Zixiu Wang
Towards End-to-End Alignment of User Satisfaction via Questionnaire in Video Recommendation
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Short-video recommender systems typically optimize ranking models using dense user behavioral signals, such as clicks and watch time. However, these signals are only indirect proxies of user satisfaction and often suffer from noise and bias. Recently, explicit satisfaction feedback collected through questionnaires has emerged as a high-quality direct alignment supervision, but is extremely sparse and easily overwhelmed by abundant behavioral data, making it difficult to incorporate into online recommendation models. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework which is towards End-to-End Alignment of user Satisfaction via Questionaire, named EASQ, to enable real-time alignment of ranking models with true user satisfaction. Specifically, we first construct an independent parameter pathway for sparse questionnaire signals by combining a multi-task architecture and a lightweight LoRA module. The multi-task design separates sparse satisfaction supervision from dense behavioral signals, preventing the former from being overwhelmed. The LoRA module pre-inject these preferences in a parameter-isolated manner, ensuring stability in the backbone while optimizing user satisfaction. Furthermore, we employ a DPO-based optimization objective tailored for online learning, which aligns the main model outputs with sparse satisfaction signals in real time. This design enables end-to-end online learning, allowing the model to continuously adapt to new questionnaire feedback while maintaining the stability and effectiveness of the backbone. Extensive offline experiments and large-scale online A/B tests demonstrate that EASQ consistently improves user satisfaction metrics across multiple scenarios. EASQ has been successfully deployed in a production short-video recommendation system, delivering significant and stable business gains.
An End-to-End Multi-objective Ensemble Ranking Framework for Video Recommendation
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel End-to-end Multi-objective Ensemble Ranking framework (EMER) for the multi-objective ensemble ranking module, which is the most critical component of the short video recommendation system. EMER enhances personalization by replacing manually-designed heuristic formulas with an end-to-end modeling paradigm. EMER introduces a meticulously designed loss function to address the fundamental challenge of defining effective supervision for ensemble ranking, where no single ground-truth signal can fully capture user satisfaction. Moreover, EMER introduces novel sample organization method and transformer-based network architecture to capture the comparative relationships among candidates, which are critical for effective ranking. Additionally, we have proposed an offline-online consistent evaluation system to enhance the efficiency of offline model optimization, which is an established yet persistent challenge within the multi-objective ranking domain in industry. Abundant empirical tests are conducted on a real industrial dataset, and the results well demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework. In addition, our framework has been deployed in the primary scenarios of Kuaishou, a short video recommendation platform with hundreds of millions of daily active users, achieving a 1.39% increase in overall App Stay Time and a 0.196% increase in 7-day user Lifetime(LT7), which are substantial improvements.
Randomized Greedy Algorithms and Composable Coreset for k-Center Clustering with Outliers
Jan 07, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of {\em $k$-center clustering with outliers}. The problem has many important applications in real world, but the presence of outliers can significantly increase the computational complexity. Though a number of methods have been developed in the past decades, it is still quite challenging to design quality guaranteed algorithm with low complexity for this problem. Our idea is inspired by the greedy method, Gonzalez's algorithm, that was developed for solving the ordinary $k$-center clustering problem. Based on some novel observations, we show that a simple randomized version of this greedy strategy actually can handle outliers efficiently. We further show that this randomized greedy approach also yields small coreset for the problem in doubling metrics (even if the doubling dimension is not given), which can greatly reduce the computational complexity. Moreover, together with the partial clustering framework proposed in arXiv:1703.01539 , we prove that our coreset method can be applied to distributed data with a low communication complexity. The experimental results suggest that our algorithms can achieve near optimal solutions and yield lower complexities comparing with the existing methods.
Robust Coreset for Continuous-and-Bounded Learning (with Outliers)
Jun 30, 2021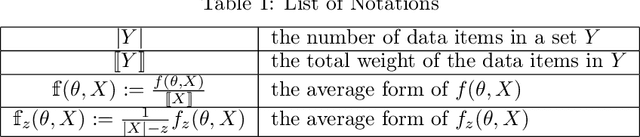



Abstract:In this big data era, we often confront large-scale data in many machine learning tasks. A common approach for dealing with large-scale data is to build a small summary, {\em e.g.,} coreset, that can efficiently represent the original input. However, real-world datasets usually contain outliers and most existing coreset construction methods are not resilient against outliers (in particular, the outliers can be located arbitrarily in the space by an adversarial attacker). In this paper, we propose a novel robust coreset method for the {\em continuous-and-bounded learning} problem (with outliers) which includes a broad range of popular optimization objectives in machine learning, like logistic regression and $ k $-means clustering. Moreover, our robust coreset can be efficiently maintained in fully-dynamic environment. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first robust and fully-dynamic coreset construction method for these optimization problems. We also conduct the experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of our robust coreset in practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge