Abhijit Ogale
Learning Visual Composition through Improved Semantic Guidance
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Visual imagery does not consist of solitary objects, but instead reflects the composition of a multitude of fluid concepts. While there have been great advances in visual representation learning, such advances have focused on building better representations for a small number of discrete objects bereft of an understanding of how these objects are interacting. One can observe this limitation in representations learned through captions or contrastive learning -- where the learned model treats an image essentially as a bag of words. Several works have attempted to address this limitation through the development of bespoke learned architectures to directly address the shortcomings in compositional learning. In this work, we focus on simple, and scalable approaches. In particular, we demonstrate that by substantially improving weakly labeled data, i.e. captions, we can vastly improve the performance of standard contrastive learning approaches. Previous CLIP models achieved near chance rate on challenging tasks probing compositional learning. However, our simple approach boosts performance of CLIP substantially and surpasses all bespoke architectures. Furthermore, we showcase our results on a relatively new captioning benchmark derived from DOCCI. We demonstrate through a series of ablations that a standard CLIP model trained with enhanced data may demonstrate impressive performance on image retrieval tasks.
Towards flexible perception with visual memory
Aug 15, 2024



Abstract:Training a neural network is a monolithic endeavor, akin to carving knowledge into stone: once the process is completed, editing the knowledge in a network is nearly impossible, since all information is distributed across the network's weights. We here explore a simple, compelling alternative by marrying the representational power of deep neural networks with the flexibility of a database. Decomposing the task of image classification into image similarity (from a pre-trained embedding) and search (via fast nearest neighbor retrieval from a knowledge database), we build a simple and flexible visual memory that has the following key capabilities: (1.) The ability to flexibly add data across scales: from individual samples all the way to entire classes and billion-scale data; (2.) The ability to remove data through unlearning and memory pruning; (3.) An interpretable decision-mechanism on which we can intervene to control its behavior. Taken together, these capabilities comprehensively demonstrate the benefits of an explicit visual memory. We hope that it might contribute to a conversation on how knowledge should be represented in deep vision models -- beyond carving it in ``stone'' weights.
MaMMUT: A Simple Architecture for Joint Learning for MultiModal Tasks
Mar 30, 2023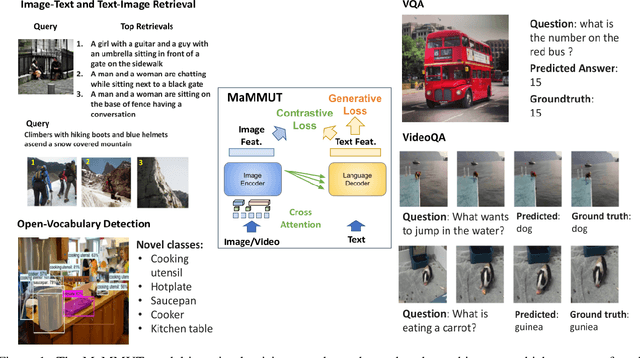
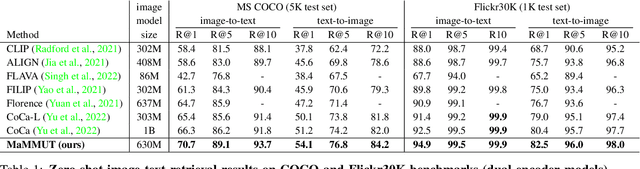
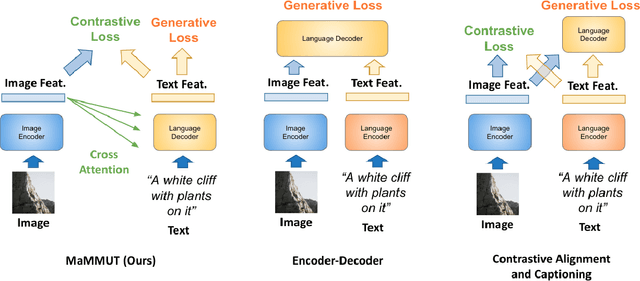
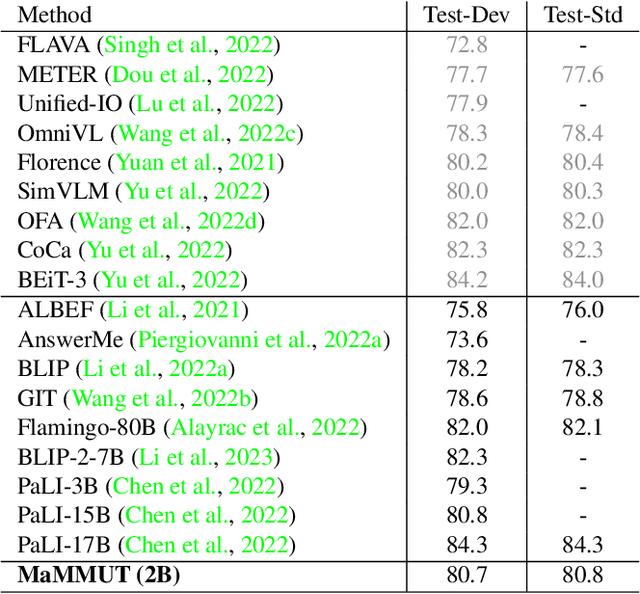
Abstract:The development of language models have moved from encoder-decoder to decoder-only designs. In addition, the common knowledge has it that the two most popular multimodal tasks, the generative and contrastive tasks, tend to conflict with one another, are hard to accommodate in one architecture, and further need complex adaptations for downstream tasks. We propose a novel paradigm of training with a decoder-only model for multimodal tasks, which is surprisingly effective in jointly learning of these disparate vision-language tasks. This is done with a simple model, called MaMMUT. It consists of a single vision encoder and a text decoder, and is able to accommodate contrastive and generative learning by a novel two-pass approach on the text decoder. We demonstrate that joint learning of these diverse objectives is simple, effective, and maximizes the weight-sharing of the model across these tasks. Furthermore, the same architecture enables straightforward extensions to open-vocabulary object detection and video-language tasks. The model tackles a diverse range of tasks, while being modest in capacity. Our model achieves the state of the art on image-text and text-image retrieval, video question answering and open-vocabulary detection tasks, outperforming much larger and more extensively trained foundational models. It shows very competitive results on VQA and Video Captioning, especially considering its capacity. Ablations confirm the flexibility and advantages of our approach.
ChauffeurNet: Learning to Drive by Imitating the Best and Synthesizing the Worst
Dec 07, 2018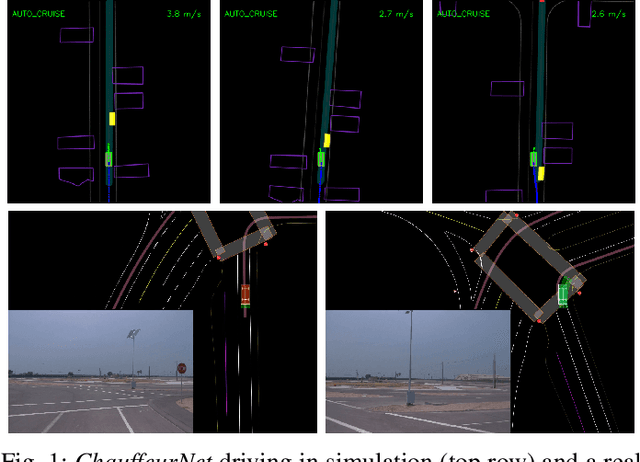
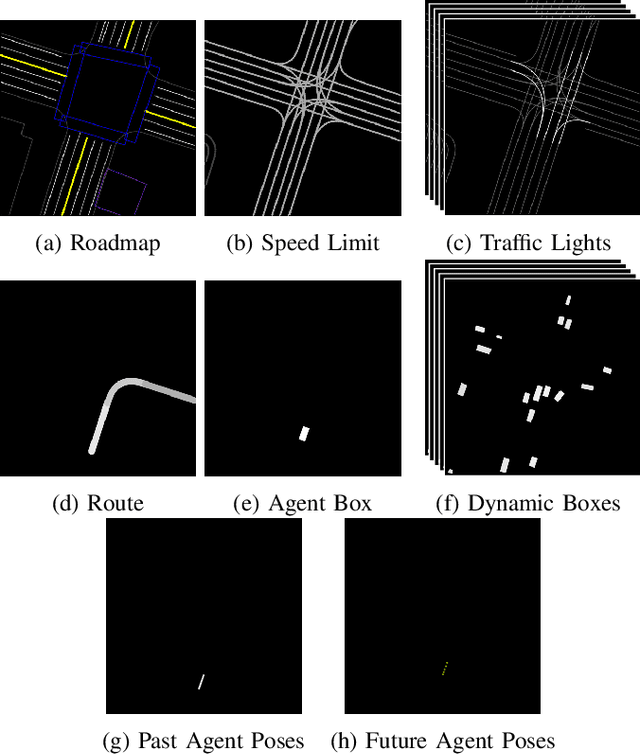

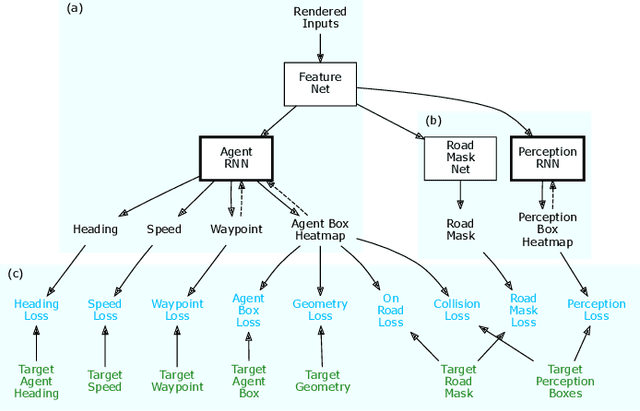
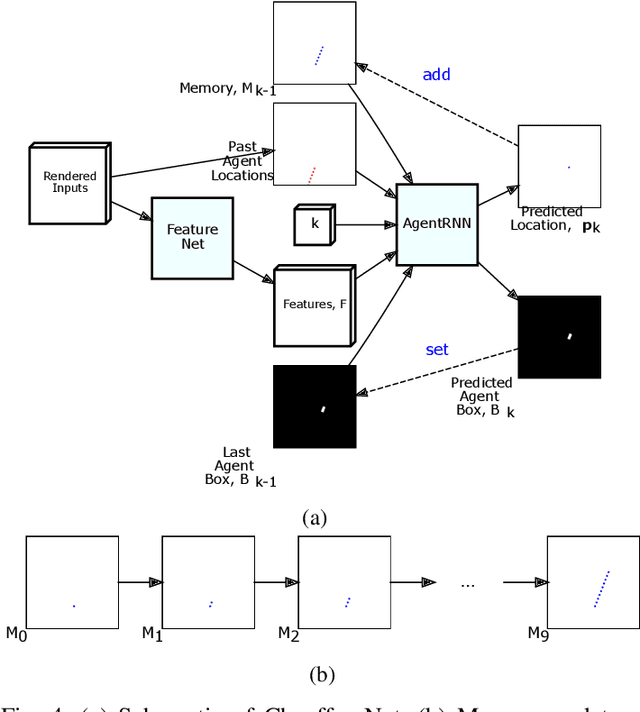
Abstract:Our goal is to train a policy for autonomous driving via imitation learning that is robust enough to drive a real vehicle. We find that standard behavior cloning is insufficient for handling complex driving scenarios, even when we leverage a perception system for preprocessing the input and a controller for executing the output on the car: 30 million examples are still not enough. We propose exposing the learner to synthesized data in the form of perturbations to the expert's driving, which creates interesting situations such as collisions and/or going off the road. Rather than purely imitating all data, we augment the imitation loss with additional losses that penalize undesirable events and encourage progress -- the perturbations then provide an important signal for these losses and lead to robustness of the learned model. We show that the ChauffeurNet model can handle complex situations in simulation, and present ablation experiments that emphasize the importance of each of our proposed changes and show that the model is responding to the appropriate causal factors. Finally, we demonstrate the model driving a car in the real world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge