Adam Crespi
AnthroNet: Conditional Generation of Humans via Anthropometrics
Sep 07, 2023Abstract:We present a novel human body model formulated by an extensive set of anthropocentric measurements, which is capable of generating a wide range of human body shapes and poses. The proposed model enables direct modeling of specific human identities through a deep generative architecture, which can produce humans in any arbitrary pose. It is the first of its kind to have been trained end-to-end using only synthetically generated data, which not only provides highly accurate human mesh representations but also allows for precise anthropometry of the body. Moreover, using a highly diverse animation library, we articulated our synthetic humans' body and hands to maximize the diversity of the learnable priors for model training. Our model was trained on a dataset of $100k$ procedurally-generated posed human meshes and their corresponding anthropometric measurements. Our synthetic data generator can be used to generate millions of unique human identities and poses for non-commercial academic research purposes.
PSP-HDRI$+$: A Synthetic Dataset Generator for Pre-Training of Human-Centric Computer Vision Models
Jul 11, 2022
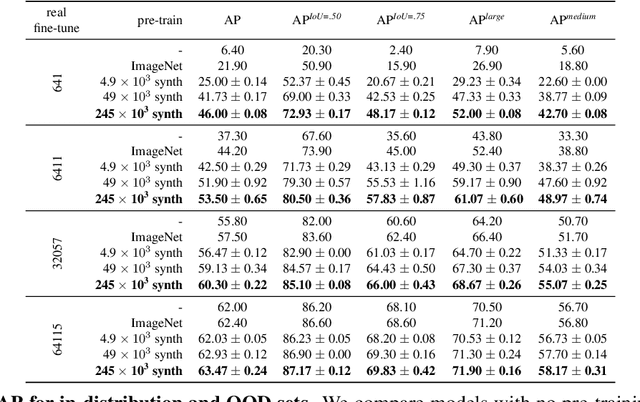
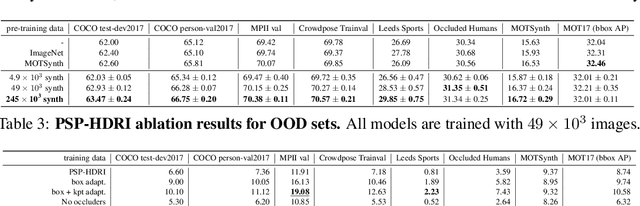
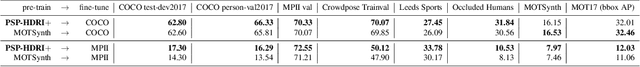
Abstract:We introduce a new synthetic data generator PSP-HDRI$+$ that proves to be a superior pre-training alternative to ImageNet and other large-scale synthetic data counterparts. We demonstrate that pre-training with our synthetic data will yield a more general model that performs better than alternatives even when tested on out-of-distribution (OOD) sets. Furthermore, using ablation studies guided by person keypoint estimation metrics with an off-the-shelf model architecture, we show how to manipulate our synthetic data generator to further improve model performance.
PeopleSansPeople: A Synthetic Data Generator for Human-Centric Computer Vision
Dec 17, 2021



Abstract:In recent years, person detection and human pose estimation have made great strides, helped by large-scale labeled datasets. However, these datasets had no guarantees or analysis of human activities, poses, or context diversity. Additionally, privacy, legal, safety, and ethical concerns may limit the ability to collect more human data. An emerging alternative to real-world data that alleviates some of these issues is synthetic data. However, creation of synthetic data generators is incredibly challenging and prevents researchers from exploring their usefulness. Therefore, we release a human-centric synthetic data generator PeopleSansPeople which contains simulation-ready 3D human assets, a parameterized lighting and camera system, and generates 2D and 3D bounding box, instance and semantic segmentation, and COCO pose labels. Using PeopleSansPeople, we performed benchmark synthetic data training using a Detectron2 Keypoint R-CNN variant [1]. We found that pre-training a network using synthetic data and fine-tuning on target real-world data (few-shot transfer to limited subsets of COCO-person train [2]) resulted in a keypoint AP of $60.37 \pm 0.48$ (COCO test-dev2017) outperforming models trained with the same real data alone (keypoint AP of $55.80$) and pre-trained with ImageNet (keypoint AP of $57.50$). This freely-available data generator should enable a wide range of research into the emerging field of simulation to real transfer learning in the critical area of human-centric computer vision.
Unity Perception: Generate Synthetic Data for Computer Vision
Jul 19, 2021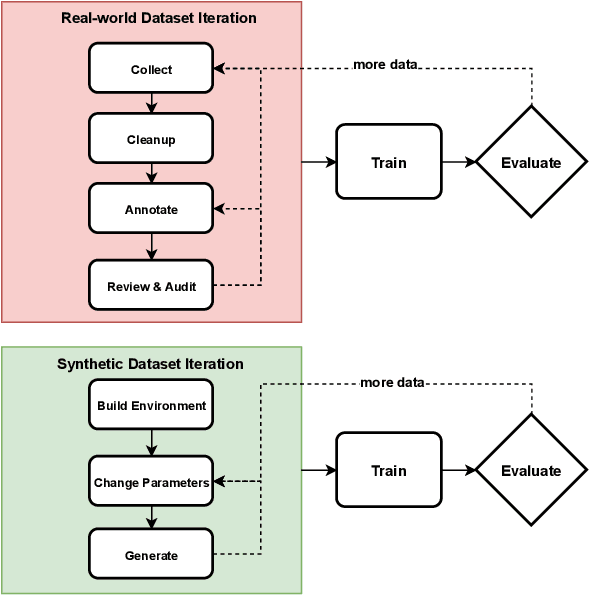
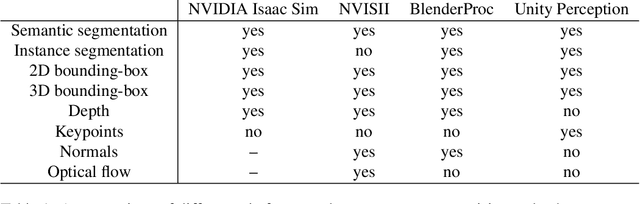
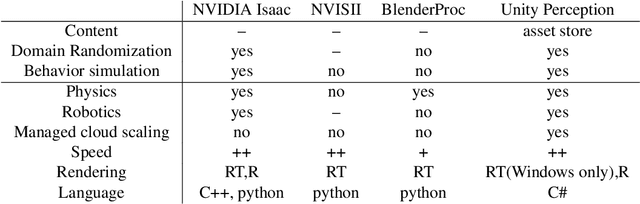
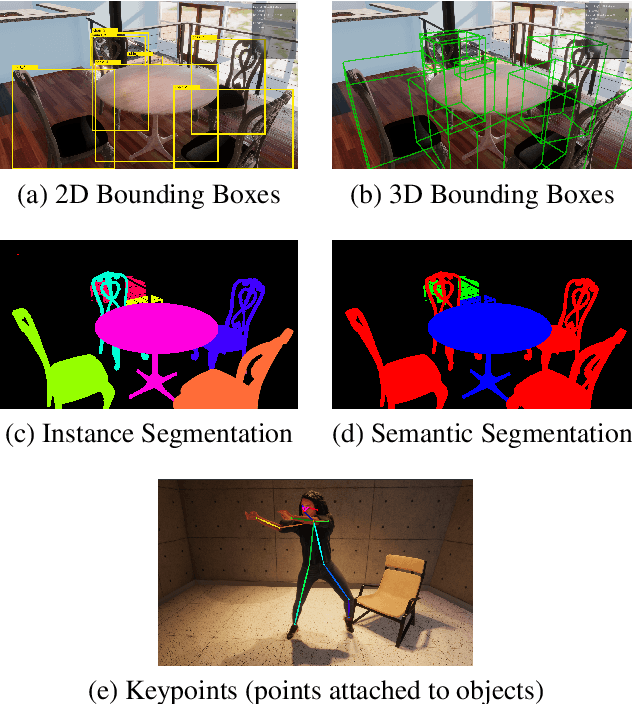
Abstract:We introduce the Unity Perception package which aims to simplify and accelerate the process of generating synthetic datasets for computer vision tasks by offering an easy-to-use and highly customizable toolset. This open-source package extends the Unity Editor and engine components to generate perfectly annotated examples for several common computer vision tasks. Additionally, it offers an extensible Randomization framework that lets the user quickly construct and configure randomized simulation parameters in order to introduce variation into the generated datasets. We provide an overview of the provided tools and how they work, and demonstrate the value of the generated synthetic datasets by training a 2D object detection model. The model trained with mostly synthetic data outperforms the model trained using only real data.
Obstacle Tower: A Generalization Challenge in Vision, Control, and Planning
Feb 04, 2019
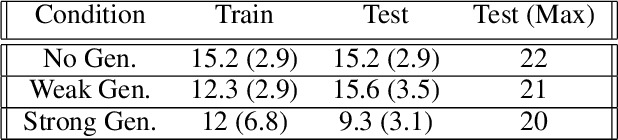

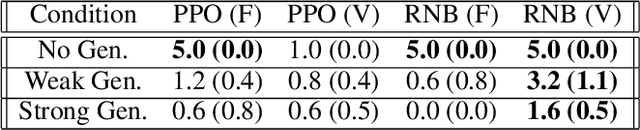
Abstract:The rapid pace of research in Deep Reinforcement Learning has been driven by the presence of fast and challenging simulation environments. These environments often take the form of games; with tasks ranging from simple board games, to classic home console games, to modern strategy games. We propose a new benchmark called Obstacle Tower: a high visual fidelity, 3D, 3rd person, procedurally generated game environment. An agent in the Obstacle Tower must learn to solve both low-level control and high-level planning problems in tandem while learning from pixels and a sparse reward signal. Unlike other similar benchmarks such as the ALE, evaluation of agent performance in Obstacle Tower is based on an agent's ability to perform well on unseen instances of the environment. In this paper we outline the environment and provide a set of initial baseline results produced by current state-of-the-art Deep RL methods as well as human players. In all cases these algorithms fail to produce agents capable of performing anywhere near human level on a set of evaluations designed to test both memorization and generalization ability. As such, we believe that the Obstacle Tower has the potential to serve as a helpful Deep RL benchmark now and into the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge