Amir Markovitz
GLASS: Global to Local Attention for Scene-Text Spotting
Aug 05, 2022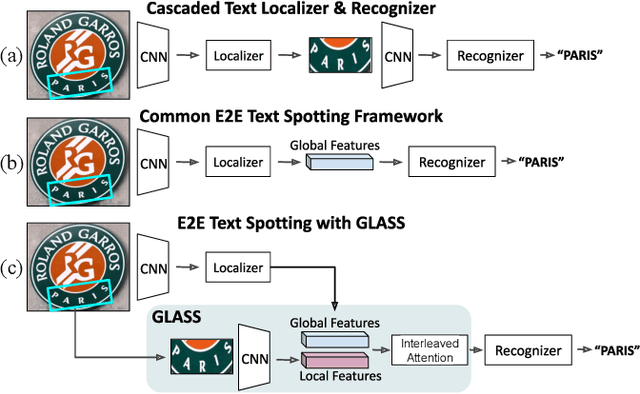
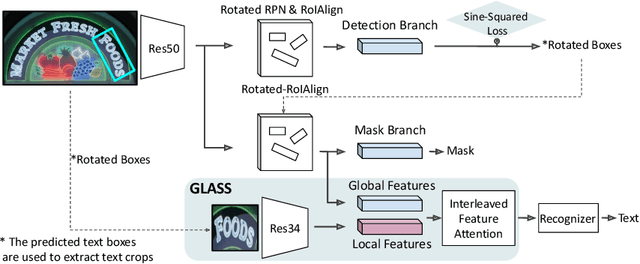
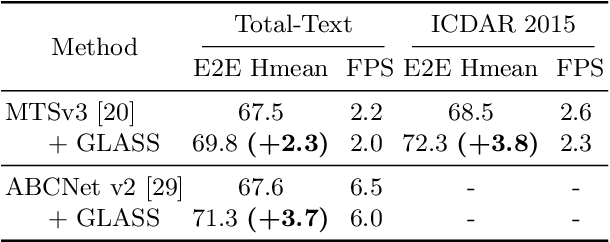
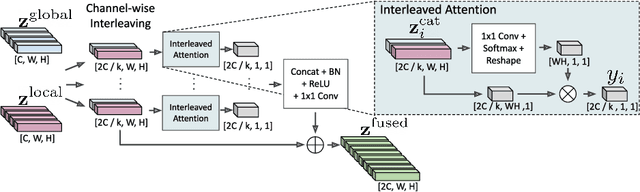
Abstract:In recent years, the dominant paradigm for text spotting is to combine the tasks of text detection and recognition into a single end-to-end framework. Under this paradigm, both tasks are accomplished by operating over a shared global feature map extracted from the input image. Among the main challenges that end-to-end approaches face is the performance degradation when recognizing text across scale variations (smaller or larger text), and arbitrary word rotation angles. In this work, we address these challenges by proposing a novel global-to-local attention mechanism for text spotting, termed GLASS, that fuses together global and local features. The global features are extracted from the shared backbone, preserving contextual information from the entire image, while the local features are computed individually on resized, high-resolution rotated word crops. The information extracted from the local crops alleviates much of the inherent difficulties with scale and word rotation. We show a performance analysis across scales and angles, highlighting improvement over scale and angle extremities. In addition, we introduce an orientation-aware loss term supervising the detection task, and show its contribution to both detection and recognition performance across all angles. Finally, we show that GLASS is general by incorporating it into other leading text spotting architectures, improving their text spotting performance. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple benchmarks, including the newly released TextOCR.
On Calibration of Scene-Text Recognition Models
Dec 23, 2020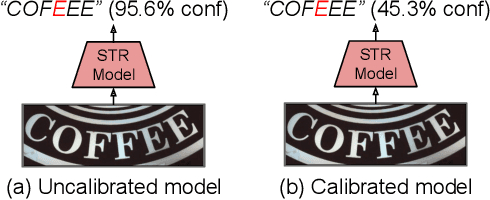
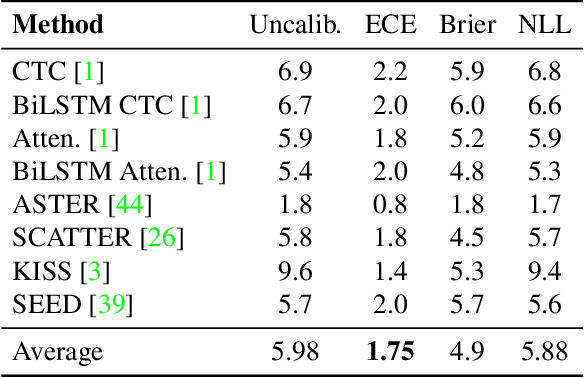
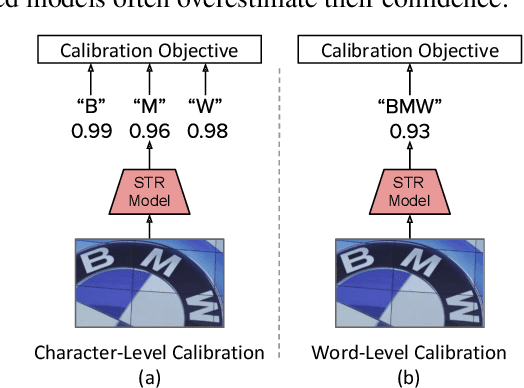
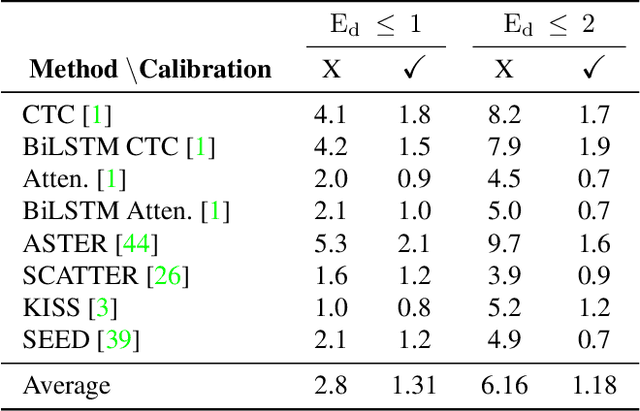
Abstract:In this work, we study the problem of word-level confidence calibration for scene-text recognition (STR). Although the topic of confidence calibration has been an active research area for the last several decades, the case of structured and sequence prediction calibration has been scarcely explored. We analyze several recent STR methods and show that they are consistently overconfident. We then focus on the calibration of STR models on the word rather than the character level. In particular, we demonstrate that for attention based decoders, calibration of individual character predictions increases word-level calibration error compared to an uncalibrated model. In addition, we apply existing calibration methodologies as well as new sequence-based extensions to numerous STR models, demonstrating reduced calibration error by up to a factor of nearly 7. Finally, we show consistently improved accuracy results by applying our proposed sequence calibration method as a preprocessing step to beam-search.
Can You Read Me Now? Content Aware Rectification using Angle Supervision
Aug 05, 2020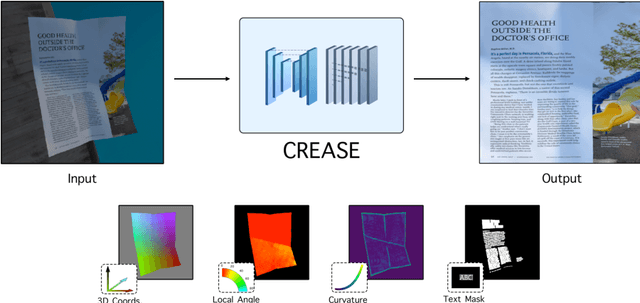
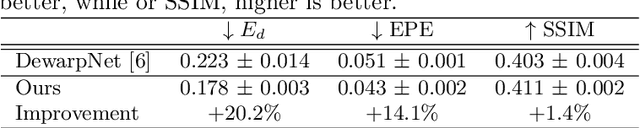
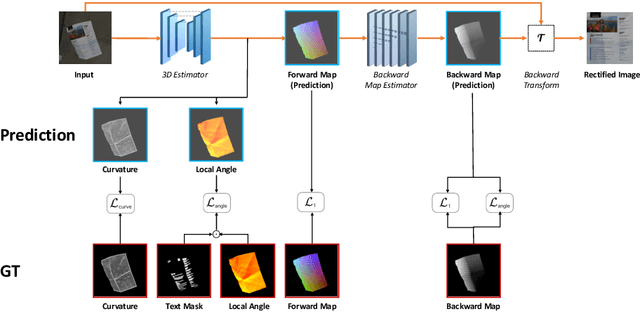
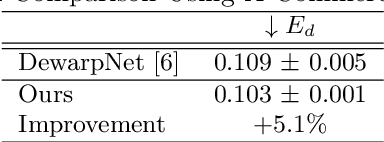
Abstract:The ubiquity of smartphone cameras has led to more and more documents being captured by cameras rather than scanned. Unlike flatbed scanners, photographed documents are often folded and crumpled, resulting in large local variance in text structure. The problem of document rectification is fundamental to the Optical Character Recognition (OCR) process on documents, and its ability to overcome geometric distortions significantly affects recognition accuracy. Despite the great progress in recent OCR systems, most still rely on a pre-process that ensures the text lines are straight and axis aligned. Recent works have tackled the problem of rectifying document images taken in-the-wild using various supervision signals and alignment means. However, they focused on global features that can be extracted from the document's boundaries, ignoring various signals that could be obtained from the document's content. We present CREASE: Content Aware Rectification using Angle Supervision, the first learned method for document rectification that relies on the document's content, the location of the words and specifically their orientation, as hints to assist in the rectification process. We utilize a novel pixel-wise angle regression approach and a curvature estimation side-task for optimizing our rectification model. Our method surpasses previous approaches in terms of OCR accuracy, geometric error and visual similarity.
Graph Embedded Pose Clustering for Anomaly Detection
Dec 26, 2019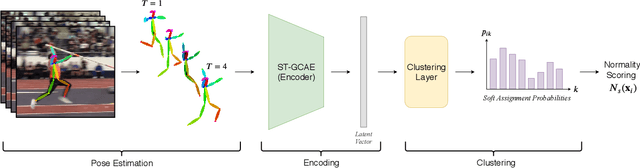
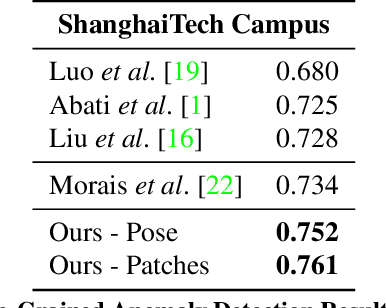

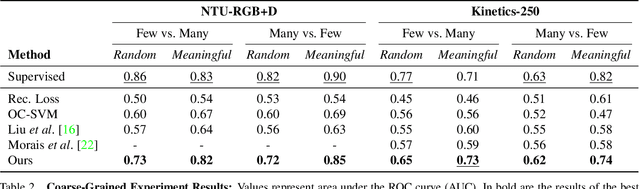
Abstract:We propose a new method for anomaly detection of human actions. Our method works directly on human pose graphs that can be computed from an input video sequence. This makes the analysis independent of nuisance parameters such as viewpoint or illumination. We map these graphs to a latent space and cluster them. Each action is then represented by its soft-assignment to each of the clusters. This gives a kind of "bag of words" representation to the data, where every action is represented by its similarity to a group of base action-words. Then, we use a Dirichlet process based mixture, that is useful for handling proportional data such as our soft-assignment vectors, to determine if an action is normal or not. We evaluate our method on two types of data sets. The first is a fine-grained anomaly detection data set (e.g. ShanghaiTech) where we wish to detect unusual variations of some action. The second is a coarse-grained anomaly detection data set (e.g.,\ a Kinetics-based data set) where few actions are considered normal, and every other action should be considered abnormal. Extensive experiments on the benchmarks show that our method performs considerably better than other state of the art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge