Abul Hasnat
MemeLens: Multilingual Multitask VLMs for Memes
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Memes are a dominant medium for online communication and manipulation because meaning emerges from interactions between embedded text, imagery, and cultural context. Existing meme research is distributed across tasks (hate, misogyny, propaganda, sentiment, humour) and languages, which limits cross-domain generalization. To address this gap we propose MemeLens, a unified multilingual and multitask explanation-enhanced Vision Language Model (VLM) for meme understanding. We consolidate 38 public meme datasets, filter and map dataset-specific labels into a shared taxonomy of $20$ tasks spanning harm, targets, figurative/pragmatic intent, and affect. We present a comprehensive empirical analysis across modeling paradigms, task categories, and datasets. Our findings suggest that robust meme understanding requires multimodal training, exhibits substantial variation across semantic categories, and remains sensitive to over-specialization when models are fine-tuned on individual datasets rather than trained in a unified setting. We will make the experimental resources and datasets publicly available for the community.
MemeIntel: Explainable Detection of Propagandistic and Hateful Memes
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of multimodal content on social media presents significant challenges in understanding and moderating complex, context-dependent issues such as misinformation, hate speech, and propaganda. While efforts have been made to develop resources and propose new methods for automatic detection, limited attention has been given to label detection and the generation of explanation-based rationales for predicted labels. To address this challenge, we introduce MemeIntel, an explanation-enhanced dataset for propaganda memes in Arabic and hateful memes in English, making it the first large-scale resource for these tasks. To solve these tasks, we propose a multi-stage optimization approach and train Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Our results demonstrate that this approach significantly improves performance over the base model for both \textbf{label detection} and explanation generation, outperforming the current state-of-the-art with an absolute improvement of ~3% on ArMeme and ~7% on Hateful Memes. For reproducibility and future research, we aim to make the MemeIntel dataset and experimental resources publicly available.
ArMeme: Propagandistic Content in Arabic Memes
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:With the rise of digital communication, memes have become a significant medium for cultural and political expression that is often used to mislead audiences. Identification of such misleading and persuasive multimodal content has become more important among various stakeholders, including social media platforms, policymakers, and the broader society as they often cause harm to individuals, organizations, and/or society. While there has been effort to develop AI-based automatic systems for resource-rich languages (e.g., English), it is relatively little to none for medium to low resource languages. In this study, we focused on developing an Arabic memes dataset with manual annotations of propagandistic content. We annotated ~6K Arabic memes collected from various social media platforms, which is a first resource for Arabic multimodal research. We provide a comprehensive analysis aiming to develop computational tools for their detection. We will make them publicly available for the community.
MEDIC: A Multi-Task Learning Dataset for Disaster Image Classification
Aug 29, 2021
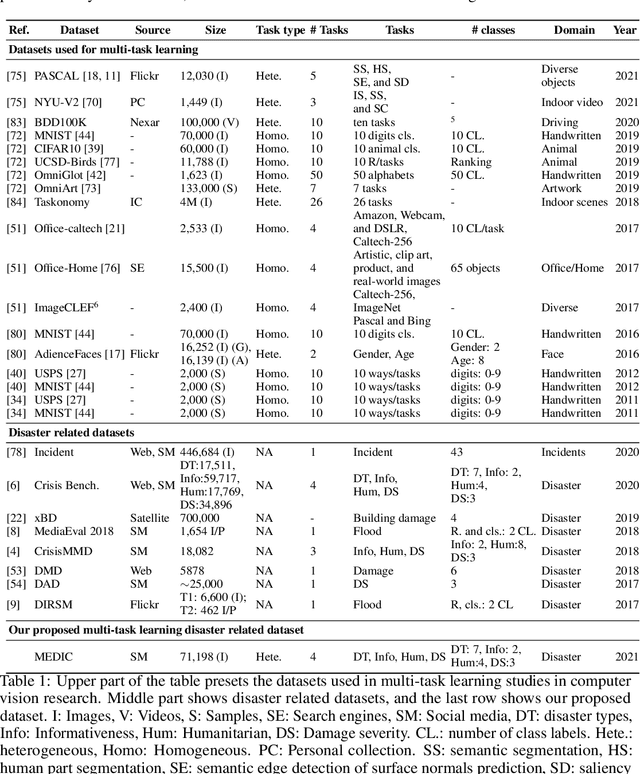
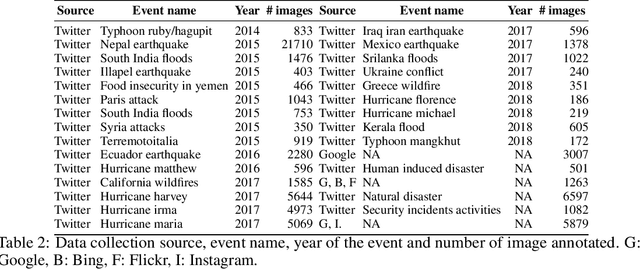

Abstract:Recent research in disaster informatics demonstrates a practical and important use case of artificial intelligence to save human lives and sufferings during post-natural disasters based on social media contents (text and images). While notable progress has been made using texts, research on exploiting the images remains relatively under-explored. To advance the image-based approach, we propose MEDIC (available at: https://crisisnlp.qcri.org/medic/index.html), which is the largest social media image classification dataset for humanitarian response consisting of 71,198 images to address four different tasks in a multi-task learning setup. This is the first dataset of its kind: social media image, disaster response, and multi-task learning research. An important property of this dataset is its high potential to contribute research on multi-task learning, which recently receives much interest from the machine learning community and has shown remarkable results in terms of memory, inference speed, performance, and generalization capability. Therefore, the proposed dataset is an important resource for advancing image-based disaster management and multi-task machine learning research.
DeepVisage: Making face recognition simple yet with powerful generalization skills
Apr 07, 2017



Abstract:Face recognition (FR) methods report significant performance by adopting the convolutional neural network (CNN) based learning methods. Although CNNs are mostly trained by optimizing the softmax loss, the recent trend shows an improvement of accuracy with different strategies, such as task-specific CNN learning with different loss functions, fine-tuning on target dataset, metric learning and concatenating features from multiple CNNs. Incorporating these tasks obviously requires additional efforts. Moreover, it demotivates the discovery of efficient CNN models for FR which are trained only with identity labels. We focus on this fact and propose an easily trainable and single CNN based FR method. Our CNN model exploits the residual learning framework. Additionally, it uses normalized features to compute the loss. Our extensive experiments show excellent generalization on different datasets. We obtain very competitive and state-of-the-art results on the LFW, IJB-A, YouTube faces and CACD datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge