Adrian Kim
Modeling Musical Onset Probabilities via Neural Distribution Learning
Feb 10, 2020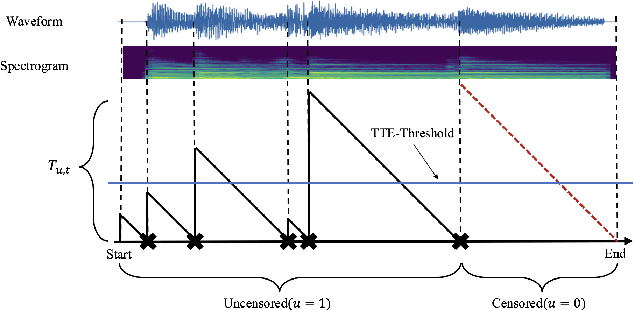
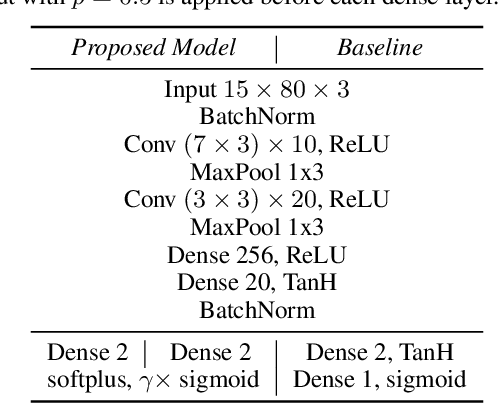
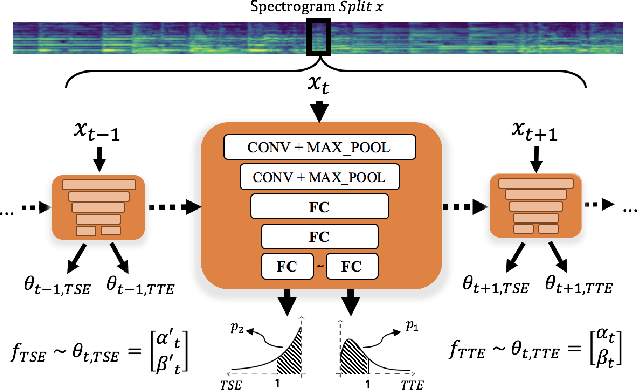
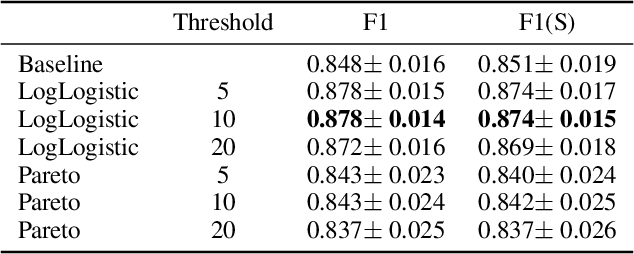
Abstract:Musical onset detection can be formulated as a time-to-event (TTE) or time-since-event (TSE) prediction task by defining music as a sequence of onset events. Here we propose a novel method to model the probability of onsets by introducing a sequential density prediction model. The proposed model estimates TTE & TSE distributions from mel-spectrograms using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a density predictor. We evaluate our model on the Bock dataset show-ing comparable results to previous deep-learning models.
Phase-aware Speech Enhancement with Deep Complex U-Net
Apr 02, 2019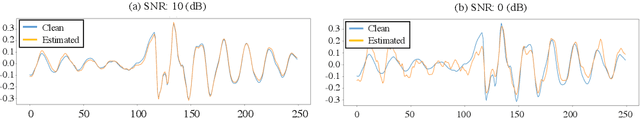
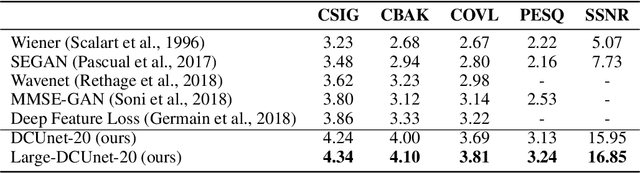
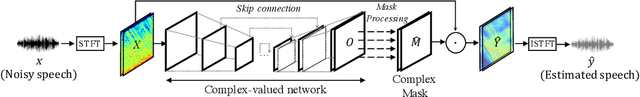
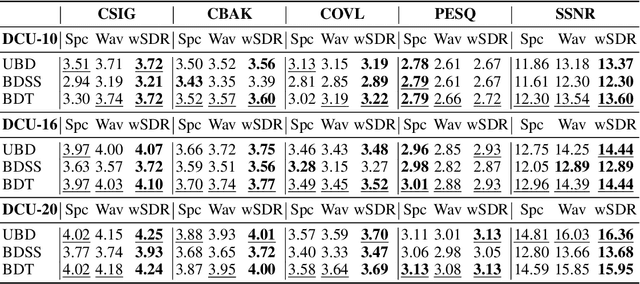
Abstract:Most deep learning-based models for speech enhancement have mainly focused on estimating the magnitude of spectrogram while reusing the phase from noisy speech for reconstruction. This is due to the difficulty of estimating the phase of clean speech. To improve speech enhancement performance, we tackle the phase estimation problem in three ways. First, we propose Deep Complex U-Net, an advanced U-Net structured model incorporating well-defined complex-valued building blocks to deal with complex-valued spectrograms. Second, we propose a polar coordinate-wise complex-valued masking method to reflect the distribution of complex ideal ratio masks. Third, we define a novel loss function, weighted source-to-distortion ratio (wSDR) loss, which is designed to directly correlate with a quantitative evaluation measure. Our model was evaluated on a mixture of the Voice Bank corpus and DEMAND database, which has been widely used by many deep learning models for speech enhancement. Ablation experiments were conducted on the mixed dataset showing that all three proposed approaches are empirically valid. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in all metrics, outperforming previous approaches by a large margin.
CHOPT : Automated Hyperparameter Optimization Framework for Cloud-Based Machine Learning Platforms
Oct 16, 2018
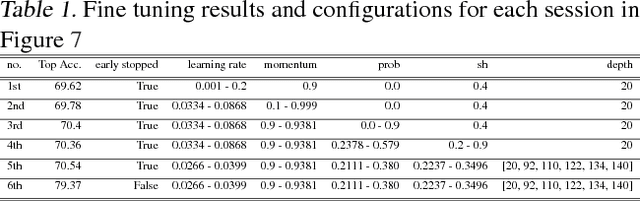

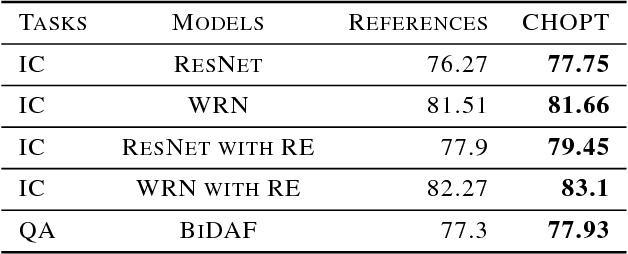
Abstract:Many hyperparameter optimization (HyperOpt) methods assume restricted computing resources and mainly focus on enhancing performance. Here we propose a novel cloud-based HyperOpt (CHOPT) framework which can efficiently utilize shared computing resources while supporting various HyperOpt algorithms. We incorporate convenient web-based user interfaces, visualization, and analysis tools, enabling users to easily control optimization procedures and build up valuable insights with an iterative analysis procedure. Furthermore, our framework can be incorporated with any cloud platform, thus complementarily increasing the efficiency of conventional deep learning frameworks. We demonstrate applications of CHOPT with tasks such as image recognition and question-answering, showing that our framework can find hyperparameter configurations competitive with previous work. We also show CHOPT is capable of providing interesting observations through its analysing tools
Automatic Music Highlight Extraction using Convolutional Recurrent Attention Networks
Dec 16, 2017



Abstract:Music highlights are valuable contents for music services. Most methods focused on low-level signal features. We propose a method for extracting highlights using high-level features from convolutional recurrent attention networks (CRAN). CRAN utilizes convolution and recurrent layers for sequential learning with an attention mechanism. The attention allows CRAN to capture significant snippets for distinguishing between genres, thus being used as a high-level feature. CRAN was evaluated on over 32,000 popular tracks in Korea for two months. Experimental results show our method outperforms three baseline methods through quantitative and qualitative evaluations. Also, we analyze the effects of attention and sequence information on performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge