performance of the conventional spectral descriptors for the non-isometric registration tasks, and outperforms recent state-of-the-art method reported in literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge