Christian Harder
From Pointwise to Powerhouse: Initialising Neural Networks with Generative Models
Oct 25, 2023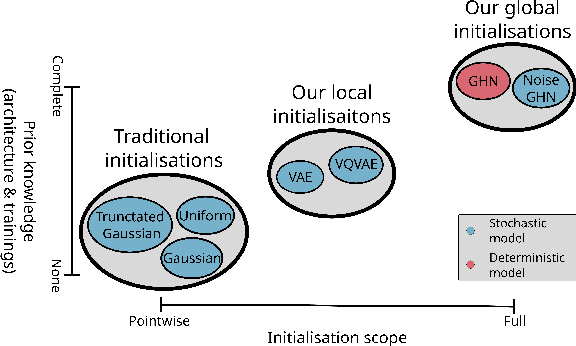
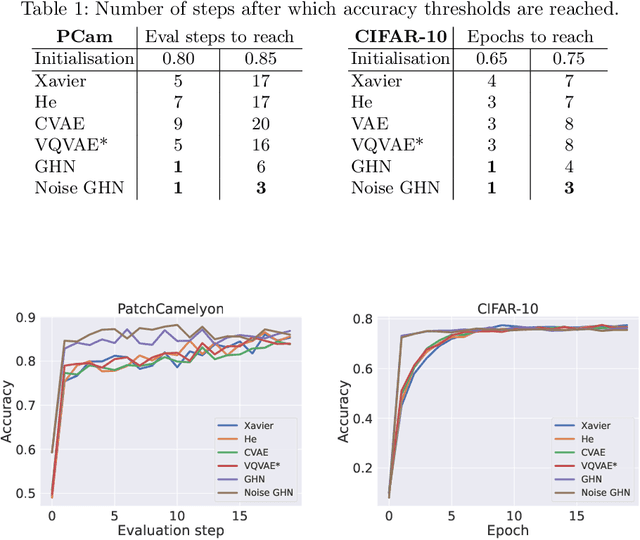
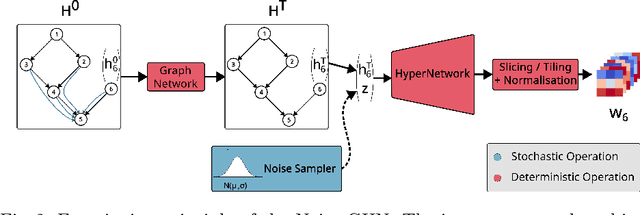
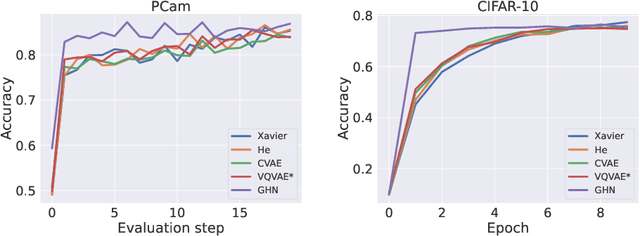
Abstract:Traditional initialisation methods, e.g. He and Xavier, have been effective in avoiding the problem of vanishing or exploding gradients in neural networks. However, they only use simple pointwise distributions, which model one-dimensional variables. Moreover, they ignore most information about the architecture and disregard past training experiences. These limitations can be overcome by employing generative models for initialisation. In this paper, we introduce two groups of new initialisation methods. First, we locally initialise weight groups by employing variational autoencoders. Secondly, we globally initialise full weight sets by employing graph hypernetworks. We thoroughly evaluate the impact of the employed generative models on state-of-the-art neural networks in terms of accuracy, convergence speed and ensembling. Our results show that global initialisations result in higher accuracy and faster initial convergence speed. However, the implementation through graph hypernetworks leads to diminished ensemble performance on out of distribution data. To counteract, we propose a modification called noise graph hypernetwork, which encourages diversity in the produced ensemble members. Furthermore, our approach might be able to transfer learned knowledge to different image distributions. Our work provides insights into the potential, the trade-offs and possible modifications of these new initialisation methods.
Quality monitoring of federated Covid-19 lesion segmentation
Dec 16, 2021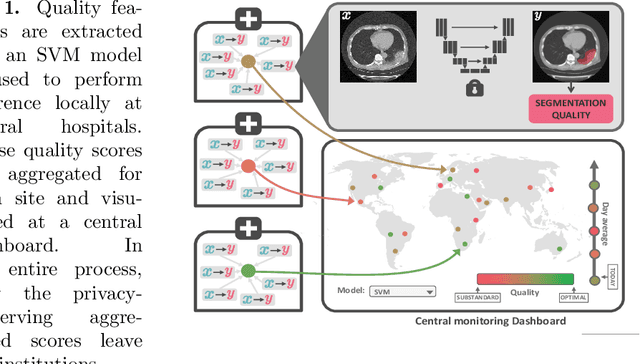
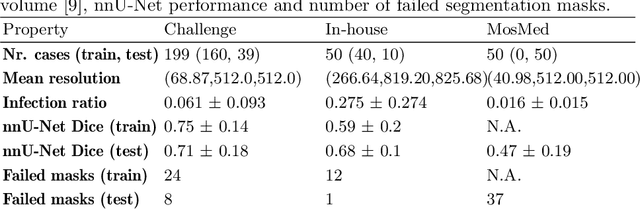
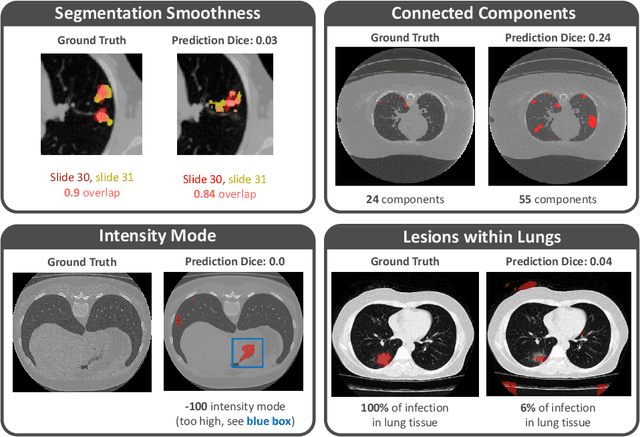
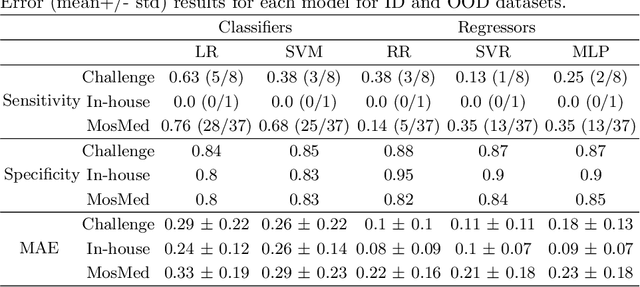
Abstract:Federated Learning is the most promising way to train robust Deep Learning models for the segmentation of Covid-19-related findings in chest CTs. By learning in a decentralized fashion, heterogeneous data can be leveraged from a variety of sources and acquisition protocols whilst ensuring patient privacy. It is, however, crucial to continuously monitor the performance of the model. Yet when it comes to the segmentation of diffuse lung lesions, a quick visual inspection is not enough to assess the quality, and thorough monitoring of all network outputs by expert radiologists is not feasible. In this work, we present an array of lightweight metrics that can be calculated locally in each hospital and then aggregated for central monitoring of a federated system. Our linear model detects over 70% of low-quality segmentations on an out-of-distribution dataset and thus reliably signals a decline in model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge