Aiguo Song
DSO-VSA: a Variable Stiffness Actuator with Decoupled Stiffness and Output Characteristics for Rehabilitation Robotics
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Stroke-induced motor impairment often results in substantial loss of upper-limb function, creating a strong demand for rehabilitation robots that enable safe and transparent physical human-robot interaction (pHRI). Variable stiffness actuators are well suited for such applications. However, in most existing designs, stiffness is coupled with the deflection angle, complicating both modeling and control. To address this limitation, this paper presents a variable stiffness actuator featuring decoupled stiffness and output behavior for rehabilitation robotics. The system integrates a variable stiffness mechanism that combines a variable-length lever with a hypocycloidal straight-line mechanism to achieve a linear torque-deflection relationship and continuous stiffness modulation from near zero to theoretically infinite. It also incorporates a differential transmission mechanism based on a planetary gear system that enables dual-motor load sharing. A cascade PI controller is further developed on the basis of the differential configuration, in which the position-loop term jointly regulates stiffness and deflection angle, effectively suppressing stiffness fluctuations and output disturbances. The performance of prototype was experimentally validated through stiffness calibration, stiffness regulation, torque control, decoupled characteristics, and dual-motor load sharing, indicating the potential for rehabilitation exoskeletons and other pHRI systems.
MRUCT: Mixed Reality Assistance for Acupuncture Guided by Ultrasonic Computed Tomography
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Chinese acupuncture practitioners primarily depend on muscle memory and tactile feedback to insert needles and accurately target acupuncture points, as the current workflow lacks imaging modalities and visual aids. Consequently, new practitioners often learn through trial and error, requiring years of experience to become proficient and earn the trust of patients. Medical students face similar challenges in mastering this skill. To address these challenges, we developed an innovative system, MRUCT, that integrates ultrasonic computed tomography (UCT) with mixed reality (MR) technology to visualize acupuncture points in real-time. This system offers offline image registration and real-time guidance during needle insertion, enabling them to accurately position needles based on anatomical structures such as bones, muscles, and auto-generated reference points, with the potential for clinical implementation. In this paper, we outline the non-rigid registration methods used to reconstruct anatomical structures from UCT data, as well as the key design considerations of the MR system. We evaluated two different 3D user interface (3DUI) designs and compared the performance of our system to traditional workflows for both new practitioners and medical students. The results highlight the potential of MR to enhance therapeutic medical practices and demonstrate the effectiveness of the system we developed.
DipMe: Haptic Recognition of Granular Media for Tangible Interactive Applications
Nov 13, 2024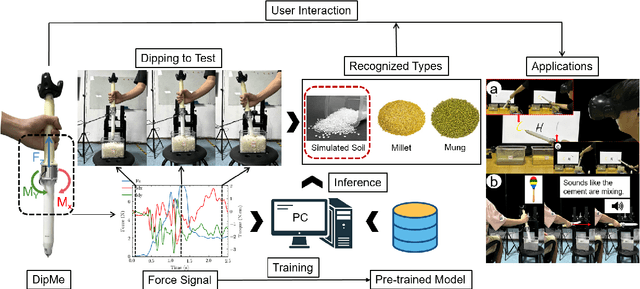
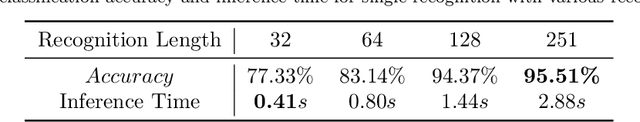
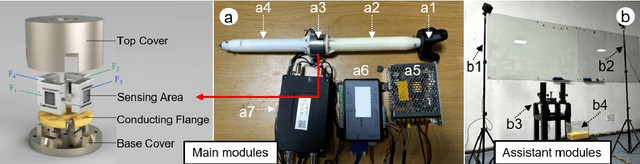
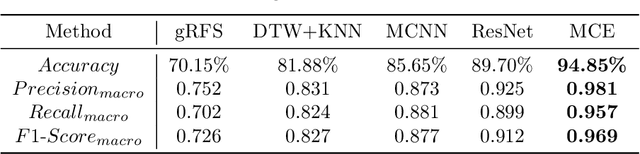
Abstract:While tangible user interface has shown its power in naturally interacting with rigid or soft objects, users cannot conveniently use different types of granular materials as the interaction media. We introduce DipMe as a smart device to recognize the types of granular media in real time, which can be used to connect the granular materials in the physical world with various virtual content. Other than vision-based solutions, we propose a dip operation of our device and exploit the haptic signals to recognize different types of granular materials. With modern machine learning tools, we find the haptic signals from different granular media are distinguishable by DipMe. With the online granular object recognition, we build several tangible interactive applications, demonstrating the effects of DipMe in perceiving granular materials and its potential in developing a tangible user interface with granular objects as the new media.
Image-Based Visual Servoing for Enhanced Cooperation of Dual-Arm Manipulation
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:The cooperation of a pair of robot manipulators is required to manipulate a target object without any fixtures. The conventional control methods coordinate the end-effector pose of each manipulator with that of the other using their kinematics and joint coordinate measurements. Yet, the manipulators' inaccurate kinematics and joint coordinate measurements can cause significant pose synchronization errors in practice. This paper thus proposes an image-based visual servoing approach for enhancing the cooperation of a dual-arm manipulation system. On top of the classical control, the visual servoing controller lets each manipulator use its carried camera to measure the image features of the other's marker and adapt its end-effector pose with the counterpart on the move. Because visual measurements are robust to kinematic errors, the proposed control can reduce the end-effector pose synchronization errors and the fluctuations of the interaction forces of the pair of manipulators on the move. Theoretical analyses have rigorously proven the stability of the closed-loop system. Comparative experiments on real robots have substantiated the effectiveness of the proposed control.
Learning Multimodal Confidence for Intention Recognition in Human-Robot Interaction
May 23, 2024



Abstract:The rapid development of collaborative robotics has provided a new possibility of helping the elderly who has difficulties in daily life, allowing robots to operate according to specific intentions. However, efficient human-robot cooperation requires natural, accurate and reliable intention recognition in shared environments. The current paramount challenge for this is reducing the uncertainty of multimodal fused intention to be recognized and reasoning adaptively a more reliable result despite current interactive condition. In this work we propose a novel learning-based multimodal fusion framework Batch Multimodal Confidence Learning for Opinion Pool (BMCLOP). Our approach combines Bayesian multimodal fusion method and batch confidence learning algorithm to improve accuracy, uncertainty reduction and success rate given the interactive condition. In particular, the generic and practical multimodal intention recognition framework can be easily extended further. Our desired assistive scenarios consider three modalities gestures, speech and gaze, all of which produce categorical distributions over all the finite intentions. The proposed method is validated with a six-DoF robot through extensive experiments and exhibits high performance compared to baselines.
An Instrumented Wheel-On-Limb System of Planetary Rovers for Wheel-Terrain Interactions: System Conception and Preliminary Design
Apr 06, 2022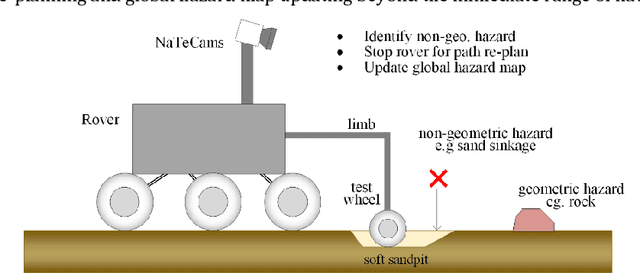

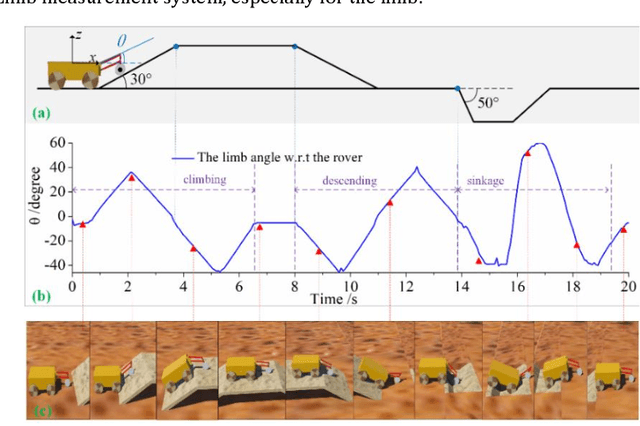
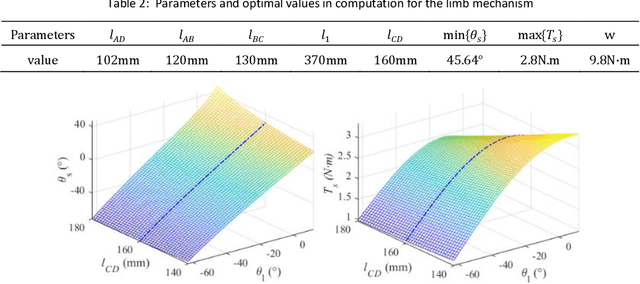
Abstract:Understanding the wheel-terrain interaction is of great importance to improve the maneuverability and traversability of the rovers. A well-developed sensing device carried by the rover would greatly facilitate the complex risk-reducing operations on sandy terrains. In this paper, an instrumented wheel-on-limb (WOL) system of planetary rovers for wheel-terrain interaction characterization is presented. Assuming the function of a passive suspension of the wheel, the WOL system allows itself to follow the terrain contour, and keep the wheel remain lowered onto the ground during rover motion including climbing and descending, as well as deploy and place the wheel on the ground before a drive commanding. The system concept, functional requirements, and pre-design work, as well as the system integration are presented.
Structural Combinatorial of Network Information System of Systems based on Evolutionary Optimization Method
Feb 22, 2020
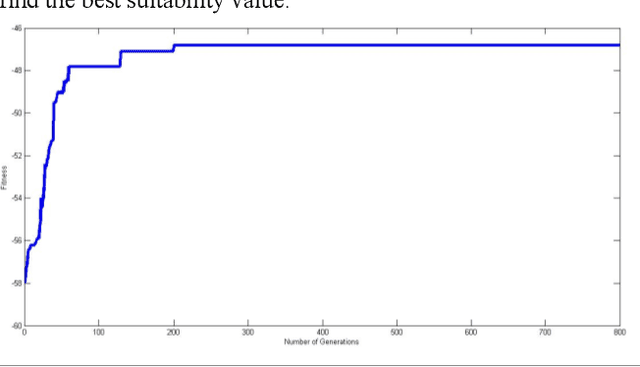
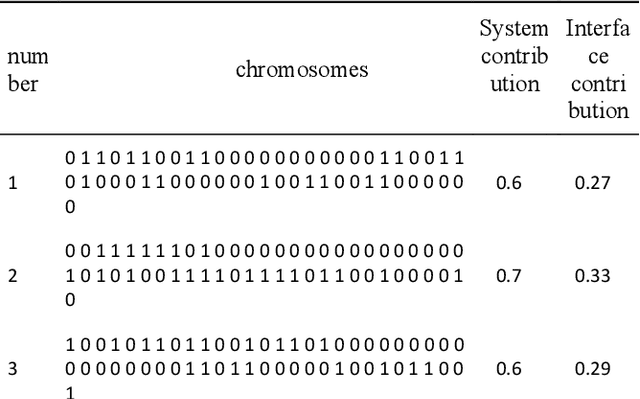
Abstract:The network information system is a military information network system with evolution characteristics. Evolution is a process of replacement between disorder and order, chaos and equilibrium. Given that the concept of evolution originates from biological systems, in this article, the evolution of network information architecture is analyzed by genetic algorithms, and the network information architecture is represented by chromosomes. Besides, the genetic algorithm is also applied to find the optimal chromosome in the architecture space. The evolutionary simulation is used to predict the optimal scheme of the network information architecture and provide a reference for system construction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge