Zheng You
ASM-UNet: Adaptive Scan Mamba Integrating Group Commonalities and Individual Variations for Fine-Grained Segmentation
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Precise lesion resection depends on accurately identifying fine-grained anatomical structures. While many coarse-grained segmentation (CGS) methods have been successful in large-scale segmentation (e.g., organs), they fall short in clinical scenarios requiring fine-grained segmentation (FGS), which remains challenging due to frequent individual variations in small-scale anatomical structures. Although recent Mamba-based models have advanced medical image segmentation, they often rely on fixed manually-defined scanning orders, which limit their adaptability to individual variations in FGS. To address this, we propose ASM-UNet, a novel Mamba-based architecture for FGS. It introduces adaptive scan scores to dynamically guide the scanning order, generated by combining group-level commonalities and individual-level variations. Experiments on two public datasets (ACDC and Synapse) and a newly proposed challenging biliary tract FGS dataset, namely BTMS, demonstrate that ASM-UNet achieves superior performance in both CGS and FGS tasks. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/YqunYang/ASM-UNet.
Onfocus Detection: Identifying Individual-Camera Eye Contact from Unconstrained Images
Mar 29, 2021Abstract:Onfocus detection aims at identifying whether the focus of the individual captured by a camera is on the camera or not. Based on the behavioral research, the focus of an individual during face-to-camera communication leads to a special type of eye contact, i.e., the individual-camera eye contact, which is a powerful signal in social communication and plays a crucial role in recognizing irregular individual status (e.g., lying or suffering mental disease) and special purposes (e.g., seeking help or attracting fans). Thus, developing effective onfocus detection algorithms is of significance for assisting the criminal investigation, disease discovery, and social behavior analysis. However, the review of the literature shows that very few efforts have been made toward the development of onfocus detector due to the lack of large-scale public available datasets as well as the challenging nature of this task. To this end, this paper engages in the onfocus detection research by addressing the above two issues. Firstly, we build a large-scale onfocus detection dataset, named as the OnFocus Detection In the Wild (OFDIW). It consists of 20,623 images in unconstrained capture conditions (thus called ``in the wild'') and contains individuals with diverse emotions, ages, facial characteristics, and rich interactions with surrounding objects and background scenes. On top of that, we propose a novel end-to-end deep model, i.e., the eye-context interaction inferring network (ECIIN), for onfocus detection, which explores eye-context interaction via dynamic capsule routing. Finally, comprehensive experiments are conducted on the proposed OFDIW dataset to benchmark the existing learning models and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed ECIIN. The project (containing both datasets and codes) is at https://github.com/wintercho/focus.
COVID-19 Chest CT Image Segmentation -- A Deep Convolutional Neural Network Solution
Apr 26, 2020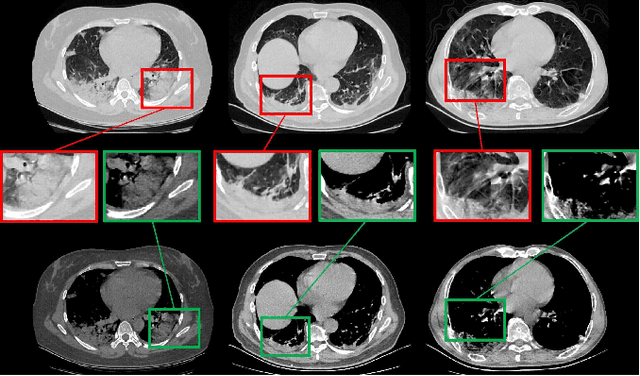
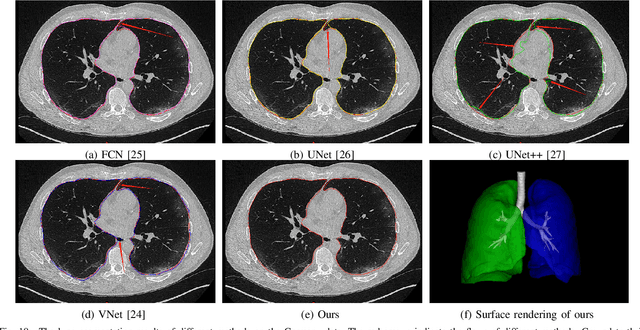
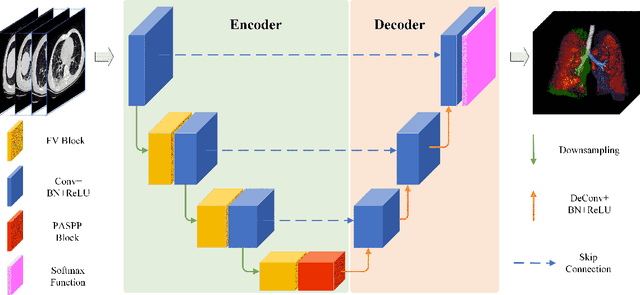
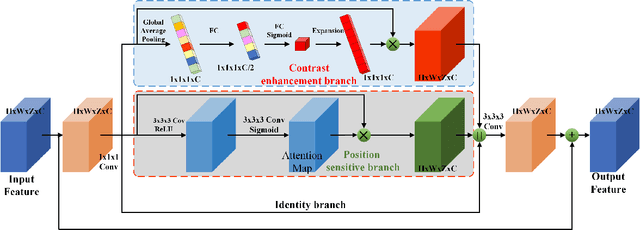
Abstract:A novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was detected and has spread rapidly across various countries around the world since the end of the year 2019, Computed Tomography (CT) images have been used as a crucial alternative to the time-consuming RT-PCR test. However, pure manual segmentation of CT images faces a serious challenge with the increase of suspected cases, resulting in urgent requirements for accurate and automatic segmentation of COVID-19 infections. Unfortunately, since the imaging characteristics of the COVID-19 infection are diverse and similar to the backgrounds, existing medical image segmentation methods cannot achieve satisfactory performance. In this work, we try to establish a new deep convolutional neural network tailored for segmenting the chest CT images with COVID-19 infections. We firstly maintain a large and new chest CT image dataset consisting of 165,667 annotated chest CT images from 861 patients with confirmed COVID-19. Inspired by the observation that the boundary of the infected lung can be enhanced by adjusting the global intensity, in the proposed deep CNN, we introduce a feature variation block which adaptively adjusts the global properties of the features for segmenting COVID-19 infection. The proposed FV block can enhance the capability of feature representation effectively and adaptively for diverse cases. We fuse features at different scales by proposing Progressive Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling to handle the sophisticated infection areas with diverse appearance and shapes. We conducted experiments on the data collected in China and Germany and show that the proposed deep CNN can produce impressive performance effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge