Zhengkun Rong
DreamActor-M2: Universal Character Image Animation via Spatiotemporal In-Context Learning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Character image animation aims to synthesize high-fidelity videos by transferring motion from a driving sequence to a static reference image. Despite recent advancements, existing methods suffer from two fundamental challenges: (1) suboptimal motion injection strategies that lead to a trade-off between identity preservation and motion consistency, manifesting as a "see-saw", and (2) an over-reliance on explicit pose priors (e.g., skeletons), which inadequately capture intricate dynamics and hinder generalization to arbitrary, non-humanoid characters. To address these challenges, we present DreamActor-M2, a universal animation framework that reimagines motion conditioning as an in-context learning problem. Our approach follows a two-stage paradigm. First, we bridge the input modality gap by fusing reference appearance and motion cues into a unified latent space, enabling the model to jointly reason about spatial identity and temporal dynamics by leveraging the generative prior of foundational models. Second, we introduce a self-bootstrapped data synthesis pipeline that curates pseudo cross-identity training pairs, facilitating a seamless transition from pose-dependent control to direct, end-to-end RGB-driven animation. This strategy significantly enhances generalization across diverse characters and motion scenarios. To facilitate comprehensive evaluation, we further introduce AW Bench, a versatile benchmark encompassing a wide spectrum of characters types and motion scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DreamActor-M2 achieves state-of-the-art performance, delivering superior visual fidelity and robust cross-domain generalization. Project Page: https://grisoon.github.io/DreamActor-M2/
DreamActor-M1: Holistic, Expressive and Robust Human Image Animation with Hybrid Guidance
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:While recent image-based human animation methods achieve realistic body and facial motion synthesis, critical gaps remain in fine-grained holistic controllability, multi-scale adaptability, and long-term temporal coherence, which leads to their lower expressiveness and robustness. We propose a diffusion transformer (DiT) based framework, DreamActor-M1, with hybrid guidance to overcome these limitations. For motion guidance, our hybrid control signals that integrate implicit facial representations, 3D head spheres, and 3D body skeletons achieve robust control of facial expressions and body movements, while producing expressive and identity-preserving animations. For scale adaptation, to handle various body poses and image scales ranging from portraits to full-body views, we employ a progressive training strategy using data with varying resolutions and scales. For appearance guidance, we integrate motion patterns from sequential frames with complementary visual references, ensuring long-term temporal coherence for unseen regions during complex movements. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art works, delivering expressive results for portraits, upper-body, and full-body generation with robust long-term consistency. Project Page: https://grisoon.github.io/DreamActor-M1/.
INFP: Audio-Driven Interactive Head Generation in Dyadic Conversations
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Imagine having a conversation with a socially intelligent agent. It can attentively listen to your words and offer visual and linguistic feedback promptly. This seamless interaction allows for multiple rounds of conversation to flow smoothly and naturally. In pursuit of actualizing it, we propose INFP, a novel audio-driven head generation framework for dyadic interaction. Unlike previous head generation works that only focus on single-sided communication, or require manual role assignment and explicit role switching, our model drives the agent portrait dynamically alternates between speaking and listening state, guided by the input dyadic audio. Specifically, INFP comprises a Motion-Based Head Imitation stage and an Audio-Guided Motion Generation stage. The first stage learns to project facial communicative behaviors from real-life conversation videos into a low-dimensional motion latent space, and use the motion latent codes to animate a static image. The second stage learns the mapping from the input dyadic audio to motion latent codes through denoising, leading to the audio-driven head generation in interactive scenarios. To facilitate this line of research, we introduce DyConv, a large scale dataset of rich dyadic conversations collected from the Internet. Extensive experiments and visualizations demonstrate superior performance and effectiveness of our method. Project Page: https://grisoon.github.io/INFP/.
MobilePortrait: Real-Time One-Shot Neural Head Avatars on Mobile Devices
Jul 08, 2024
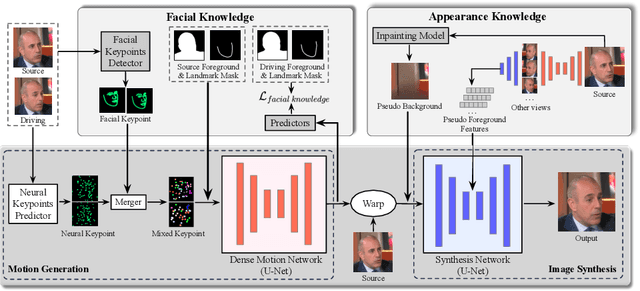


Abstract:Existing neural head avatars methods have achieved significant progress in the image quality and motion range of portrait animation. However, these methods neglect the computational overhead, and to the best of our knowledge, none is designed to run on mobile devices. This paper presents MobilePortrait, a lightweight one-shot neural head avatars method that reduces learning complexity by integrating external knowledge into both the motion modeling and image synthesis, enabling real-time inference on mobile devices. Specifically, we introduce a mixed representation of explicit and implicit keypoints for precise motion modeling and precomputed visual features for enhanced foreground and background synthesis. With these two key designs and using simple U-Nets as backbones, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance with less than one-tenth the computational demand. It has been validated to reach speeds of over 100 FPS on mobile devices and support both video and audio-driven inputs.
Superior and Pragmatic Talking Face Generation with Teacher-Student Framework
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:Talking face generation technology creates talking videos from arbitrary appearance and motion signal, with the "arbitrary" offering ease of use but also introducing challenges in practical applications. Existing methods work well with standard inputs but suffer serious performance degradation with intricate real-world ones. Moreover, efficiency is also an important concern in deployment. To comprehensively address these issues, we introduce SuperFace, a teacher-student framework that balances quality, robustness, cost and editability. We first propose a simple but effective teacher model capable of handling inputs of varying qualities to generate high-quality results. Building on this, we devise an efficient distillation strategy to acquire an identity-specific student model that maintains quality with significantly reduced computational load. Our experiments validate that SuperFace offers a more comprehensive solution than existing methods for the four mentioned objectives, especially in reducing FLOPs by 99\% with the student model. SuperFace can be driven by both video and audio and allows for localized facial attributes editing.
DUT-LFSaliency: Versatile Dataset and Light Field-to-RGB Saliency Detection
Dec 30, 2020

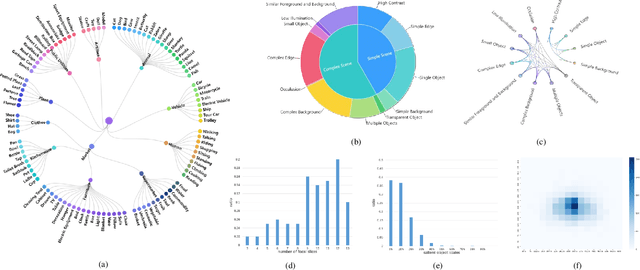

Abstract:Light field data exhibit favorable characteristics conducive to saliency detection. The success of learning-based light field saliency detection is heavily dependent on how a comprehensive dataset can be constructed for higher generalizability of models, how high dimensional light field data can be effectively exploited, and how a flexible model can be designed to achieve versatility for desktop computers and mobile devices. To answer these questions, first we introduce a large-scale dataset to enable versatile applications for RGB, RGB-D and light field saliency detection, containing 102 classes and 4204 samples. Second, we present an asymmetrical two-stream model consisting of the Focal stream and RGB stream. The Focal stream is designed to achieve higher performance on desktop computers and transfer focusness knowledge to the RGB stream, relying on two tailor-made modules. The RGB stream guarantees the flexibility and memory/computation efficiency on mobile devices through three distillation schemes. Experiments demonstrate that our Focal stream achieves state-of-the-arts performance. The RGB stream achieves Top-2 F-measure on DUTLF-V2, which tremendously minimizes the model size by 83% and boosts FPS by 5 times, compared with the best performing method. Furthermore, our proposed distillation schemes are applicable to RGB saliency models, achieving impressive performance gains while ensuring flexibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge