Aditya Ranjan
Characterizing GPU Resilience and Impact on AI/HPC Systems
Mar 14, 2025Abstract:In this study, we characterize GPU failures in Delta, the current large-scale AI system with over 600 petaflops of peak compute throughput. The system comprises GPU and non-GPU nodes with modern AI accelerators, such as NVIDIA A40, A100, and H100 GPUs. The study uses two and a half years of data on GPU errors. We evaluate the resilience of GPU hardware components to determine the vulnerability of different GPU components to failure and their impact on the GPU and node availability. We measure the key propagation paths in GPU hardware, GPU interconnect (NVLink), and GPU memory. Finally, we evaluate the impact of the observed GPU errors on user jobs. Our key findings are: (i) Contrary to common beliefs, GPU memory is over 30x more reliable than GPU hardware in terms of MTBE (mean time between errors). (ii) The newly introduced GSP (GPU System Processor) is the most vulnerable GPU hardware component. (iii) NVLink errors did not always lead to user job failure, and we attribute it to the underlying error detection and retry mechanisms employed. (iv) We show multiple examples of hardware errors originating from one of the key GPU hardware components, leading to application failure. (v) We project the impact of GPU node availability on larger scales with emulation and find that significant overprovisioning between 5-20% would be necessary to handle GPU failures. If GPU availability were improved to 99.9%, the overprovisioning would be reduced by 4x.
Democratizing AI: Open-source Scalable LLM Training on GPU-based Supercomputers
Feb 12, 2025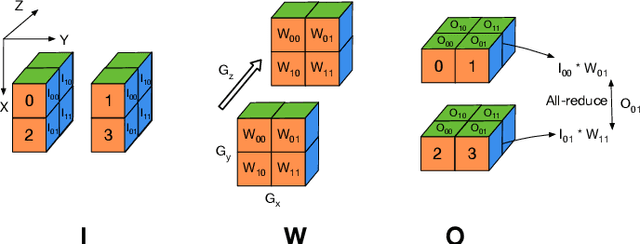
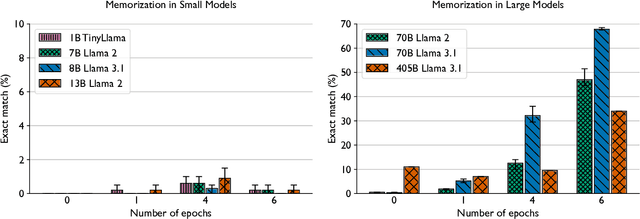
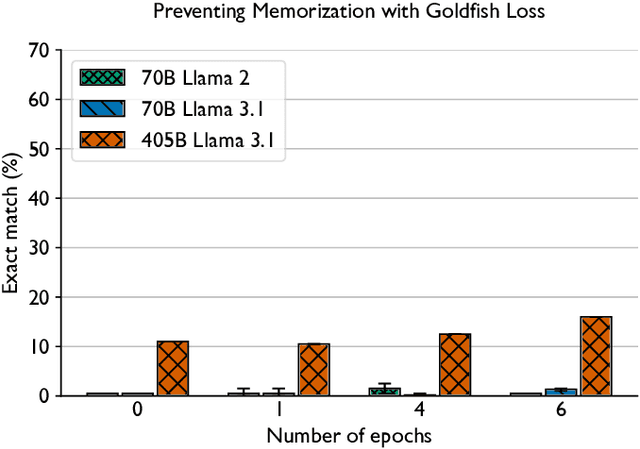
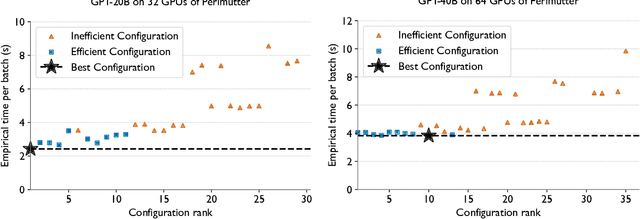
Abstract:Training and fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) with hundreds of billions to trillions of parameters requires tens of thousands of GPUs, and a highly scalable software stack. In this work, we present a novel four-dimensional hybrid parallel algorithm implemented in a highly scalable, portable, open-source framework called AxoNN. We describe several performance optimizations in AxoNN to improve matrix multiply kernel performance, overlap non-blocking collectives with computation, and performance modeling to choose performance optimal configurations. These have resulted in unprecedented scaling and peak flop/s (bf16) for training of GPT-style transformer models on Perlmutter (620.1 Petaflop/s), Frontier (1.381 Exaflop/s) and Alps (1.423 Exaflop/s). While the abilities of LLMs improve with the number of trainable parameters, so do privacy and copyright risks caused by memorization of training data, which can cause disclosure of sensitive or private information at inference time. We highlight this side effect of scale through experiments that explore "catastrophic memorization", where models are sufficiently large to memorize training data in a single pass, and present an approach to prevent it. As part of this study, we demonstrate fine-tuning of a 405-billion parameter LLM using AxoNN on Frontier.
OrganiQ: Mitigating Classical Resource Bottlenecks of Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks on NISQ-Era Machines
Sep 29, 2024Abstract:Driven by swift progress in hardware capabilities, quantum machine learning has emerged as a research area of interest. Recently, quantum image generation has produced promising results. However, prior quantum image generation techniques rely on classical neural networks, limiting their quantum potential and image quality. To overcome this, we introduce OrganiQ, the first quantum GAN capable of producing high-quality images without using classical neural networks.
SLIQ: Quantum Image Similarity Networks on Noisy Quantum Computers
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:Exploration into quantum machine learning has grown tremendously in recent years due to the ability of quantum computers to speed up classical programs. However, these efforts have yet to solve unsupervised similarity detection tasks due to the challenge of porting them to run on quantum computers. To overcome this challenge, we propose SLIQ, the first open-sourced work for resource-efficient quantum similarity detection networks, built with practical and effective quantum learning and variance-reducing algorithms.
MosaiQ: Quantum Generative Adversarial Networks for Image Generation on NISQ Computers
Aug 22, 2023Abstract:Quantum machine learning and vision have come to the fore recently, with hardware advances enabling rapid advancement in the capabilities of quantum machines. Recently, quantum image generation has been explored with many potential advantages over non-quantum techniques; however, previous techniques have suffered from poor quality and robustness. To address these problems, we introduce, MosaiQ, a high-quality quantum image generation GAN framework that can be executed on today's Near-term Intermediate Scale Quantum (NISQ) computers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge