Alexander Mattick
Optimizing Quantum Circuits via ZX Diagrams using Reinforcement Learning and Graph Neural Networks
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:Quantum computing is currently strongly limited by the impact of noise, in particular introduced by the application of two-qubit gates. For this reason, reducing the number of two-qubit gates is of paramount importance on noisy intermediate-scale quantum hardware. To advance towards more reliable quantum computing, we introduce a framework based on ZX calculus, graph-neural networks and reinforcement learning for quantum circuit optimization. By combining reinforcement learning and tree search, our method addresses the challenge of selecting optimal sequences of ZX calculus rewrite rules. Instead of relying on existing heuristic rules for minimizing circuits, our method trains a novel reinforcement learning policy that directly operates on ZX-graphs, therefore allowing us to search through the space of all possible circuit transformations to find a circuit significantly minimizing the number of CNOT gates. This way we can scale beyond hard-coded rules towards discovering arbitrary optimization rules. We demonstrate our method's competetiveness with state-of-the-art circuit optimizers and generalization capabilities on large sets of diverse random circuits.
Reinforcement Learning for Node Selection in Branch-and-Bound
Sep 29, 2023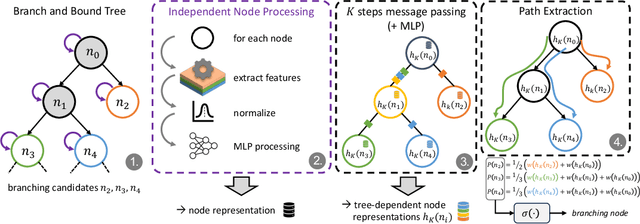
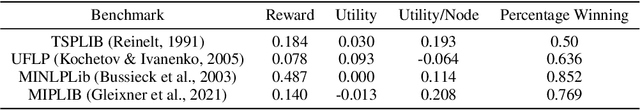
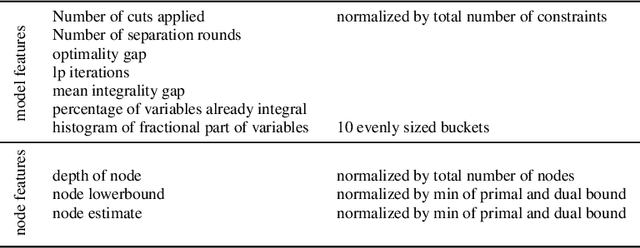
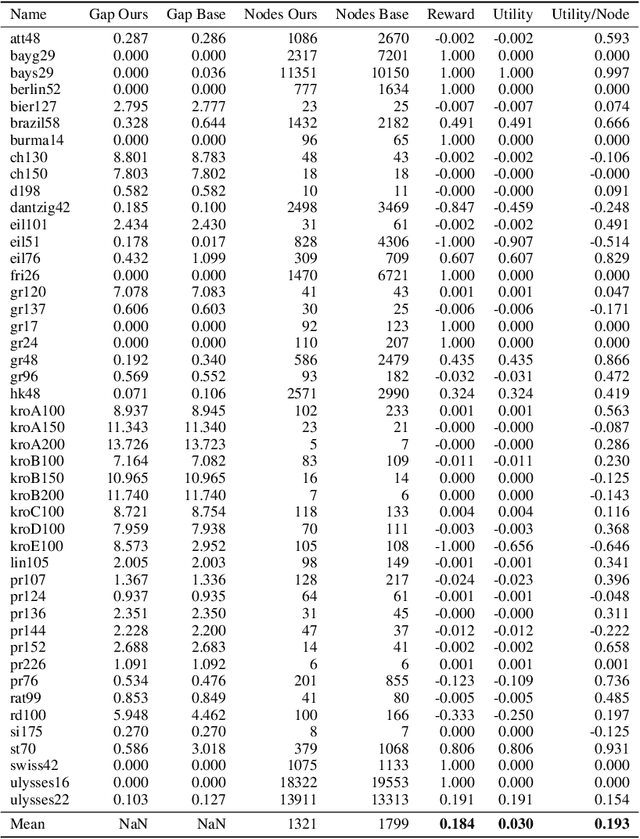
Abstract:A big challenge in branch and bound lies in identifying the optimal node within the search tree from which to proceed. Current state-of-the-art selectors utilize either hand-crafted ensembles that automatically switch between naive sub-node selectors, or learned node selectors that rely on individual node data. We propose a novel bi-simulation technique that uses reinforcement learning (RL) while considering the entire tree state, rather than just isolated nodes. To achieve this, we train a graph neural network that produces a probability distribution based on the path from the model's root to its ``to-be-selected'' leaves. Modelling node-selection as a probability distribution allows us to train the model using state-of-the-art RL techniques that capture both intrinsic node-quality and node-evaluation costs. Our method induces a high quality node selection policy on a set of varied and complex problem sets, despite only being trained on specially designed, synthetic TSP instances. Experiments on several benchmarks show significant improvements in optimality gap reductions and per-node efficiency under strict time constraints.
OpenAssistant Conversations -- Democratizing Large Language Model Alignment
Apr 14, 2023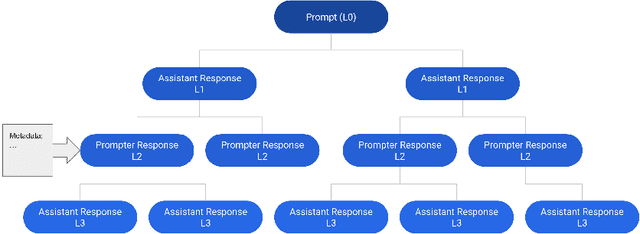
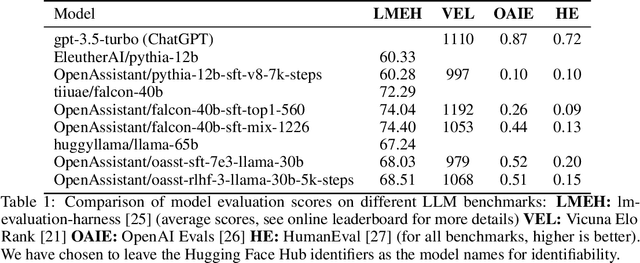
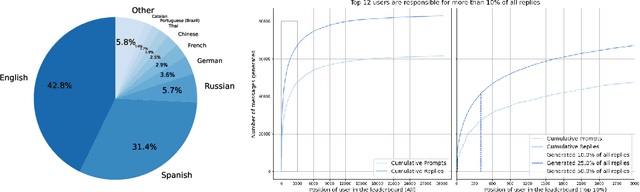
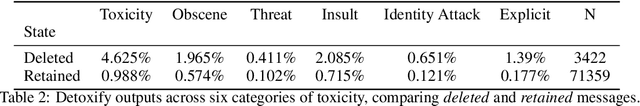
Abstract:Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences has proven to drastically improve usability and has driven rapid adoption as demonstrated by ChatGPT. Alignment techniques such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) greatly reduce the required skill and domain knowledge to effectively harness the capabilities of LLMs, increasing their accessibility and utility across various domains. However, state-of-the-art alignment techniques like RLHF rely on high-quality human feedback data, which is expensive to create and often remains proprietary. In an effort to democratize research on large-scale alignment, we release OpenAssistant Conversations, a human-generated, human-annotated assistant-style conversation corpus consisting of 161,443 messages distributed across 66,497 conversation trees, in 35 different languages, annotated with 461,292 quality ratings. The corpus is a product of a worldwide crowd-sourcing effort involving over 13,500 volunteers. To demonstrate the OpenAssistant Conversations dataset's effectiveness, we present OpenAssistant, the first fully open-source large-scale instruction-tuned model to be trained on human data. A preference study revealed that OpenAssistant replies are comparably preferred to GPT-3.5-turbo (ChatGPT) with a relative winrate of 48.3% vs. 51.7% respectively. We release our code and data under fully permissive licenses.
SmartPatch: Improving Handwritten Word Imitation with Patch Discriminators
May 21, 2021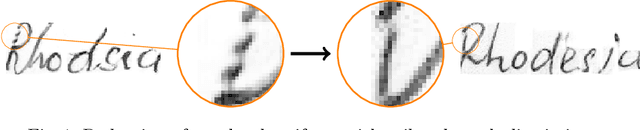
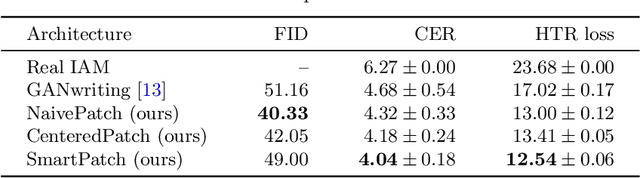
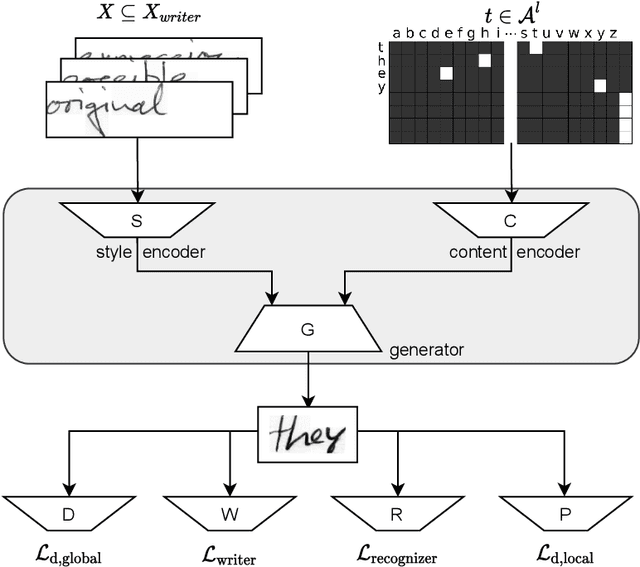

Abstract:As of recent generative adversarial networks have allowed for big leaps in the realism of generated images in diverse domains, not the least of which being handwritten text generation. The generation of realistic-looking hand-written text is important because it can be used for data augmentation in handwritten text recognition (HTR) systems or human-computer interaction. We propose SmartPatch, a new technique increasing the performance of current state-of-the-art methods by augmenting the training feedback with a tailored solution to mitigate pen-level artifacts. We combine the well-known patch loss with information gathered from the parallel trained handwritten text recognition system and the separate characters of the word. This leads to a more enhanced local discriminator and results in more realistic and higher-quality generated handwritten words.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge