Aaryan Singhal
ThunderKittens: Simple, Fast, and Adorable AI Kernels
Oct 27, 2024Abstract:The challenge of mapping AI architectures to GPU hardware is creating a critical bottleneck in AI progress. Despite substantial efforts, hand-written custom kernels fail to meet their theoretical performance thresholds, even on well-established operations like linear attention. The diverse hardware capabilities of GPUs might suggest that we need a wide variety of techniques to achieve high performance. However, our work explores whether a small number of key abstractions can drastically simplify the process. We present ThunderKittens (TK), a framework for writing performant AI kernels while remaining easy to use and maintain. Our abstractions map to the three levels of the GPU hierarchy: (1) at the warp-level, we provide 16x16 matrix tiles as basic data structures and PyTorch-like parallel compute operations over tiles, (2) at the thread-block level, we provide a template for overlapping asynchronous operations across parallel warps, and (3) at the grid-level, we provide support to help hide the block launch and tear-down, and memory costs. We show the value of TK by providing kernels that match or outperform prior kernels for a range of AI operations. We match CuBLAS and FlashAttention-3 on GEMM and attention inference performance and outperform the strongest baselines by $10-40\%$ on attention backwards, $8\times$ on state space models, and $14\times$ on linear attention.
LoLCATs: On Low-Rank Linearizing of Large Language Models
Oct 14, 2024
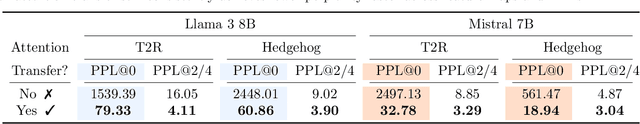
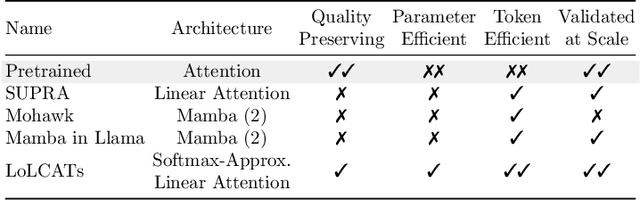

Abstract:Recent works show we can linearize large language models (LLMs) -- swapping the quadratic attentions of popular Transformer-based LLMs with subquadratic analogs, such as linear attention -- avoiding the expensive pretraining costs. However, linearizing LLMs often significantly degrades model quality, still requires training over billions of tokens, and remains limited to smaller 1.3B to 7B LLMs. We thus propose Low-rank Linear Conversion via Attention Transfer (LoLCATs), a simple two-step method that improves LLM linearizing quality with orders of magnitudes less memory and compute. We base these steps on two findings. First, we can replace an LLM's softmax attentions with closely-approximating linear attentions, simply by training the linear attentions to match their softmax counterparts with an output MSE loss ("attention transfer"). Then, this enables adjusting for approximation errors and recovering LLM quality simply with low-rank adaptation (LoRA). LoLCATs significantly improves linearizing quality, training efficiency, and scalability. We significantly reduce the linearizing quality gap and produce state-of-the-art subquadratic LLMs from Llama 3 8B and Mistral 7B v0.1, leading to 20+ points of improvement on 5-shot MMLU. Furthermore, LoLCATs does so with only 0.2% of past methods' model parameters and 0.4% of their training tokens. Finally, we apply LoLCATs to create the first linearized 70B and 405B LLMs (50x larger than prior work). When compared with prior approaches under the same compute budgets, LoLCATs significantly improves linearizing quality, closing the gap between linearized and original Llama 3.1 70B and 405B LLMs by 77.8% and 78.1% on 5-shot MMLU.
Just read twice: closing the recall gap for recurrent language models
Jul 07, 2024



Abstract:Recurrent large language models that compete with Transformers in language modeling perplexity are emerging at a rapid rate (e.g., Mamba, RWKV). Excitingly, these architectures use a constant amount of memory during inference. However, due to the limited memory, recurrent LMs cannot recall and use all the information in long contexts leading to brittle in-context learning (ICL) quality. A key challenge for efficient LMs is selecting what information to store versus discard. In this work, we observe the order in which information is shown to the LM impacts the selection difficulty. To formalize this, we show that the hardness of information recall reduces to the hardness of a problem called set disjointness (SD), a quintessential problem in communication complexity that requires a streaming algorithm (e.g., recurrent model) to decide whether inputted sets are disjoint. We empirically and theoretically show that the recurrent memory required to solve SD changes with set order, i.e., whether the smaller set appears first in-context. Our analysis suggests, to mitigate the reliance on data order, we can put information in the right order in-context or process prompts non-causally. Towards that end, we propose: (1) JRT-Prompt, where context gets repeated multiple times in the prompt, effectively showing the model all data orders. This gives $11.0 \pm 1.3$ points of improvement, averaged across $16$ recurrent LMs and the $6$ ICL tasks, with $11.9\times$ higher throughput than FlashAttention-2 for generation prefill (length $32$k, batch size $16$, NVidia H100). We then propose (2) JRT-RNN, which uses non-causal prefix-linear-attention to process prompts and provides $99\%$ of Transformer quality at $360$M params., $30$B tokens and $96\%$ at $1.3$B params., $50$B tokens on average across the tasks, with $19.2\times$ higher throughput for prefill than FA2.
Real-time Control of Electric Autonomous Mobility-on-Demand Systems via Graph Reinforcement Learning
Nov 09, 2023



Abstract:Operators of Electric Autonomous Mobility-on-Demand (E-AMoD) fleets need to make several real-time decisions such as matching available cars to ride requests, rebalancing idle cars to areas of high demand, and charging vehicles to ensure sufficient range. While this problem can be posed as a linear program that optimizes flows over a space-charge-time graph, the size of the resulting optimization problem does not allow for real-time implementation in realistic settings. In this work, we present the E-AMoD control problem through the lens of reinforcement learning and propose a graph network-based framework to achieve drastically improved scalability and superior performance over heuristics. Specifically, we adopt a bi-level formulation where we (1) leverage a graph network-based RL agent to specify a desired next state in the space-charge graph, and (2) solve more tractable linear programs to best achieve the desired state while ensuring feasibility. Experiments using real-world data from San Francisco and New York City show that our approach achieves up to 89% of the profits of the theoretically-optimal solution while achieving more than a 100x speedup in computational time. Furthermore, our approach outperforms the best domain-specific heuristics with comparable runtimes, with an increase in profits by up to 3x. Finally, we highlight promising zero-shot transfer capabilities of our learned policy on tasks such as inter-city generalization and service area expansion, thus showing the utility, scalability, and flexibility of our framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge