Andreas Bucher
When Generative AI Meets Workplace Learning: Creating A Realistic & Motivating Learning Experience With A Generative PCA
May 24, 2024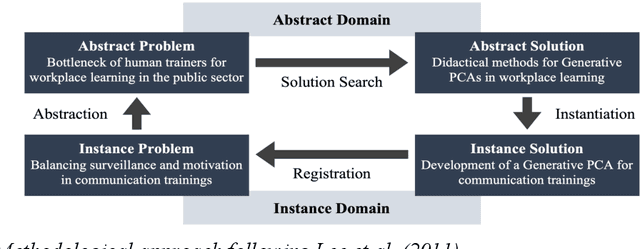
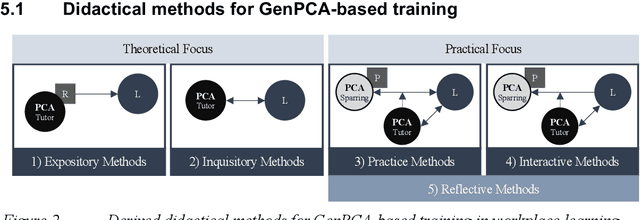
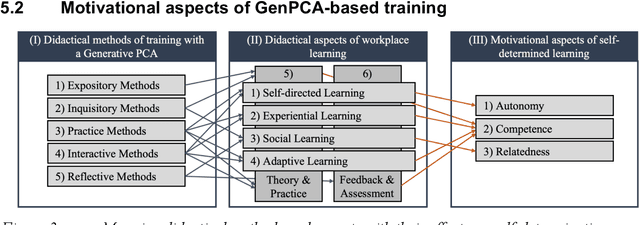
Abstract:Workplace learning is used to train employees systematically, e.g., via e-learning or in 1:1 training. However, this is often deemed ineffective and costly. Whereas pure e-learning lacks the possibility of conversational exercise and personal contact, 1:1 training with human instructors involves a high level of personnel and organizational costs. Hence, pedagogical conversational agents (PCAs), based on generative AI, seem to compensate for the disadvantages of both forms. Following Action Design Research, this paper describes an organizational communication training with a Generative PCA (GenPCA). The evaluation shows promising results: the agent was perceived positively among employees and contributed to an improvement in self-determined learning. However, the integration of such agent comes not without limitations. We conclude with suggestions concerning the didactical methods, which are supported by a GenPCA, and possible improvements of such an agent for workplace learning.
Real-World Federated Learning in Radiology: Hurdles to overcome and Benefits to gain
May 15, 2024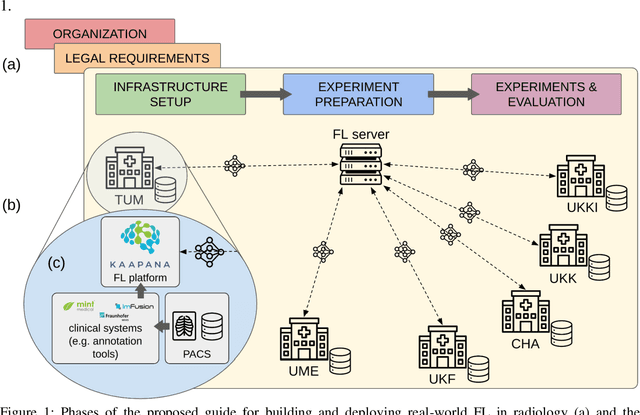



Abstract:Objective: Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training while keeping data locally. Currently, most FL studies in radiology are conducted in simulated environments due to numerous hurdles impeding its translation into practice. The few existing real-world FL initiatives rarely communicate specific measures taken to overcome these hurdles, leaving behind a significant knowledge gap. Minding efforts to implement real-world FL, there is a notable lack of comprehensive assessment comparing FL to less complex alternatives. Materials & Methods: We extensively reviewed FL literature, categorizing insights along with our findings according to their nature and phase while establishing a FL initiative, summarized to a comprehensive guide. We developed our own FL infrastructure within the German Radiological Cooperative Network (RACOON) and demonstrated its functionality by training FL models on lung pathology segmentation tasks across six university hospitals. We extensively evaluated FL against less complex alternatives in three distinct evaluation scenarios. Results: The proposed guide outlines essential steps, identified hurdles, and proposed solutions for establishing successful FL initiatives conducting real-world experiments. Our experimental results show that FL outperforms less complex alternatives in all evaluation scenarios, justifying the effort required to translate FL into real-world applications. Discussion & Conclusion: Our proposed guide aims to aid future FL researchers in circumventing pitfalls and accelerating translation of FL into radiological applications. Our results underscore the value of efforts needed to translate FL into real-world applications by demonstrating advantageous performance over alternatives, and emphasize the importance of strategic organization, robust management of distributed data and infrastructure in real-world settings.
Distance-based detection of out-of-distribution silent failures for Covid-19 lung lesion segmentation
Aug 05, 2022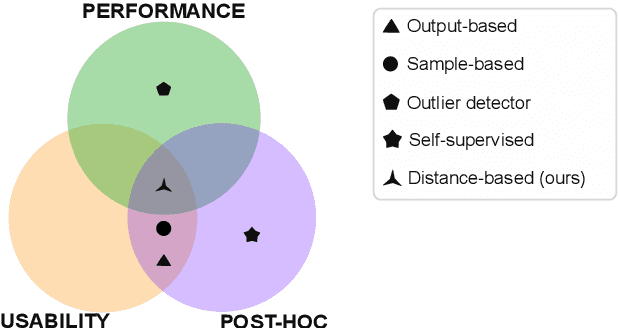
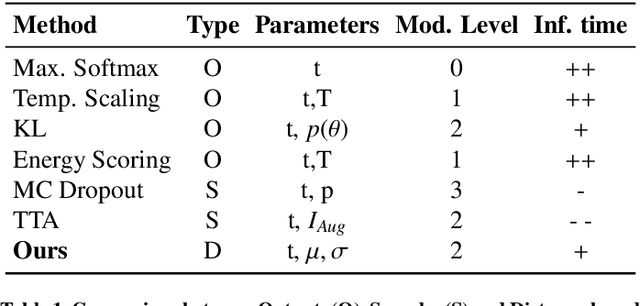
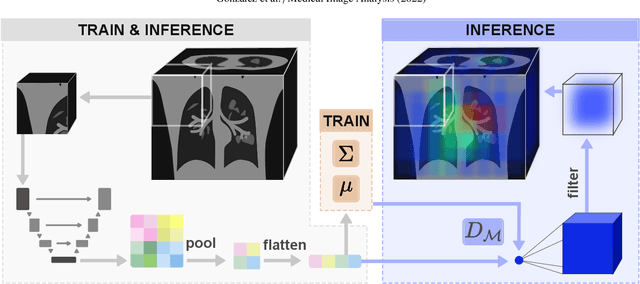
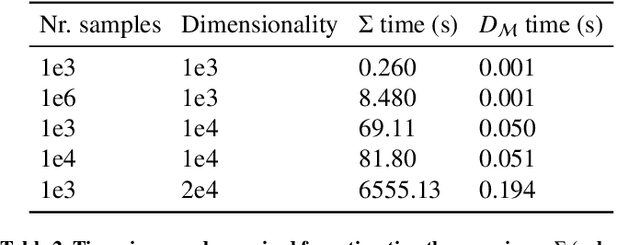
Abstract:Automatic segmentation of ground glass opacities and consolidations in chest computer tomography (CT) scans can potentially ease the burden of radiologists during times of high resource utilisation. However, deep learning models are not trusted in the clinical routine due to failing silently on out-of-distribution (OOD) data. We propose a lightweight OOD detection method that leverages the Mahalanobis distance in the feature space and seamlessly integrates into state-of-the-art segmentation pipelines. The simple approach can even augment pre-trained models with clinically relevant uncertainty quantification. We validate our method across four chest CT distribution shifts and two magnetic resonance imaging applications, namely segmentation of the hippocampus and the prostate. Our results show that the proposed method effectively detects far- and near-OOD samples across all explored scenarios.
Quality monitoring of federated Covid-19 lesion segmentation
Dec 16, 2021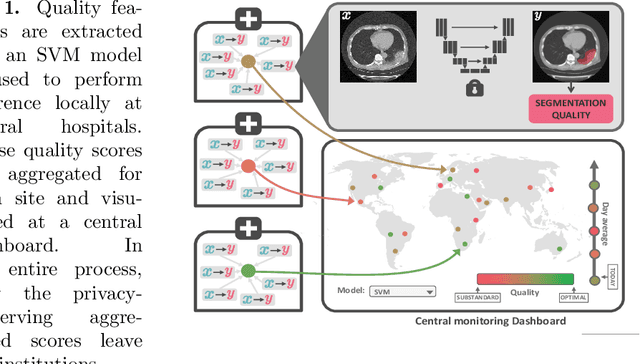
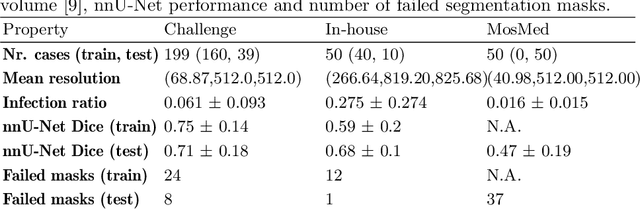
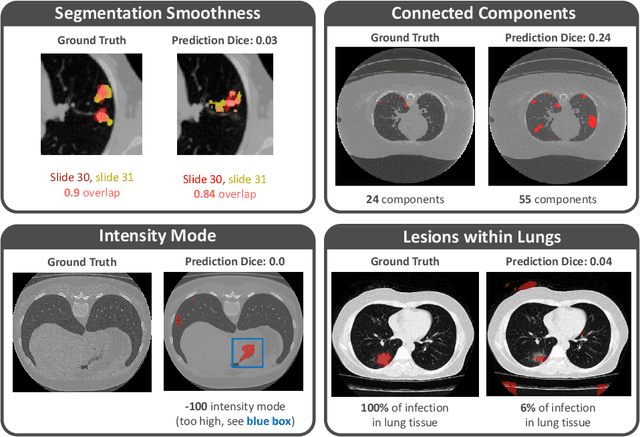
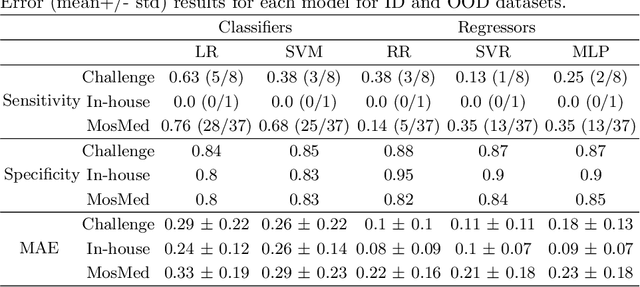
Abstract:Federated Learning is the most promising way to train robust Deep Learning models for the segmentation of Covid-19-related findings in chest CTs. By learning in a decentralized fashion, heterogeneous data can be leveraged from a variety of sources and acquisition protocols whilst ensuring patient privacy. It is, however, crucial to continuously monitor the performance of the model. Yet when it comes to the segmentation of diffuse lung lesions, a quick visual inspection is not enough to assess the quality, and thorough monitoring of all network outputs by expert radiologists is not feasible. In this work, we present an array of lightweight metrics that can be calculated locally in each hospital and then aggregated for central monitoring of a federated system. Our linear model detects over 70% of low-quality segmentations on an out-of-distribution dataset and thus reliably signals a decline in model performance.
Detecting when pre-trained nnU-Net models fail silently for Covid-19 lung lesion segmentation
Jul 14, 2021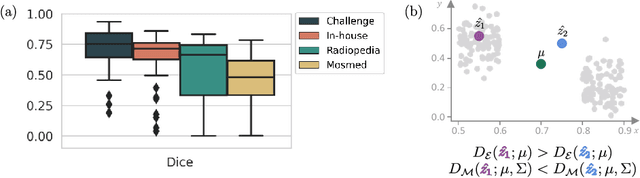
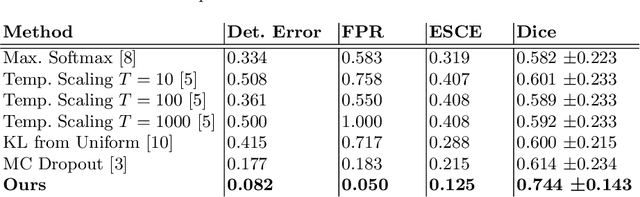
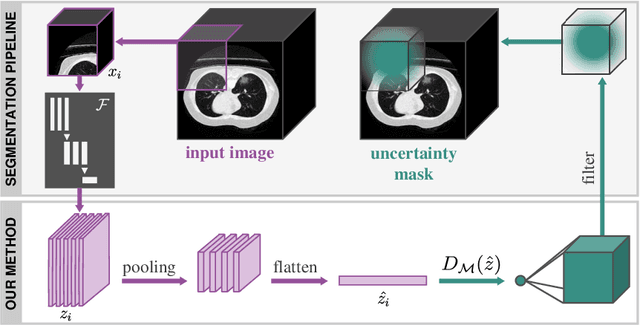
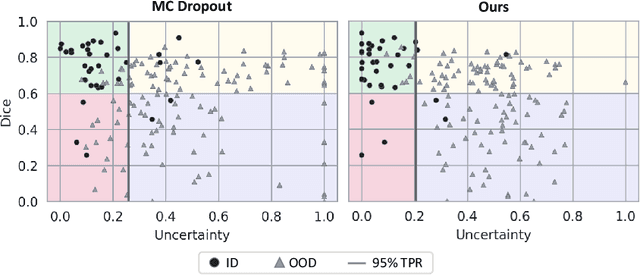
Abstract:Automatic segmentation of lung lesions in computer tomography has the potential to ease the burden of clinicians during the Covid-19 pandemic. Yet predictive deep learning models are not trusted in the clinical routine due to failing silently in out-of-distribution (OOD) data. We propose a lightweight OOD detection method that exploits the Mahalanobis distance in the feature space. The proposed approach can be seamlessly integrated into state-of-the-art segmentation pipelines without requiring changes in model architecture or training procedure, and can therefore be used to assess the suitability of pre-trained models to new data. We validate our method with a patch-based nnU-Net architecture trained with a multi-institutional dataset and find that it effectively detects samples that the model segments incorrectly.
M3d-CAM: A PyTorch library to generate 3D data attention maps for medical deep learning
Jul 01, 2020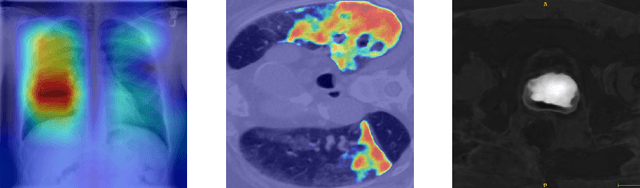
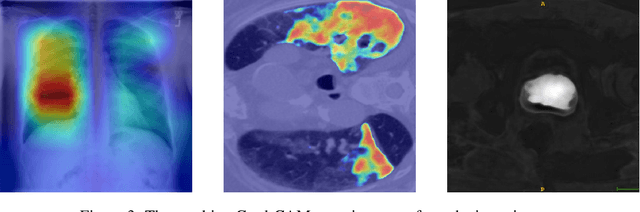
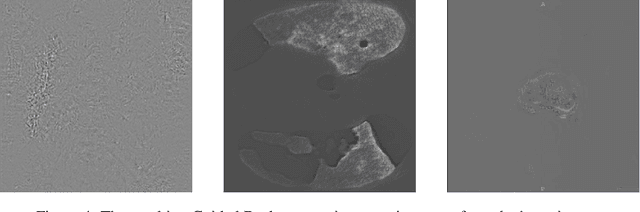
Abstract:M3d-CAM is an easy to use library for generating attention maps of CNN-based PyTorch models improving the interpretability of model predictions for humans. The attention maps can be generated with multiple methods like Guided Backpropagation, Grad-CAM, Guided Grad-CAM and Grad-CAM++. These attention maps visualize the regions in the input data that influenced the model prediction the most at a certain layer. Furthermore, M3d-CAM supports 2D and 3D data for the task of classification as well as for segmentation. A key feature is also that in most cases only a single line of code is required for generating attention maps for a model making M3d-CAM basically plug and play.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge