Yolov7
Papers and Code
Dynamic Mask-Based Backdoor Attack Against Vision AI Models: A Case Study on Mushroom Detection
Jan 26, 2026Deep learning has revolutionized numerous tasks within the computer vision field, including image classification, image segmentation, and object detection. However, the increasing deployment of deep learning models has exposed them to various adversarial attacks, including backdoor attacks. This paper presents a novel dynamic mask-based backdoor attack method, specifically designed for object detection models. We exploit a dataset poisoning technique to embed a malicious trigger, rendering any models trained on this compromised dataset vulnerable to our backdoor attack. We particularly focus on a mushroom detection dataset to demonstrate the practical risks posed by such attacks on critical real-life domains. Our work also emphasizes the importance of creating a detailed backdoor attack scenario to illustrate the significant risks associated with the outsourcing practice. Our approach leverages SAM, a recent and powerful image segmentation AI model, to create masks for dynamic trigger placement, introducing a new and stealthy attack method. Through extensive experimentation, we show that our sophisticated attack scenario maintains high accuracy on clean data with the YOLOv7 object detection model while achieving high attack success rates on poisoned samples. Our approach surpasses traditional methods for backdoor injection, which are based on static and consistent patterns. Our findings underscore the urgent need for robust countermeasures to protect deep learning models from these evolving adversarial threats.
Detection Fire in Camera RGB-NIR
Dec 29, 2025Improving the accuracy of fire detection using infrared night vision cameras remains a challenging task. Previous studies have reported strong performance with popular detection models. For example, YOLOv7 achieved an mAP50-95 of 0.51 using an input image size of 640 x 1280, RT-DETR reached an mAP50-95 of 0.65 with an image size of 640 x 640, and YOLOv9 obtained an mAP50-95 of 0.598 at the same resolution. Despite these results, limitations in dataset construction continue to cause issues, particularly the frequent misclassification of bright artificial lights as fire. This report presents three main contributions: an additional NIR dataset, a two-stage detection model, and Patched-YOLO. First, to address data scarcity, we explore and apply various data augmentation strategies for both the NIR dataset and the classification dataset. Second, to improve night-time fire detection accuracy while reducing false positives caused by artificial lights, we propose a two-stage pipeline combining YOLOv11 and EfficientNetV2-B0. The proposed approach achieves higher detection accuracy compared to previous methods, particularly for night-time fire detection. Third, to improve fire detection in RGB images, especially for small and distant objects, we introduce Patched-YOLO, which enhances the model's detection capability through patch-based processing. Further details of these contributions are discussed in the following sections.
BoardVision: Deployment-ready and Robust Motherboard Defect Detection with YOLO+Faster-RCNN Ensemble
Oct 16, 2025Motherboard defect detection is critical for ensuring reliability in high-volume electronics manufacturing. While prior research in PCB inspection has largely targeted bare-board or trace-level defects, assembly-level inspection of full motherboards inspection remains underexplored. In this work, we present BoardVision, a reproducible framework for detecting assembly-level defects such as missing screws, loose fan wiring, and surface scratches. We benchmark two representative detectors - YOLOv7 and Faster R-CNN, under controlled conditions on the MiracleFactory motherboard dataset, providing the first systematic comparison in this domain. To mitigate the limitations of single models, where YOLO excels in precision but underperforms in recall and Faster R-CNN shows the reverse, we propose a lightweight ensemble, Confidence-Temporal Voting (CTV Voter), that balances precision and recall through interpretable rules. We further evaluate robustness under realistic perturbations including sharpness, brightness, and orientation changes, highlighting stability challenges often overlooked in motherboard defect detection. Finally, we release a deployable GUI-driven inspection tool that bridges research evaluation with operator usability. Together, these contributions demonstrate how computer vision techniques can transition from benchmark results to practical quality assurance for assembly-level motherboard manufacturing.
Automated Defect Detection for Mass-Produced Electronic Components Based on YOLO Object Detection Models
Oct 02, 2025Since the defect detection of conventional industry components is time-consuming and labor-intensive, it leads to a significant burden on quality inspection personnel and makes it difficult to manage product quality. In this paper, we propose an automated defect detection system for the dual in-line package (DIP) that is widely used in industry, using digital camera optics and a deep learning (DL)-based model. The two most common defect categories of DIP are examined: (1) surface defects, and (2) pin-leg defects. However, the lack of defective component images leads to a challenge for detection tasks. To solve this problem, the ConSinGAN is used to generate a suitable-sized dataset for training and testing. Four varieties of the YOLO model are investigated (v3, v4, v7, and v9), both in isolation and with the ConSinGAN augmentation. The proposed YOLOv7 with ConSinGAN is superior to the other YOLO versions in accuracy of 95.50\%, detection time of 285 ms, and is far superior to threshold-based approaches. In addition, the supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system is developed, and the associated sensor architecture is described. The proposed automated defect detection can be easily established with numerous types of defects or insufficient defect data.
* 12 pages, 16 figures, 7 tables, and published in IEEE Sensors Journal
ORB: Operating Room Bot, Automating Operating Room Logistics through Mobile Manipulation
Sep 19, 2025
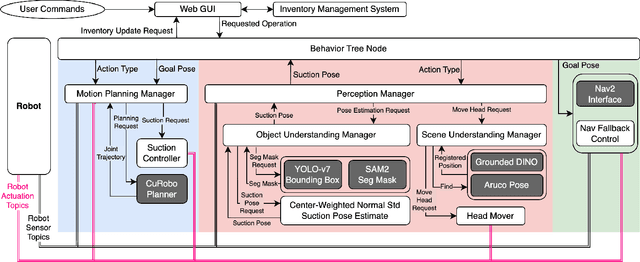


Efficiently delivering items to an ongoing surgery in a hospital operating room can be a matter of life or death. In modern hospital settings, delivery robots have successfully transported bulk items between rooms and floors. However, automating item-level operating room logistics presents unique challenges in perception, efficiency, and maintaining sterility. We propose the Operating Room Bot (ORB), a robot framework to automate logistics tasks in hospital operating rooms (OR). ORB leverages a robust, hierarchical behavior tree (BT) architecture to integrate diverse functionalities of object recognition, scene interpretation, and GPU-accelerated motion planning. The contributions of this paper include: (1) a modular software architecture facilitating robust mobile manipulation through behavior trees; (2) a novel real-time object recognition pipeline integrating YOLOv7, Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2), and Grounded DINO; (3) the adaptation of the cuRobo parallelized trajectory optimization framework to real-time, collision-free mobile manipulation; and (4) empirical validation demonstrating an 80% success rate in OR supply retrieval and a 96% success rate in restocking operations. These contributions establish ORB as a reliable and adaptable system for autonomous OR logistics.
Enhancing Egocentric Object Detection in Static Environments using Graph-based Spatial Anomaly Detection and Correction
Aug 11, 2025In many real-world applications involving static environments, the spatial layout of objects remains consistent across instances. However, state-of-the-art object detection models often fail to leverage this spatial prior, resulting in inconsistent predictions, missed detections, or misclassifications, particularly in cluttered or occluded scenes. In this work, we propose a graph-based post-processing pipeline that explicitly models the spatial relationships between objects to correct detection anomalies in egocentric frames. Using a graph neural network (GNN) trained on manually annotated data, our model identifies invalid object class labels and predicts corrected class labels based on their neighbourhood context. We evaluate our approach both as a standalone anomaly detection and correction framework and as a post-processing module for standard object detectors such as YOLOv7 and RT-DETR. Experiments demonstrate that incorporating this spatial reasoning significantly improves detection performance, with mAP@50 gains of up to 4%. This method highlights the potential of leveraging the environment's spatial structure to improve reliability in object detection systems.
Lightweight Multi-Frame Integration for Robust YOLO Object Detection in Videos
Jun 25, 2025Modern image-based object detection models, such as YOLOv7, primarily process individual frames independently, thus ignoring valuable temporal context naturally present in videos. Meanwhile, existing video-based detection methods often introduce complex temporal modules, significantly increasing model size and computational complexity. In practical applications such as surveillance and autonomous driving, transient challenges including motion blur, occlusions, and abrupt appearance changes can severely degrade single-frame detection performance. To address these issues, we propose a straightforward yet highly effective strategy: stacking multiple consecutive frames as input to a YOLO-based detector while supervising only the output corresponding to a single target frame. This approach leverages temporal information with minimal modifications to existing architectures, preserving simplicity, computational efficiency, and real-time inference capability. Extensive experiments on the challenging MOT20Det and our BOAT360 datasets demonstrate that our method improves detection robustness, especially for lightweight models, effectively narrowing the gap between compact and heavy detection networks. Additionally, we contribute the BOAT360 benchmark dataset, comprising annotated fisheye video sequences captured from a boat, to support future research in multi-frame video object detection in challenging real-world scenarios.
ISTD-YOLO: A Multi-Scale Lightweight High-Performance Infrared Small Target Detection Algorithm
Apr 19, 2025Aiming at the detection difficulties of infrared images such as complex background, low signal-to-noise ratio, small target size and weak brightness, a lightweight infrared small target detection algorithm ISTD-YOLO based on improved YOLOv7 was proposed. Firstly, the YOLOv7 network structure was lightweight reconstructed, and a three-scale lightweight network architecture was designed. Then, the ELAN-W module of the model neck network is replaced by VoV-GSCSP to reduce the computational cost and the complexity of the network structure. Secondly, a parameter-free attention mechanism was introduced into the neck network to enhance the relevance of local con-text information. Finally, the Normalized Wasserstein Distance (NWD) was used to optimize the commonly used IoU index to enhance the localization and detection accuracy of small targets. Experimental results show that compared with YOLOv7 and the current mainstream algorithms, ISTD-YOLO can effectively improve the detection effect, and all indicators are effectively improved, which can achieve high-quality detection of infrared small targets.
AI-Driven Multi-Stage Computer Vision System for Defect Detection in Laser-Engraved Industrial Nameplates
Mar 05, 2025Automated defect detection in industrial manufacturing is essential for maintaining product quality and minimizing production errors. In air disc brake manufacturing, ensuring the precision of laser-engraved nameplates is crucial for accurate product identification and quality control. Engraving errors, such as misprints or missing characters, can compromise both aesthetics and functionality, leading to material waste and production delays. This paper presents a proof of concept for an AI-driven computer vision system that inspects and verifies laser-engraved nameplates, detecting defects in logos and alphanumeric strings. The system integrates object detection using YOLOv7, optical character recognition (OCR) with Tesseract, and anomaly detection through a residual variational autoencoder (ResVAE) along with other computer vision methods to enable comprehensive inspections at multiple stages. Experimental results demonstrate the system's effectiveness, achieving 91.33% accuracy and 100% recall, ensuring that defective nameplates are consistently detected and addressed. This solution highlights the potential of AI-driven visual inspection to enhance quality control, reduce manual inspection efforts, and improve overall manufacturing efficiency.
Improved YOLOv7 model for insulator defect detection
Feb 11, 2025Insulators are crucial insulation components and structural supports in power grids, playing a vital role in the transmission lines. Due to temperature fluctuations, internal stress, or damage from hail, insulators are prone to injury. Automatic detection of damaged insulators faces challenges such as diverse types, small defect targets, and complex backgrounds and shapes. Most research for detecting insulator defects has focused on a single defect type or a specific material. However, the insulators in the grid's transmission lines have different colors and materials. Various insulator defects coexist, and the existing methods have difficulty meeting the practical application requirements. Current methods suffer from low detection accuracy and mAP0.5 cannot meet application requirements. This paper proposes an improved YOLOv7 model for multi-type insulator defect detection. First, our model replaces the SPPCSPC module with the RFB module to enhance the network's feature extraction capability. Second, a CA mechanism is introduced into the head part to enhance the network's feature representation ability and to improve detection accuracy. Third, a WIoU loss function is employed to address the low-quality samples hindering model generalization during training, thereby improving the model's overall performance. The experimental results indicate that the proposed model exhibits enhancements across various performance metrics. Specifically, there is a 1.6% advancement in mAP_0.5, a corresponding 1.6% enhancement in mAP_0.5:0.95, a 1.3% elevation in precision, and a 1% increase in recall. Moreover, the model achieves parameter reduction by 3.2 million, leading to a decrease of 2.5 GFLOPS in computational cost. Notably, there is also an improvement of 2.81 milliseconds in single-image detection speed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge