Alexander Spangher
DiscoSum: Discourse-aware News Summarization
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in text summarization have predominantly leveraged large language models to generate concise summaries. However, language models often do not maintain long-term discourse structure, especially in news articles, where organizational flow significantly influences reader engagement. We introduce a novel approach to integrating discourse structure into summarization processes, focusing specifically on news articles across various media. We present a novel summarization dataset where news articles are summarized multiple times in different ways across different social media platforms (e.g. LinkedIn, Facebook, etc.). We develop a novel news discourse schema to describe summarization structures and a novel algorithm, DiscoSum, which employs beam search technique for structure-aware summarization, enabling the transformation of news stories to meet different stylistic and structural demands. Both human and automatic evaluation results demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in maintaining narrative fidelity and meeting structural requirements.
NewsEdits 2.0: Learning the Intentions Behind Updating News
Nov 27, 2024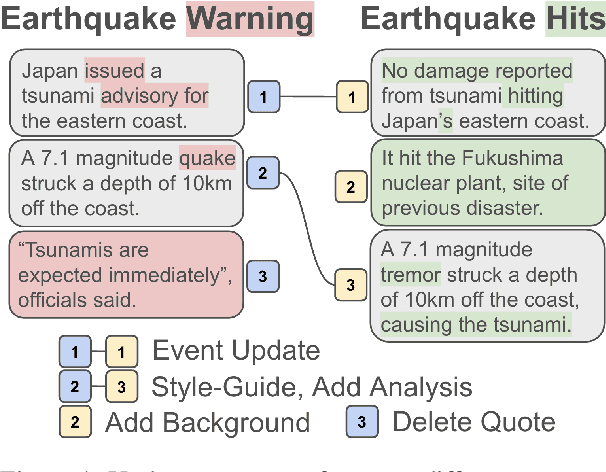



Abstract:As events progress, news articles often update with new information: if we are not cautious, we risk propagating outdated facts. In this work, we hypothesize that linguistic features indicate factual fluidity, and that we can predict which facts in a news article will update using solely the text of a news article (i.e. not external resources like search engines). We test this hypothesis, first, by isolating fact-updates in large news revisions corpora. News articles may update for many reasons (e.g. factual, stylistic, narrative). We introduce the NewsEdits 2.0 taxonomy, an edit-intentions schema that separates fact updates from stylistic and narrative updates in news writing. We annotate over 9,200 pairs of sentence revisions and train high-scoring ensemble models to apply this schema. Then, taking a large dataset of silver-labeled pairs, we show that we can predict when facts will update in older article drafts with high precision. Finally, to demonstrate the usefulness of these findings, we construct a language model question asking (LLM-QA) abstention task. We wish the LLM to abstain from answering questions when information is likely to become outdated. Using our predictions, we show, LLM absention reaches near oracle levels of accuracy.
NewsInterview: a Dataset and a Playground to Evaluate LLMs' Ground Gap via Informational Interviews
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in generating coherent text but often struggle with grounding language and strategic dialogue. To address this gap, we focus on journalistic interviews, a domain rich in grounding communication and abundant in data. We curate a dataset of 40,000 two-person informational interviews from NPR and CNN, and reveal that LLMs are significantly less likely than human interviewers to use acknowledgements and to pivot to higher-level questions. Realizing that a fundamental deficit exists in multi-turn planning and strategic thinking, we develop a realistic simulated environment, incorporating source personas and persuasive elements, in order to facilitate the development of agents with longer-horizon rewards. Our experiments show that while source LLMs mimic human behavior in information sharing, interviewer LLMs struggle with recognizing when questions are answered and engaging persuasively, leading to suboptimal information extraction across model size and capability. These findings underscore the need for enhancing LLMs' strategic dialogue capabilities.
PatentEdits: Framing Patent Novelty as Textual Entailment
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:A patent must be deemed novel and non-obvious in order to be granted by the US Patent Office (USPTO). If it is not, a US patent examiner will cite the prior work, or prior art, that invalidates the novelty and issue a non-final rejection. Predicting what claims of the invention should change given the prior art is an essential and crucial step in securing invention rights, yet has not been studied before as a learnable task. In this work we introduce the PatentEdits dataset, which contains 105K examples of successful revisions that overcome objections to novelty. We design algorithms to label edits sentence by sentence, then establish how well these edits can be predicted with large language models (LLMs). We demonstrate that evaluating textual entailment between cited references and draft sentences is especially effective in predicting which inventive claims remained unchanged or are novel in relation to prior art.
Explaining Mixtures of Sources in News Articles
Nov 07, 2024Abstract:Human writers plan, then write. For large language models (LLMs) to play a role in longer-form article generation, we must understand the planning steps humans make before writing. We explore one kind of planning, source-selection in news, as a case-study for evaluating plans in long-form generation. We ask: why do specific stories call for specific kinds of sources? We imagine a generative process for story writing where a source-selection schema is first selected by a journalist, and then sources are chosen based on categories in that schema. Learning the article's plan means predicting the schema initially chosen by the journalist. Working with professional journalists, we adapt five existing schemata and introduce three new ones to describe journalistic plans for the inclusion of sources in documents. Then, inspired by Bayesian latent-variable modeling, we develop metrics to select the most likely plan, or schema, underlying a story, which we use to compare schemata. We find that two schemata: stance and social affiliation best explain source plans in most documents. However, other schemata like textual entailment explain source plans in factually rich topics like "Science". Finally, we find we can predict the most suitable schema given just the article's headline with reasonable accuracy. We see this as an important case-study for human planning, and provides a framework and approach for evaluating other kinds of plans. We release a corpora, NewsSources, with annotations for 4M articles.
Are Large Language Models Capable of Generating Human-Level Narratives?
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:This paper investigates the capability of LLMs in storytelling, focusing on narrative development and plot progression. We introduce a novel computational framework to analyze narratives through three discourse-level aspects: i) story arcs, ii) turning points, and iii) affective dimensions, including arousal and valence. By leveraging expert and automatic annotations, we uncover significant discrepancies between the LLM- and human- written stories. While human-written stories are suspenseful, arousing, and diverse in narrative structures, LLM stories are homogeneously positive and lack tension. Next, we measure narrative reasoning skills as a precursor to generative capacities, concluding that most LLMs fall short of human abilities in discourse understanding. Finally, we show that explicit integration of aforementioned discourse features can enhance storytelling, as is demonstrated by over 40% improvement in neural storytelling in terms of diversity, suspense, and arousal.
Tracking the Newsworthiness of Public Documents
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Journalists must find stories in huge amounts of textual data (e.g. leaks, bills, press releases) as part of their jobs: determining when and why text becomes news can help us understand coverage patterns and help us build assistive tools. Yet, this is challenging because very few labelled links exist, language use between corpora is very different, and text may be covered for a variety of reasons. In this work we focus on news coverage of local public policy in the San Francisco Bay Area by the San Francisco Chronicle. First, we gather news articles, public policy documents and meeting recordings and link them using probabilistic relational modeling, which we show is a low-annotation linking methodology that outperforms other retrieval-based baselines. Second, we define a new task: newsworthiness prediction, to predict if a policy item will get covered. We show that different aspects of public policy discussion yield different newsworthiness signals. Finally we perform human evaluation with expert journalists and show our systems identify policies they consider newsworthy with 68% F1 and our coverage recommendations are helpful with an 84% win-rate.
Stay on topic with Classifier-Free Guidance
Jun 30, 2023



Abstract:Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) has recently emerged in text-to-image generation as a lightweight technique to encourage prompt-adherence in generations. In this work, we demonstrate that CFG can be used broadly as an inference-time technique in pure language modeling. We show that CFG (1) improves the performance of Pythia, GPT-2 and LLaMA-family models across an array of tasks: Q\&A, reasoning, code generation, and machine translation, achieving SOTA on LAMBADA with LLaMA-7B over PaLM-540B; (2) brings improvements equivalent to a model with twice the parameter-count; (3) can stack alongside other inference-time methods like Chain-of-Thought and Self-Consistency, yielding further improvements in difficult tasks; (4) can be used to increase the faithfulness and coherence of assistants in challenging form-driven and content-driven prompts: in a human evaluation we show a 75\% preference for GPT4All using CFG over baseline.
Identifying Informational Sources in News Articles
May 24, 2023



Abstract:News articles are driven by the informational sources journalists use in reporting. Modeling when, how and why sources get used together in stories can help us better understand the information we consume and even help journalists with the task of producing it. In this work, we take steps toward this goal by constructing the largest and widest-ranging annotated dataset, to date, of informational sources used in news writing. We show that our dataset can be used to train high-performing models for information detection and source attribution. We further introduce a novel task, source prediction, to study the compositionality of sources in news articles. We show good performance on this task, which we argue is an important proof for narrative science exploring the internal structure of news articles and aiding in planning-based language generation, and an important step towards a source-recommendation system to aid journalists.
Sequentially Controlled Text Generation
Jan 05, 2023



Abstract:While GPT-2 generates sentences that are remarkably human-like, longer documents can ramble and do not follow human-like writing structure. We study the problem of imposing structure on long-range text. We propose a novel controlled text generation task, sequentially controlled text generation, and identify a dataset, NewsDiscourse as a starting point for this task. We develop a sequential controlled text generation pipeline with generation and editing. We test different degrees of structural awareness and show that, in general, more structural awareness results in higher control-accuracy, grammaticality, coherency and topicality, approaching human-level writing performance.
* 19 pages. 10 pages main body, 3 pages references, 6 pages appendix
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge