Ziyan He
Auto-Formulating Dynamic Programming Problems with Large Language Models
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:Dynamic programming (DP) is a fundamental method in operations research, but formulating DP models has traditionally required expert knowledge of both the problem context and DP techniques. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer the potential to automate this process. However, DP problems pose unique challenges due to their inherently stochastic transitions and the limited availability of training data. These factors make it difficult to directly apply existing LLM-based models or frameworks developed for other optimization problems, such as linear or integer programming. We introduce DP-Bench, the first benchmark covering a wide range of textbook-level DP problems to enable systematic evaluation. We present Dynamic Programming Language Model (DPLM), a 7B-parameter specialized model that achieves performance comparable to state-of-the-art LLMs like OpenAI's o1 and DeepSeek-R1, and surpasses them on hard problems. Central to DPLM's effectiveness is DualReflect, our novel synthetic data generation pipeline, designed to scale up training data from a limited set of initial examples. DualReflect combines forward generation for diversity and backward generation for reliability. Our results reveal a key insight: backward generation is favored in low-data regimes for its strong correctness guarantees, while forward generation, though lacking such guarantees, becomes increasingly valuable at scale for introducing diverse formulations. This trade-off highlights the complementary strengths of both approaches and the importance of combining them.
Solving Integrated Process Planning and Scheduling Problem via Graph Neural Network Based Deep Reinforcement Learning
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:The Integrated Process Planning and Scheduling (IPPS) problem combines process route planning and shop scheduling to achieve high efficiency in manufacturing and maximize resource utilization, which is crucial for modern manufacturing systems. Traditional methods using Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP) and heuristic algorithms can not well balance solution quality and speed when solving IPPS. In this paper, we propose a novel end-to-end Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) method. We model the IPPS problem as a Markov Decision Process (MDP) and employ a Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (GNN) to capture the complex relationships among operations, machines, and jobs. To optimize the scheduling strategy, we use Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO). Experimental results show that, compared to traditional methods, our approach significantly improves solution efficiency and quality in large-scale IPPS instances, providing superior scheduling strategies for modern intelligent manufacturing systems.
DDC-PIM: Efficient Algorithm/Architecture Co-design for Doubling Data Capacity of SRAM-based Processing-In-Memory
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Processing-in-memory (PIM), as a novel computing paradigm, provides significant performance benefits from the aspect of effective data movement reduction. SRAM-based PIM has been demonstrated as one of the most promising candidates due to its endurance and compatibility. However, the integration density of SRAM-based PIM is much lower than other non-volatile memory-based ones, due to its inherent 6T structure for storing a single bit. Within comparable area constraints, SRAM-based PIM exhibits notably lower capacity. Thus, aiming to unleash its capacity potential, we propose DDC-PIM, an efficient algorithm/architecture co-design methodology that effectively doubles the equivalent data capacity. At the algorithmic level, we propose a filter-wise complementary correlation (FCC) algorithm to obtain a bitwise complementary pair. At the architecture level, we exploit the intrinsic cross-coupled structure of 6T SRAM to store the bitwise complementary pair in their complementary states ($Q/\overline{Q}$), thereby maximizing the data capacity of each SRAM cell. The dual-broadcast input structure and reconfigurable unit support both depthwise and pointwise convolution, adhering to the requirements of various neural networks. Evaluation results show that DDC-PIM yields about $2.84\times$ speedup on MobileNetV2 and $2.69\times$ on EfficientNet-B0 with negligible accuracy loss compared with PIM baseline implementation. Compared with state-of-the-art SRAM-based PIM macros, DDC-PIM achieves up to $8.41\times$ and $2.75\times$ improvement in weight density and area efficiency, respectively.
Inferring Remote Channel State Information: Cramér-Rao Lower Bound and Deep Learning Implementation
Dec 04, 2018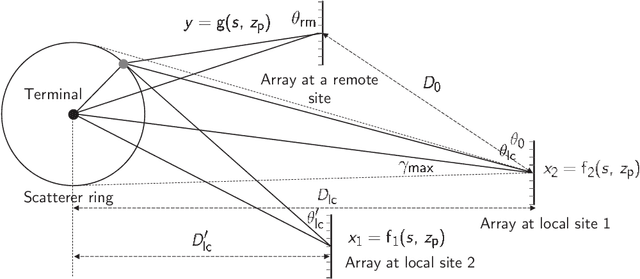
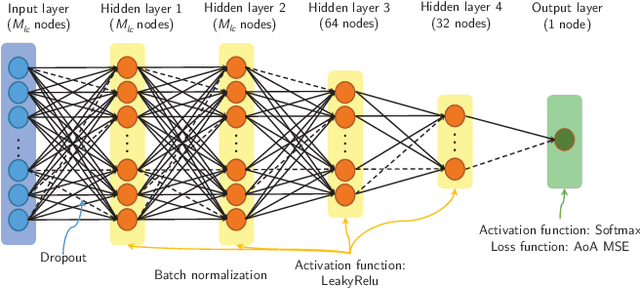
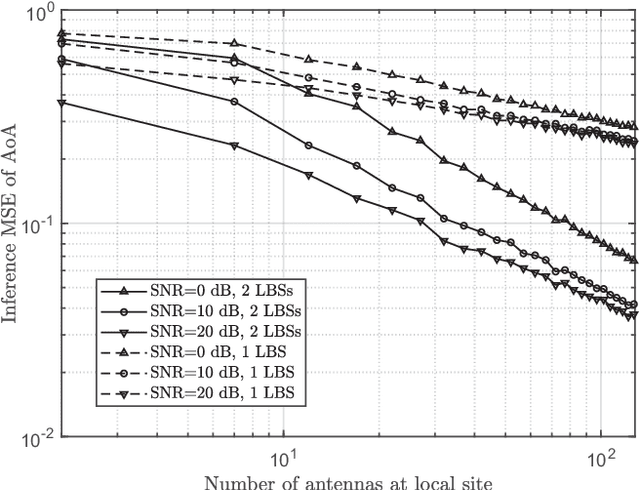
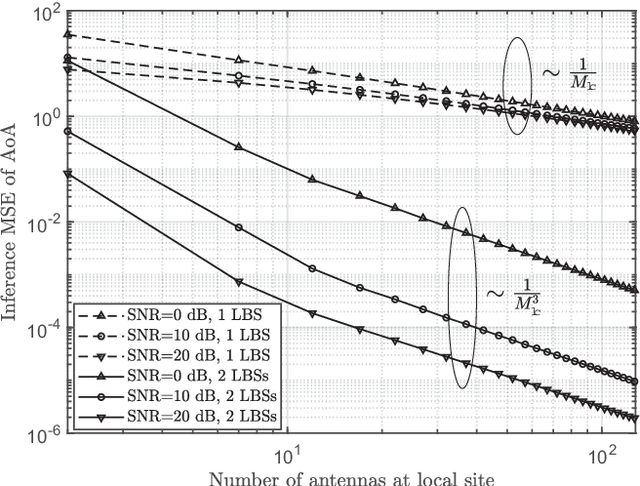
Abstract:Channel state information (CSI) is of vital importance in wireless communication systems. Existing CSI acquisition methods usually rely on pilot transmissions, and geographically separated base stations (BSs) with non-correlated CSI need to be assigned with orthogonal pilots which occupy excessive system resources. Our previous work adopts a data-driven deep learning based approach which leverages the CSI at a local BS to infer the CSI remotely, however the relevance of CSI between separated BSs is not specified explicitly. In this paper, we exploit a model-based methodology to derive the Cram\'er-Rao lower bound (CRLB) of remote CSI inference given the local CSI. Although the model is simplified, the derived CRLB explicitly illustrates the relationship between the inference performance and several key system parameters, e.g., terminal distance and antenna array size. In particular, it shows that by leveraging multiple local BSs, the inference error exhibits a larger power-law decay rate (w.r.t. number of antennas), compared with a single local BS; this explains and validates our findings in evaluating the deep-neural-network-based (DNN-based) CSI inference. We further improve on the DNN-based method by employing dropout and deeper networks, and show an inference performance of approximately $90\%$ accuracy in a realistic scenario with CSI generated by a ray-tracing simulator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge