Alex Zook
3D-Generalist: Self-Improving Vision-Language-Action Models for Crafting 3D Worlds
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Despite large-scale pretraining endowing models with language and vision reasoning capabilities, improving their spatial reasoning capability remains challenging due to the lack of data grounded in the 3D world. While it is possible for humans to manually create immersive and interactive worlds through 3D graphics, as seen in applications such as VR, gaming, and robotics, this process remains highly labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose a scalable method for generating high-quality 3D environments that can serve as training data for foundation models. We recast 3D environment building as a sequential decision-making problem, employing Vision-Language-Models (VLMs) as policies that output actions to jointly craft a 3D environment's layout, materials, lighting, and assets. Our proposed framework, 3D-Generalist, trains VLMs to generate more prompt-aligned 3D environments via self-improvement fine-tuning. We demonstrate the effectiveness of 3D-Generalist and the proposed training strategy in generating simulation-ready 3D environments. Furthermore, we demonstrate its quality and scalability in synthetic data generation by pretraining a vision foundation model on the generated data. After fine-tuning the pre-trained model on downstream tasks, we show that it surpasses models pre-trained on meticulously human-crafted synthetic data and approaches results achieved with real data orders of magnitude larger.
GRS: Generating Robotic Simulation Tasks from Real-World Images
Oct 20, 2024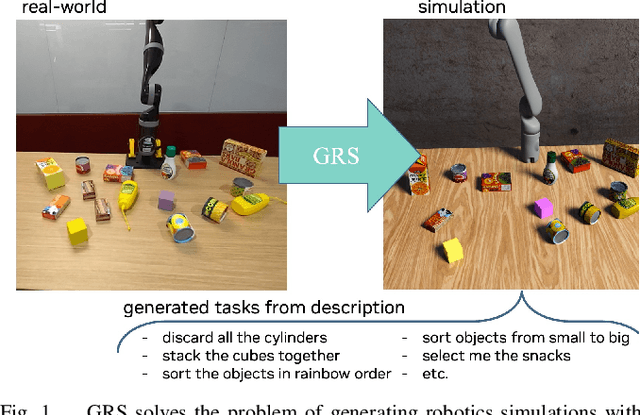
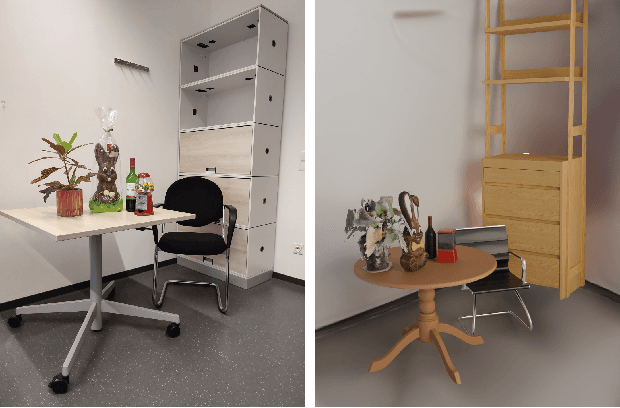
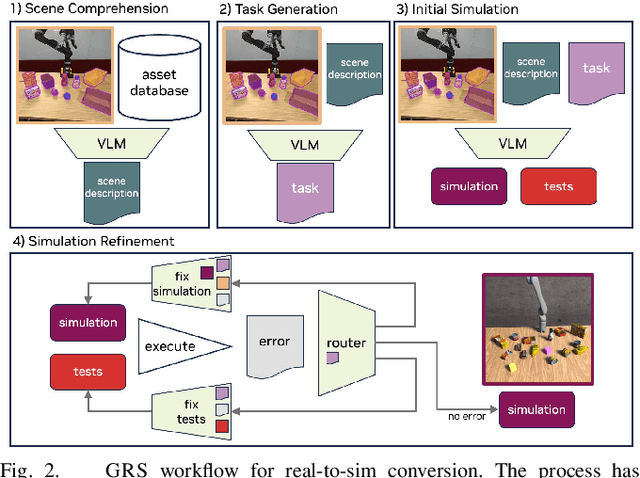


Abstract:We introduce GRS (Generating Robotic Simulation tasks), a novel system to address the challenge of real-to-sim in robotics, computer vision, and AR/VR. GRS enables the creation of digital twin simulations from single real-world RGB-D observations, complete with diverse, solvable tasks for virtual agent training. We use state-of-the-art vision-language models (VLMs) to achieve a comprehensive real-to-sim pipeline. GRS operates in three stages: 1) scene comprehension using SAM2 for object segmentation and VLMs for object description, 2) matching identified objects with simulation-ready assets, and 3) generating contextually appropriate robotic tasks. Our approach ensures simulations align with task specifications by generating test suites designed to verify adherence to the task specification. We introduce a router that iteratively refines the simulation and test code to ensure the simulation is solvable by a robot policy while remaining aligned to the task specification. Our experiments demonstrate the system's efficacy in accurately identifying object correspondence, which allows us to generate task environments that closely match input environments, and enhance automated simulation task generation through our novel router mechanism.
FactorSim: Generative Simulation via Factorized Representation
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Generating simulations to train intelligent agents in game-playing and robotics from natural language input, from user input or task documentation, remains an open-ended challenge. Existing approaches focus on parts of this challenge, such as generating reward functions or task hyperparameters. Unlike previous work, we introduce FACTORSIM that generates full simulations in code from language input that can be used to train agents. Exploiting the structural modularity specific to coded simulations, we propose to use a factored partially observable Markov decision process representation that allows us to reduce context dependence during each step of the generation. For evaluation, we introduce a generative simulation benchmark that assesses the generated simulation code's accuracy and effectiveness in facilitating zero-shot transfers in reinforcement learning settings. We show that FACTORSIM outperforms existing methods in generating simulations regarding prompt alignment (e.g., accuracy), zero-shot transfer abilities, and human evaluation. We also demonstrate its effectiveness in generating robotic tasks.
PeopleSansPeople: A Synthetic Data Generator for Human-Centric Computer Vision
Dec 17, 2021



Abstract:In recent years, person detection and human pose estimation have made great strides, helped by large-scale labeled datasets. However, these datasets had no guarantees or analysis of human activities, poses, or context diversity. Additionally, privacy, legal, safety, and ethical concerns may limit the ability to collect more human data. An emerging alternative to real-world data that alleviates some of these issues is synthetic data. However, creation of synthetic data generators is incredibly challenging and prevents researchers from exploring their usefulness. Therefore, we release a human-centric synthetic data generator PeopleSansPeople which contains simulation-ready 3D human assets, a parameterized lighting and camera system, and generates 2D and 3D bounding box, instance and semantic segmentation, and COCO pose labels. Using PeopleSansPeople, we performed benchmark synthetic data training using a Detectron2 Keypoint R-CNN variant [1]. We found that pre-training a network using synthetic data and fine-tuning on target real-world data (few-shot transfer to limited subsets of COCO-person train [2]) resulted in a keypoint AP of $60.37 \pm 0.48$ (COCO test-dev2017) outperforming models trained with the same real data alone (keypoint AP of $55.80$) and pre-trained with ImageNet (keypoint AP of $57.50$). This freely-available data generator should enable a wide range of research into the emerging field of simulation to real transfer learning in the critical area of human-centric computer vision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge