Zhe Gao
Pathwise Test-Time Correction for Autoregressive Long Video Generation
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Distilled autoregressive diffusion models facilitate real-time short video synthesis but suffer from severe error accumulation during long-sequence generation. While existing Test-Time Optimization (TTO) methods prove effective for images or short clips, we identify that they fail to mitigate drift in extended sequences due to unstable reward landscapes and the hypersensitivity of distilled parameters. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Test-Time Correction (TTC), a training-free alternative. Specifically, TTC utilizes the initial frame as a stable reference anchor to calibrate intermediate stochastic states along the sampling trajectory. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method seamlessly integrates with various distilled models, extending generation lengths with negligible overhead while matching the quality of resource-intensive training-based methods on 30-second benchmarks.
FusionMAE: large-scale pretrained model to optimize and simplify diagnostic and control of fusion plasma
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:In magnetically confined fusion device, the complex, multiscale, and nonlinear dynamics of plasmas necessitate the integration of extensive diagnostic systems to effectively monitor and control plasma behaviour. The complexity and uncertainty arising from these extensive systems and their tangled interrelations has long posed a significant obstacle to the acceleration of fusion energy development. In this work, a large-scale model, fusion masked auto-encoder (FusionMAE) is pre-trained to compress the information from 88 diagnostic signals into a concrete embedding, to provide a unified interface between diagnostic systems and control actuators. Two mechanisms are proposed to ensure a meaningful embedding: compression-reduction and missing-signal reconstruction. Upon completion of pre-training, the model acquires the capability for 'virtual backup diagnosis', enabling the inference of missing diagnostic data with 96.7% reliability. Furthermore, the model demonstrates three emergent capabilities: automatic data analysis, universal control-diagnosis interface, and enhancement of control performance on multiple tasks. This work pioneers large-scale AI model integration in fusion energy, demonstrating how pre-trained embeddings can simplify the system interface, reducing necessary diagnostic systems and optimize operation performance for future fusion reactors.
DeepSuM: Deep Sufficient Modality Learning Framework
Mar 03, 2025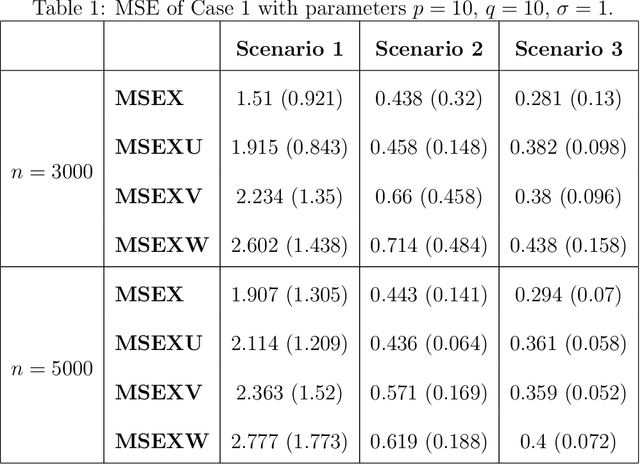
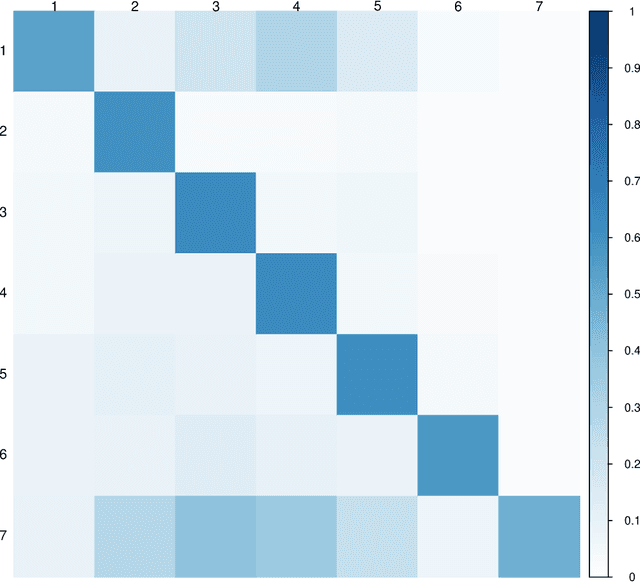
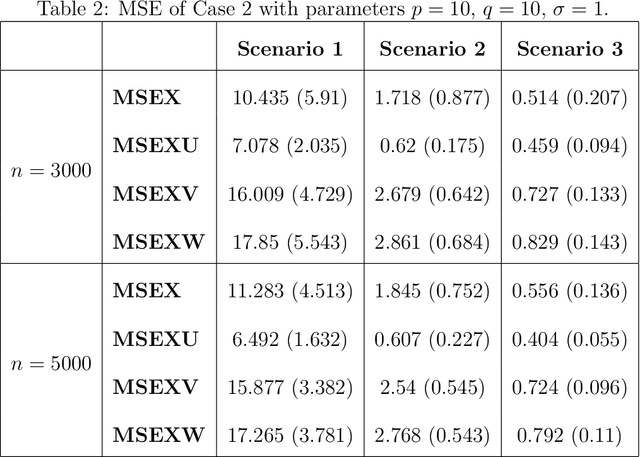
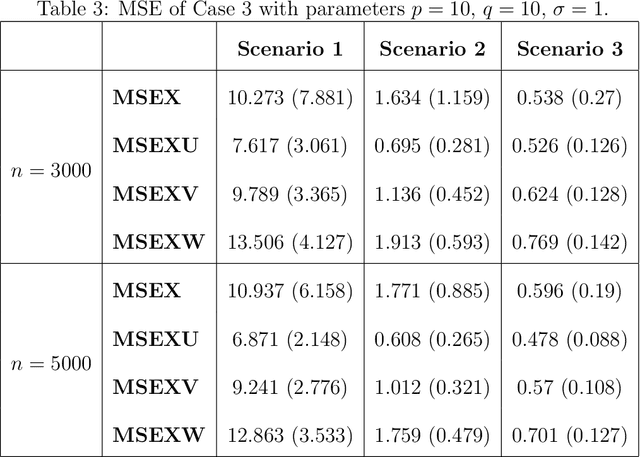
Abstract:Multimodal learning has become a pivotal approach in developing robust learning models with applications spanning multimedia, robotics, large language models, and healthcare. The efficiency of multimodal systems is a critical concern, given the varying costs and resource demands of different modalities. This underscores the necessity for effective modality selection to balance performance gains against resource expenditures. In this study, we propose a novel framework for modality selection that independently learns the representation of each modality. This approach allows for the assessment of each modality's significance within its unique representation space, enabling the development of tailored encoders and facilitating the joint analysis of modalities with distinct characteristics. Our framework aims to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of multimodal learning by optimizing modality integration and selection.
C$^3$DG: Conditional Domain Generalization for Hyperspectral Imagery Classification with Convergence and Constrained-risk Theories
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Hyperspectral imagery (HSI) classification may suffer the challenge of hyperspectral-monospectra, where different classes present similar spectra. Joint spatial-spectral feature extraction is a popular solution for the problem, but this strategy tends to inflate accuracy since test pixels may exist in training patches. Domain generalization methods show promising potential, but they still fail to distinguish similar spectra across varying domains, in addition, the theoretical support is usually ignored. In this paper, we only rely on spectral information to solve the hyperspectral-monospectra problem, and propose a Convergence and Error-Constrained Conditional Domain Generalization method for Hyperspectral Imagery Classification (C$^3$DG). The major contributions of this paper include two aspects: the Conditional Revising Inference Block (CRIB), and the corresponding theories for model convergence and generalization errors. CRIB is the kernel structure of the proposed method, which employs a shared encoder and multi-branch decoders to fully leverage the conditional distribution during training, achieving a decoupling that aligns with the generation mechanisms of HSI. Moreover, to ensure model convergence and maintain controllable error, we propose the optimization convergence theorem and risk upper bound theorem. In the optimization convergence theorem, we ensure the model convergence by demonstrating that the gradients of the loss terms are not contradictory. In the risk upper bound theorem, our theoretical analysis explores the relationship between test-time training and recent related work to establish a concrete bound for error. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets indicate the superiority of C$^3$DG.
Time to Transfer: Predicting and Evaluating Machine-Human Chatting Handoff
Dec 14, 2020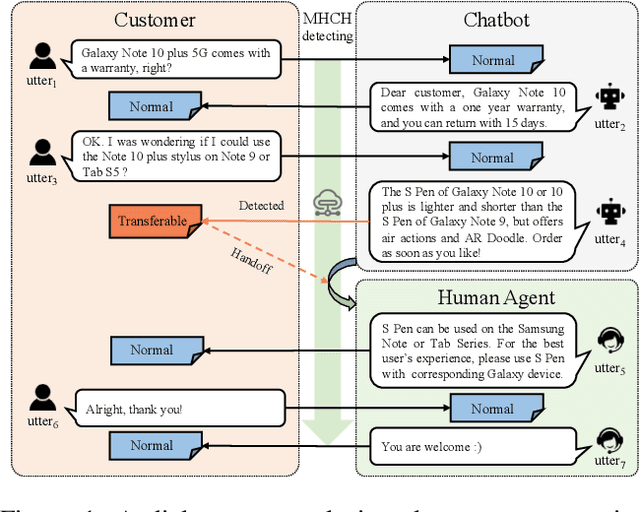
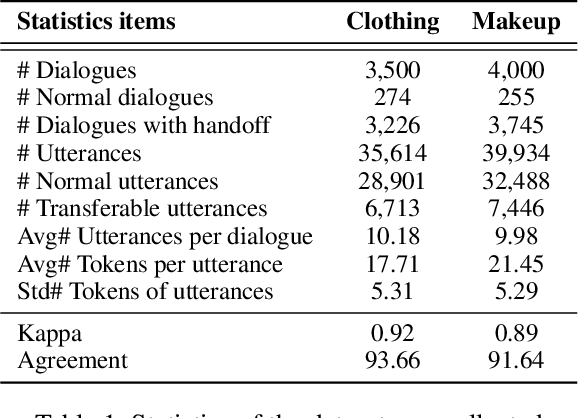

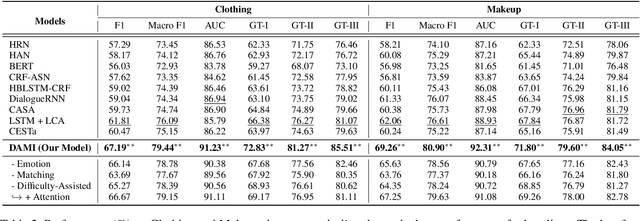
Abstract:Is chatbot able to completely replace the human agent? The short answer could be - "it depends...". For some challenging cases, e.g., dialogue's topical spectrum spreads beyond the training corpus coverage, the chatbot may malfunction and return unsatisfied utterances. This problem can be addressed by introducing the Machine-Human Chatting Handoff (MHCH), which enables human-algorithm collaboration. To detect the normal/transferable utterances, we propose a Difficulty-Assisted Matching Inference (DAMI) network, utilizing difficulty-assisted encoding to enhance the representations of utterances. Moreover, a matching inference mechanism is introduced to capture the contextual matching features. A new evaluation metric, Golden Transfer within Tolerance (GT-T), is proposed to assess the performance by considering the tolerance property of the MHCH. To provide insights into the task and validate the proposed model, we collect two new datasets. Extensive experimental results are presented and contrasted against a series of baseline models to demonstrate the efficacy of our model on MHCH.
Read Beyond the Lines: Understanding the Implied Textual Meaning via a Skim and Intensive Reading Model
Jan 16, 2020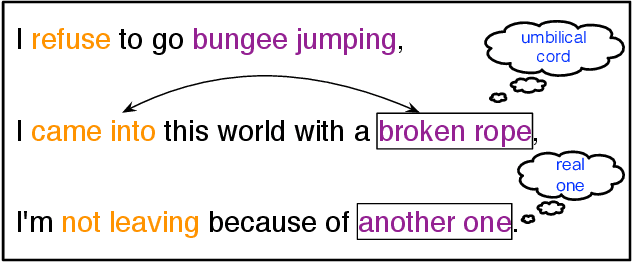
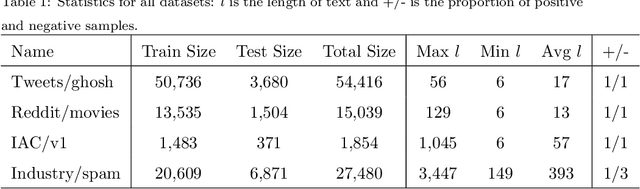
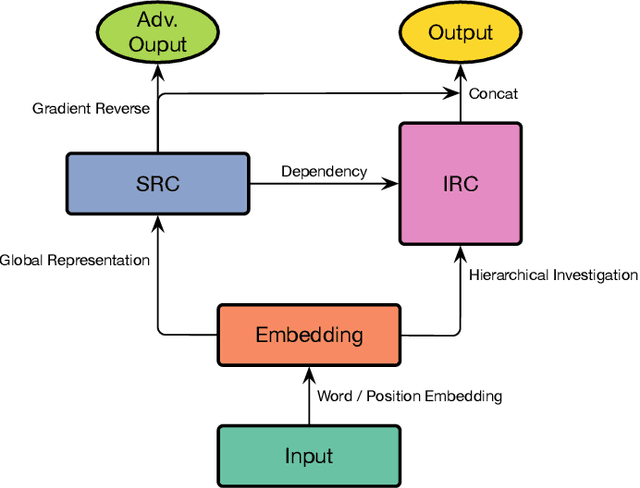
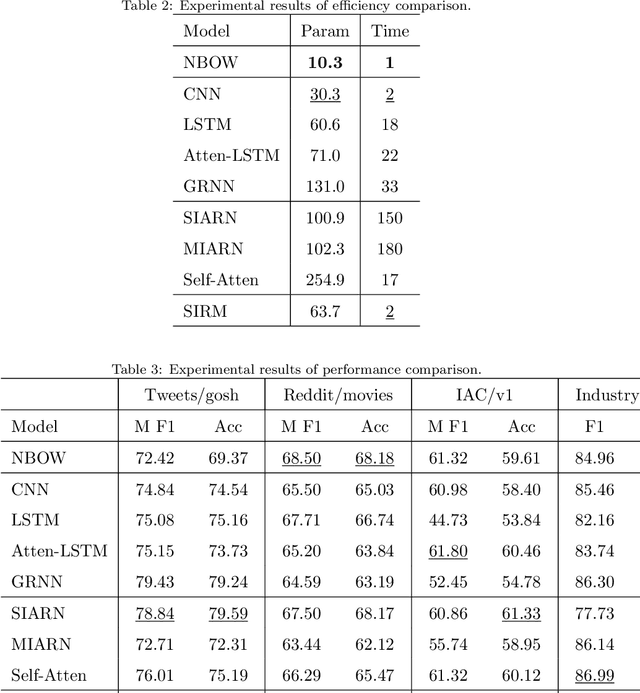
Abstract:The nonliteral interpretation of a text is hard to be understood by machine models due to its high context-sensitivity and heavy usage of figurative language. In this study, inspired by human reading comprehension, we propose a novel, simple, and effective deep neural framework, called Skim and Intensive Reading Model (SIRM), for figuring out implied textual meaning. The proposed SIRM consists of two main components, namely the skim reading component and intensive reading component. N-gram features are quickly extracted from the skim reading component, which is a combination of several convolutional neural networks, as skim (entire) information. An intensive reading component enables a hierarchical investigation for both local (sentence) and global (paragraph) representation, which encapsulates the current embedding and the contextual information with a dense connection. More specifically, the contextual information includes the near-neighbor information and the skim information mentioned above. Finally, besides the normal training loss function, we employ an adversarial loss function as a penalty over the skim reading component to eliminate noisy information arisen from special figurative words in the training data. To verify the effectiveness, robustness, and efficiency of the proposed architecture, we conduct extensive comparative experiments on several sarcasm benchmarks and an industrial spam dataset with metaphors. Experimental results indicate that (1) the proposed model, which benefits from context modeling and consideration of figurative language, outperforms existing state-of-the-art solutions, with comparable parameter scale and training speed; (2) the SIRM yields superior robustness in terms of parameter size sensitivity; (3) compared with ablation and addition variants of the SIRM, the final framework is efficient enough.
Detect Camouflaged Spam Content via StoneSkipping: Graph and Text Joint Embedding for Chinese Character Variation Representation
Aug 30, 2019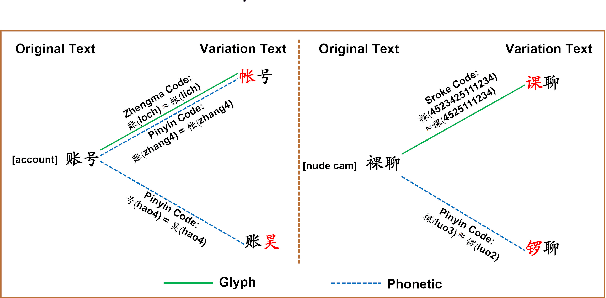
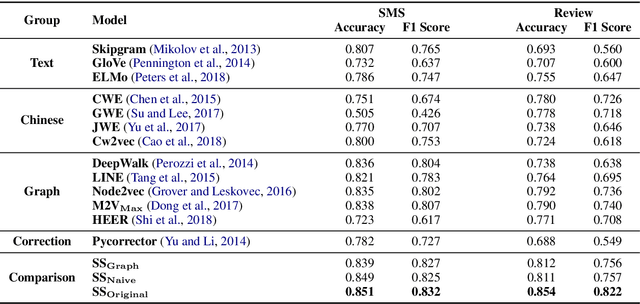
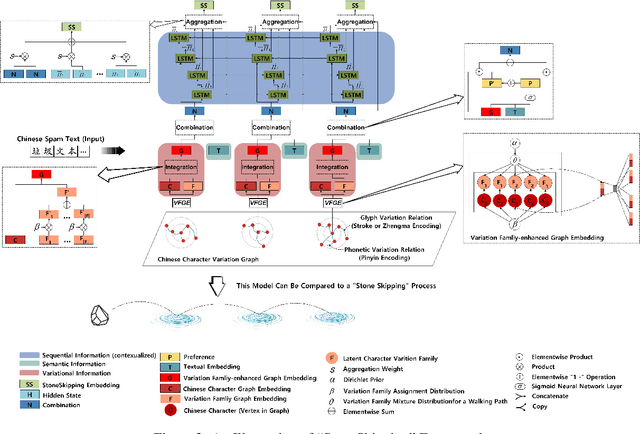
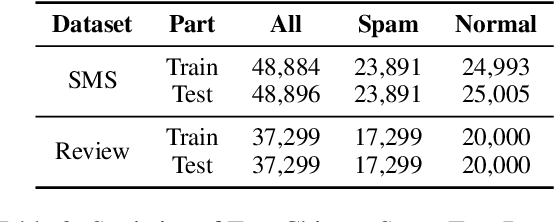
Abstract:The task of Chinese text spam detection is very challenging due to both glyph and phonetic variations of Chinese characters. This paper proposes a novel framework to jointly model Chinese variational, semantic, and contextualized representations for Chinese text spam detection task. In particular, a Variation Family-enhanced Graph Embedding (VFGE) algorithm is designed based on a Chinese character variation graph. The VFGE can learn both the graph embeddings of the Chinese characters (local) and the latent variation families (global). Furthermore, an enhanced bidirectional language model, with a combination gate function and an aggregation learning function, is proposed to integrate the graph and text information while capturing the sequential information. Extensive experiments have been conducted on both SMS and review datasets, to show the proposed method outperforms a series of state-of-the-art models for Chinese spam detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge