Adam Lilja
GASP: Unifying Geometric and Semantic Self-Supervised Pre-training for Autonomous Driving
Mar 19, 2025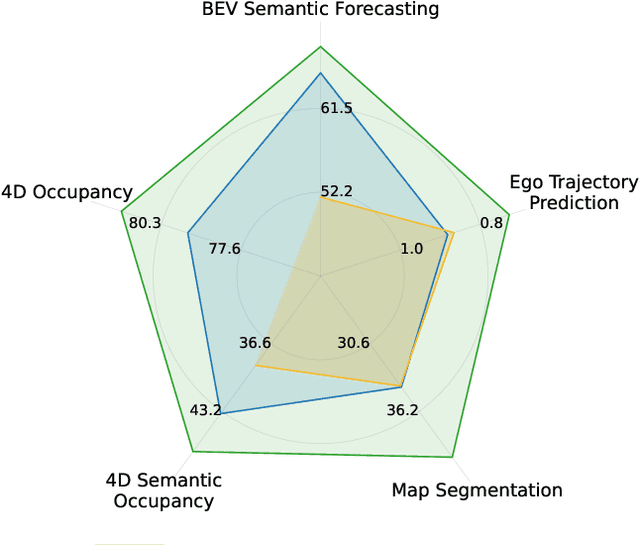
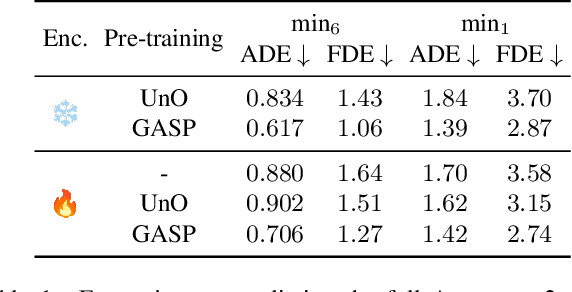
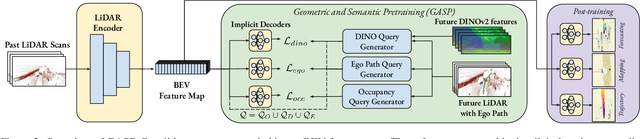
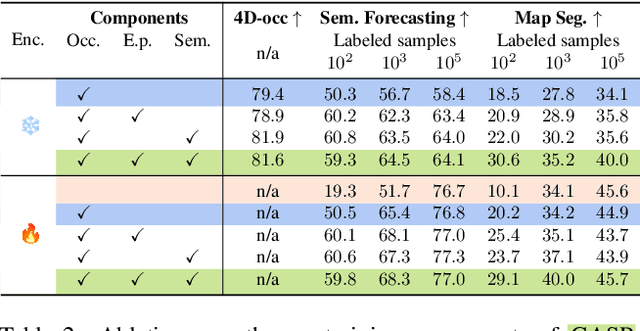
Abstract:Self-supervised pre-training based on next-token prediction has enabled large language models to capture the underlying structure of text, and has led to unprecedented performance on a large array of tasks when applied at scale. Similarly, autonomous driving generates vast amounts of spatiotemporal data, alluding to the possibility of harnessing scale to learn the underlying geometric and semantic structure of the environment and its evolution over time. In this direction, we propose a geometric and semantic self-supervised pre-training method, GASP, that learns a unified representation by predicting, at any queried future point in spacetime, (1) general occupancy, capturing the evolving structure of the 3D scene; (2) ego occupancy, modeling the ego vehicle path through the environment; and (3) distilled high-level features from a vision foundation model. By modeling geometric and semantic 4D occupancy fields instead of raw sensor measurements, the model learns a structured, generalizable representation of the environment and its evolution through time. We validate GASP on multiple autonomous driving benchmarks, demonstrating significant improvements in semantic occupancy forecasting, online mapping, and ego trajectory prediction. Our results demonstrate that continuous 4D geometric and semantic occupancy prediction provides a scalable and effective pre-training paradigm for autonomous driving. For code and additional visualizations, see \href{https://research.zenseact.com/publications/gasp/.
Exploring Semi-Supervised Learning for Online Mapping
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Online mapping is important for scaling autonomous driving beyond well-defined areas. Training a model to produce a local map, including lane markers, road edges, and pedestrian crossings using only onboard sensory information, traditionally requires extensive labelled data, which is difficult and costly to obtain. This paper draws inspiration from semi-supervised learning techniques in other domains, demonstrating their applicability to online mapping. Additionally, we propose a simple yet effective method to exploit inherent attributes of online mapping to further enhance performance by fusing the teacher's pseudo-labels from multiple samples. The performance gap to using all labels is reduced from 29.6 to 3.4 mIoU on Argoverse, and from 12 to 3.4 mIoU on NuScenes utilising only 10% of the labelled data. We also demonstrate strong performance in extrapolating to new cities outside those in the training data. Specifically, for challenging nuScenes, adapting from Boston to Singapore, performance increases by 6.6 mIoU when unlabelled data from Singapore is included in training.
Are NeRFs ready for autonomous driving? Towards closing the real-to-simulation gap
Mar 24, 2024Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) have emerged as promising tools for advancing autonomous driving (AD) research, offering scalable closed-loop simulation and data augmentation capabilities. However, to trust the results achieved in simulation, one needs to ensure that AD systems perceive real and rendered data in the same way. Although the performance of rendering methods is increasing, many scenarios will remain inherently challenging to reconstruct faithfully. To this end, we propose a novel perspective for addressing the real-to-simulated data gap. Rather than solely focusing on improving rendering fidelity, we explore simple yet effective methods to enhance perception model robustness to NeRF artifacts without compromising performance on real data. Moreover, we conduct the first large-scale investigation into the real-to-simulated data gap in an AD setting using a state-of-the-art neural rendering technique. Specifically, we evaluate object detectors and an online mapping model on real and simulated data, and study the effects of different pre-training strategies. Our results show notable improvements in model robustness to simulated data, even improving real-world performance in some cases. Last, we delve into the correlation between the real-to-simulated gap and image reconstruction metrics, identifying FID and LPIPS as strong indicators.
Localization Is All You Evaluate: Data Leakage in Online Mapping Datasets and How to Fix It
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:Data leakage is a critical issue when training and evaluating any method based on supervised learning. The state-of-the-art methods for online mapping are based on supervised learning and are trained predominantly using two datasets: nuScenes and Argoverse 2. These datasets revisit the same geographic locations across training, validation, and test sets. Specifically, over $80$% of nuScenes and $40$% of Argoverse 2 validation and test samples are located less than $5$ m from a training sample. This allows methods to localize within a memorized implicit map during testing and leads to inflated performance numbers being reported. To reveal the true performance in unseen environments, we introduce geographical splits of the data. Experimental results show significantly lower performance numbers, for some methods dropping with more than $45$ mAP, when retraining and reevaluating existing online mapping models with the proposed split. Additionally, a reassessment of prior design choices reveals diverging conclusions from those based on the original split. Notably, the impact of the lifting method and the support from auxiliary tasks (e.g., depth supervision) on performance appears less substantial or follows a different trajectory than previously perceived. Geographical splits can be found https://github.com/LiljaAdam/geographical-splits
Zenseact Open Dataset: A large-scale and diverse multimodal dataset for autonomous driving
May 03, 2023



Abstract:Existing datasets for autonomous driving (AD) often lack diversity and long-range capabilities, focusing instead on 360{\deg} perception and temporal reasoning. To address this gap, we introduce Zenseact Open Dataset (ZOD), a large-scale and diverse multimodal dataset collected over two years in various European countries, covering an area 9x that of existing datasets. ZOD boasts the highest range and resolution sensors among comparable datasets, coupled with detailed keyframe annotations for 2D and 3D objects (up to 245m), road instance/semantic segmentation, traffic sign recognition, and road classification. We believe that this unique combination will facilitate breakthroughs in long-range perception and multi-task learning. The dataset is composed of Frames, Sequences, and Drives, designed to encompass both data diversity and support for spatio-temporal learning, sensor fusion, localization, and mapping. Frames consist of 100k curated camera images with two seconds of other supporting sensor data, while the 1473 Sequences and 29 Drives include the entire sensor suite for 20 seconds and a few minutes, respectively. ZOD is the only large-scale AD dataset released under a permissive license, allowing for both research and commercial use. The dataset is accompanied by an extensive development kit. Data and more information are available online (https://zod.zenseact.com).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge