Zhaochen Liu
Beyond the Visible: Benchmarking Occlusion Perception in Multimodal Large Language Models
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Occlusion perception, a critical foundation for human-level spatial understanding, embodies the challenge of integrating visual recognition and reasoning. Though multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, their performance on occlusion perception remains under-explored. To address this gap, we introduce O-Bench, the first visual question answering (VQA) benchmark specifically designed for occlusion perception. Based on SA-1B, we construct 1,365 images featuring semantically coherent occlusion scenarios through a novel layered synthesis approach. Upon this foundation, we annotate 4,588 question-answer pairs in total across five tailored tasks, employing a reliable, semi-automatic workflow. Our extensive evaluation of 22 representative MLLMs against the human baseline reveals a significant performance gap between current MLLMs and humans, which, we find, cannot be sufficiently bridged by model scaling or thinking process. We further identify three typical failure patterns, including an overly conservative bias, a fragile gestalt prediction, and a struggle with quantitative tasks. We believe O-Bench can not only provide a vital evaluation tool for occlusion perception, but also inspire the development of MLLMs for better visual intelligence. Our benchmark will be made publicly available upon paper publication.
Amodal Segmentation for Laparoscopic Surgery Video Instruments
Aug 02, 2024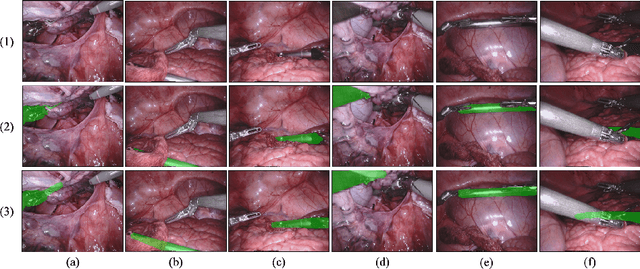
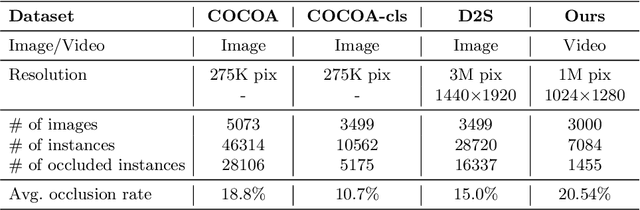
Abstract:Segmentation of surgical instruments is crucial for enhancing surgeon performance and ensuring patient safety. Conventional techniques such as binary, semantic, and instance segmentation share a common drawback: they do not accommodate the parts of instruments obscured by tissues or other instruments. Precisely predicting the full extent of these occluded instruments can significantly improve laparoscopic surgeries by providing critical guidance during operations and assisting in the analysis of potential surgical errors, as well as serving educational purposes. In this paper, we introduce Amodal Segmentation to the realm of surgical instruments in the medical field. This technique identifies both the visible and occluded parts of an object. To achieve this, we introduce a new Amoal Instruments Segmentation (AIS) dataset, which was developed by reannotating each instrument with its complete mask, utilizing the 2017 MICCAI EndoVis Robotic Instrument Segmentation Challenge dataset. Additionally, we evaluate several leading amodal segmentation methods to establish a benchmark for this new dataset.
PLUG: Revisiting Amodal Segmentation with Foundation Model and Hierarchical Focus
May 25, 2024



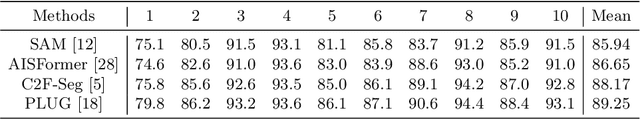
Abstract:Aiming to predict the complete shapes of partially occluded objects, amodal segmentation is an important step towards visual intelligence. With crucial significance, practical prior knowledge derives from sufficient training, while limited amodal annotations pose challenges to achieve better performance. To tackle this problem, utilizing the mighty priors accumulated in the foundation model, we propose the first SAM-based amodal segmentation approach, PLUG. Methodologically, a novel framework with hierarchical focus is presented to better adapt the task characteristics and unleash the potential capabilities of SAM. In the region level, due to the association and division in visible and occluded areas, inmodal and amodal regions are assigned as the focuses of distinct branches to avoid mutual disturbance. In the point level, we introduce the concept of uncertainty to explicitly assist the model in identifying and focusing on ambiguous points. Guided by the uncertainty map, a computation-economic point loss is applied to improve the accuracy of predicted boundaries. Experiments are conducted on several prominent datasets, and the results show that our proposed method outperforms existing methods with large margins. Even with fewer total parameters, our method still exhibits remarkable advantages.
BLADE: Box-Level Supervised Amodal Segmentation through Directed Expansion
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:Perceiving the complete shape of occluded objects is essential for human and machine intelligence. While the amodal segmentation task is to predict the complete mask of partially occluded objects, it is time-consuming and labor-intensive to annotate the pixel-level ground truth amodal masks. Box-level supervised amodal segmentation addresses this challenge by relying solely on ground truth bounding boxes and instance classes as supervision, thereby alleviating the need for exhaustive pixel-level annotations. Nevertheless, current box-level methodologies encounter limitations in generating low-resolution masks and imprecise boundaries, failing to meet the demands of practical real-world applications. We present a novel solution to tackle this problem by introducing a directed expansion approach from visible masks to corresponding amodal masks. Our approach involves a hybrid end-to-end network based on the overlapping region - the area where different instances intersect. Diverse segmentation strategies are applied for overlapping regions and non-overlapping regions according to distinct characteristics. To guide the expansion of visible masks, we introduce an elaborately-designed connectivity loss for overlapping regions, which leverages correlations with visible masks and facilitates accurate amodal segmentation. Experiments are conducted on several challenging datasets and the results show that our proposed method can outperform existing state-of-the-art methods with large margins.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge