Zhixuan Li
UGD-IML: A Unified Generative Diffusion-based Framework for Constrained and Unconstrained Image Manipulation Localization
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:In the digital age, advanced image editing tools pose a serious threat to the integrity of visual content, making image forgery detection and localization a key research focus. Most existing Image Manipulation Localization (IML) methods rely on discriminative learning and require large, high-quality annotated datasets. However, current datasets lack sufficient scale and diversity, limiting model performance in real-world scenarios. To overcome this, recent studies have explored Constrained IML (CIML), which generates pixel-level annotations through algorithmic supervision. However, existing CIML approaches often depend on complex multi-stage pipelines, making the annotation process inefficient. In this work, we propose a novel generative framework based on diffusion models, named UGD-IML, which for the first time unifies both IML and CIML tasks within a single framework. By learning the underlying data distribution, generative diffusion models inherently reduce the reliance on large-scale labeled datasets, allowing our approach to perform effectively even under limited data conditions. In addition, by leveraging a class embedding mechanism and a parameter-sharing design, our model seamlessly switches between IML and CIML modes without extra components or training overhead. Furthermore, the end-to-end design enables our model to avoid cumbersome steps in the data annotation process. Extensive experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate that UGD-IML outperforms the SOTA methods by an average of 9.66 and 4.36 in terms of F1 metrics for IML and CIML tasks, respectively. Moreover, the proposed method also excels in uncertainty estimation, visualization and robustness.
Unveiling the Invisible: Reasoning Complex Occlusions Amodally with AURA
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Amodal segmentation aims to infer the complete shape of occluded objects, even when the occluded region's appearance is unavailable. However, current amodal segmentation methods lack the capability to interact with users through text input and struggle to understand or reason about implicit and complex purposes. While methods like LISA integrate multi-modal large language models (LLMs) with segmentation for reasoning tasks, they are limited to predicting only visible object regions and face challenges in handling complex occlusion scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a novel task named amodal reasoning segmentation, aiming to predict the complete amodal shape of occluded objects while providing answers with elaborations based on user text input. We develop a generalizable dataset generation pipeline and introduce a new dataset focusing on daily life scenarios, encompassing diverse real-world occlusions. Furthermore, we present AURA (Amodal Understanding and Reasoning Assistant), a novel model with advanced global and spatial-level designs specifically tailored to handle complex occlusions. Extensive experiments validate AURA's effectiveness on the proposed dataset. The code, model, and dataset will be publicly released.
BEAT: Balanced Frequency Adaptive Tuning for Long-Term Time-Series Forecasting
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Time-series forecasting is crucial for numerous real-world applications including weather prediction and financial market modeling. While temporal-domain methods remain prevalent, frequency-domain approaches can effectively capture multi-scale periodic patterns, reduce sequence dependencies, and naturally denoise signals. However, existing approaches typically train model components for all frequencies under a unified training objective, often leading to mismatched learning speeds: high-frequency components converge faster and risk overfitting, while low-frequency components underfit due to insufficient training time. To deal with this challenge, we propose BEAT (Balanced frEquency Adaptive Tuning), a novel framework that dynamically monitors the training status for each frequency and adaptively adjusts their gradient updates. By recognizing convergence, overfitting, or underfitting for each frequency, BEAT dynamically reallocates learning priorities, moderating gradients for rapid learners and increasing those for slower ones, alleviating the tension between competing objectives across frequencies and synchronizing the overall learning process. Extensive experiments on seven real-world datasets demonstrate that BEAT consistently outperforms state-of-the-art approaches.
BLADE: Box-Level Supervised Amodal Segmentation through Directed Expansion
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:Perceiving the complete shape of occluded objects is essential for human and machine intelligence. While the amodal segmentation task is to predict the complete mask of partially occluded objects, it is time-consuming and labor-intensive to annotate the pixel-level ground truth amodal masks. Box-level supervised amodal segmentation addresses this challenge by relying solely on ground truth bounding boxes and instance classes as supervision, thereby alleviating the need for exhaustive pixel-level annotations. Nevertheless, current box-level methodologies encounter limitations in generating low-resolution masks and imprecise boundaries, failing to meet the demands of practical real-world applications. We present a novel solution to tackle this problem by introducing a directed expansion approach from visible masks to corresponding amodal masks. Our approach involves a hybrid end-to-end network based on the overlapping region - the area where different instances intersect. Diverse segmentation strategies are applied for overlapping regions and non-overlapping regions according to distinct characteristics. To guide the expansion of visible masks, we introduce an elaborately-designed connectivity loss for overlapping regions, which leverages correlations with visible masks and facilitates accurate amodal segmentation. Experiments are conducted on several challenging datasets and the results show that our proposed method can outperform existing state-of-the-art methods with large margins.
Human Perception-based Evaluation Criterion for Ultra-high Resolution Cell Membrane Segmentation
Oct 16, 2020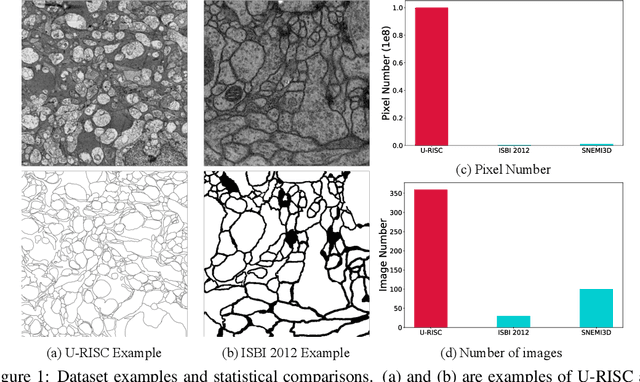

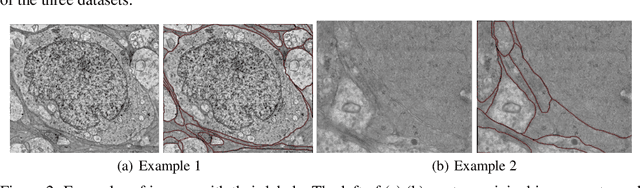
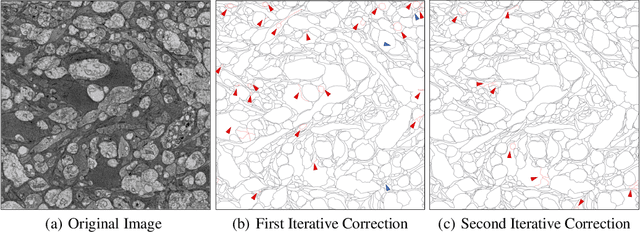
Abstract:Computer vision technology is widely used in biological and medical data analysis and understanding. However, there are still two major bottlenecks in the field of cell membrane segmentation, which seriously hinder further research: lack of sufficient high-quality data and lack of suitable evaluation criteria. In order to solve these two problems, this paper first proposes an Ultra-high Resolution Image Segmentation dataset for the Cell membrane, called U-RISC, the largest annotated Electron Microscopy (EM) dataset for the Cell membrane with multiple iterative annotations and uncompressed high-resolution raw data. During the analysis process of the U-RISC, we found that the current popular segmentation evaluation criteria are inconsistent with human perception. This interesting phenomenon is confirmed by a subjective experiment involving twenty people. Furthermore, to resolve this inconsistency, we propose a new evaluation criterion called Perceptual Hausdorff Distance (PHD) to measure the quality of cell membrane segmentation results. Detailed performance comparison and discussion of classic segmentation methods along with two iterative manual annotation results under existing evaluation criteria and PHD is given.
Robust Medical Instrument Segmentation Challenge 2019
Mar 23, 2020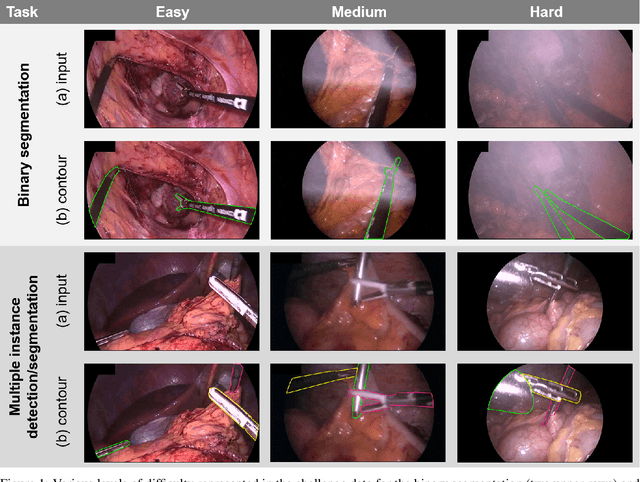
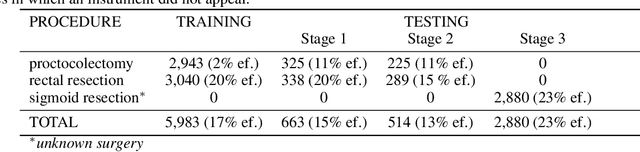
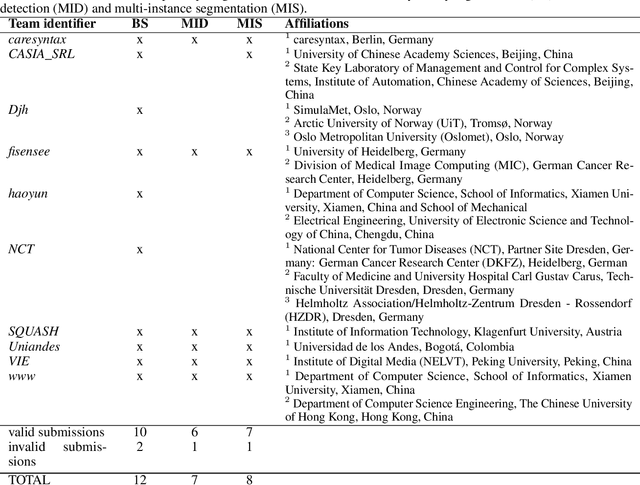
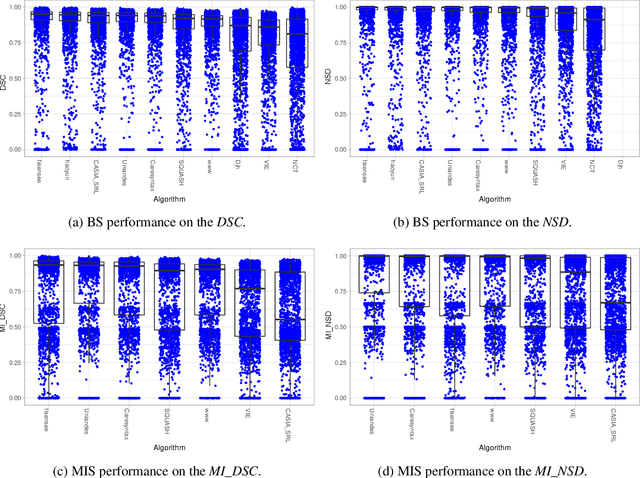
Abstract:Intraoperative tracking of laparoscopic instruments is often a prerequisite for computer and robotic-assisted interventions. While numerous methods for detecting, segmenting and tracking of medical instruments based on endoscopic video images have been proposed in the literature, key limitations remain to be addressed: Firstly, robustness, that is, the reliable performance of state-of-the-art methods when run on challenging images (e.g. in the presence of blood, smoke or motion artifacts). Secondly, generalization; algorithms trained for a specific intervention in a specific hospital should generalize to other interventions or institutions. In an effort to promote solutions for these limitations, we organized the Robust Medical Instrument Segmentation (ROBUST-MIS) challenge as an international benchmarking competition with a specific focus on the robustness and generalization capabilities of algorithms. For the first time in the field of endoscopic image processing, our challenge included a task on binary segmentation and also addressed multi-instance detection and segmentation. The challenge was based on a surgical data set comprising 10,040 annotated images acquired from a total of 30 surgical procedures from three different types of surgery. The validation of the competing methods for the three tasks (binary segmentation, multi-instance detection and multi-instance segmentation) was performed in three different stages with an increasing domain gap between the training and the test data. The results confirm the initial hypothesis, namely that algorithm performance degrades with an increasing domain gap. While the average detection and segmentation quality of the best-performing algorithms is high, future research should concentrate on detection and segmentation of small, crossing, moving and transparent instrument(s) (parts).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge