Julien Bohné
von Mises-Fisher Mixture Model-based Deep learning: Application to Face Verification
Dec 31, 2017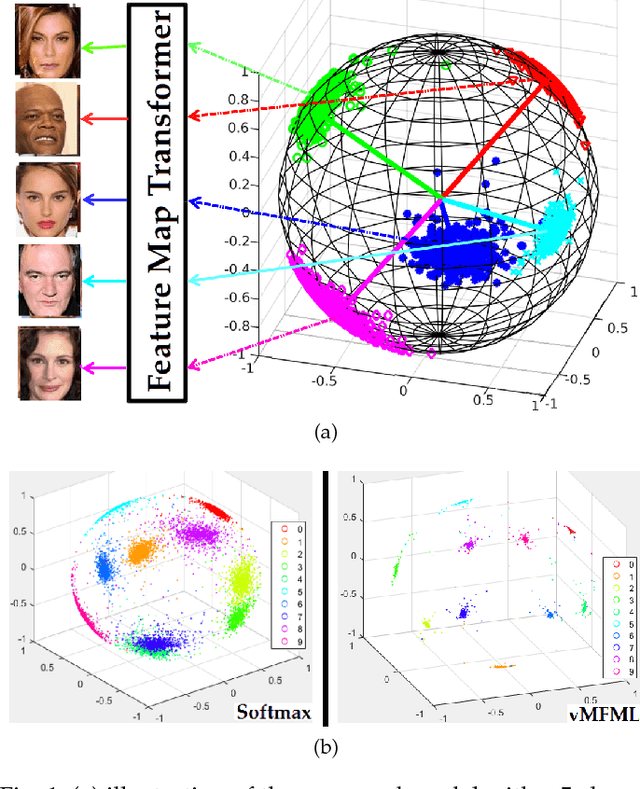
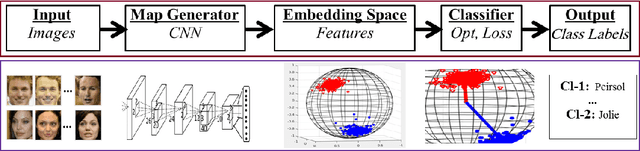
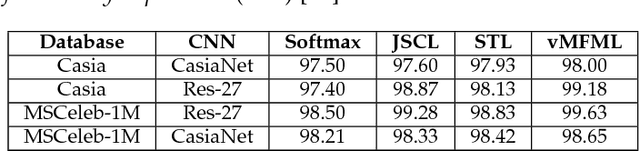
Abstract:A number of pattern recognition tasks, \textit{e.g.}, face verification, can be boiled down to classification or clustering of unit length directional feature vectors whose distance can be simply computed by their angle. In this paper, we propose the von Mises-Fisher (vMF) mixture model as the theoretical foundation for an effective deep-learning of such directional features and derive a novel vMF Mixture Loss and its corresponding vMF deep features. The proposed vMF feature learning achieves the characteristics of discriminative learning, \textit{i.e.}, compacting the instances of the same class while increasing the distance of instances from different classes. Moreover, it subsumes a number of popular loss functions as well as an effective method in deep learning, namely normalization. We conduct extensive experiments on face verification using 4 different challenging face datasets, \textit{i.e.}, LFW, YouTube faces, CACD and IJB-A. Results show the effectiveness and excellent generalization ability of the proposed approach as it achieves state-of-the-art results on the LFW, YouTube faces and CACD datasets and competitive results on the IJB-A dataset.
DeepVisage: Making face recognition simple yet with powerful generalization skills
Apr 07, 2017



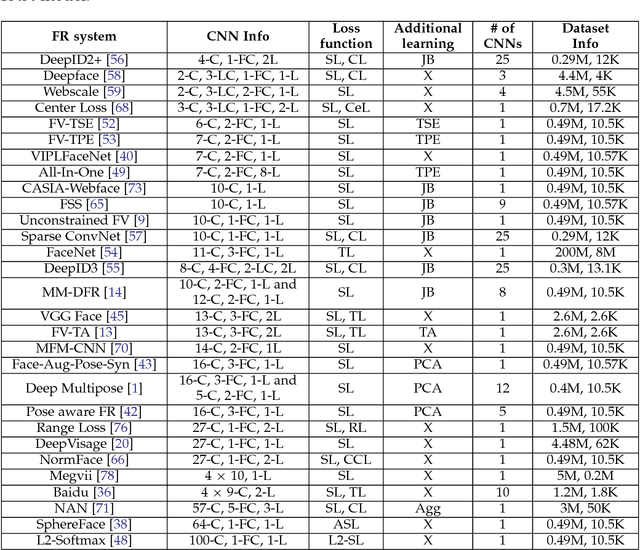
Abstract:Face recognition (FR) methods report significant performance by adopting the convolutional neural network (CNN) based learning methods. Although CNNs are mostly trained by optimizing the softmax loss, the recent trend shows an improvement of accuracy with different strategies, such as task-specific CNN learning with different loss functions, fine-tuning on target dataset, metric learning and concatenating features from multiple CNNs. Incorporating these tasks obviously requires additional efforts. Moreover, it demotivates the discovery of efficient CNN models for FR which are trained only with identity labels. We focus on this fact and propose an easily trainable and single CNN based FR method. Our CNN model exploits the residual learning framework. Additionally, it uses normalized features to compute the loss. Our extensive experiments show excellent generalization on different datasets. We obtain very competitive and state-of-the-art results on the LFW, IJB-A, YouTube faces and CACD datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge