Zeyu Song
RecGOAT: Graph Optimal Adaptive Transport for LLM-Enhanced Multimodal Recommendation with Dual Semantic Alignment
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Multimodal recommendation systems typically integrates user behavior with multimodal data from items, thereby capturing more accurate user preferences. Concurrently, with the rise of large models (LMs), multimodal recommendation is increasingly leveraging their strengths in semantic understanding and contextual reasoning. However, LM representations are inherently optimized for general semantic tasks, while recommendation models rely heavily on sparse user/item unique identity (ID) features. Existing works overlook the fundamental representational divergence between large models and recommendation systems, resulting in incompatible multimodal representations and suboptimal recommendation performance. To bridge this gap, we propose RecGOAT, a novel yet simple dual semantic alignment framework for LLM-enhanced multimodal recommendation, which offers theoretically guaranteed alignment capability. RecGOAT first employs graph attention networks to enrich collaborative semantics by modeling item-item, user-item, and user-user relationships, leveraging user/item LM representations and interaction history. Furthermore, we design a dual-granularity progressive multimodality-ID alignment framework, which achieves instance-level and distribution-level semantic alignment via cross-modal contrastive learning (CMCL) and optimal adaptive transport (OAT), respectively. Theoretically, we demonstrate that the unified representations derived from our alignment framework exhibit superior semantic consistency and comprehensiveness. Extensive experiments on three public benchmarks show that our RecGOAT achieves state-of-the-art performance, empirically validating our theoretical insights. Additionally, the deployment on a large-scale online advertising platform confirms the model's effectiveness and scalability in industrial recommendation scenarios. Code available at https://github.com/6lyc/RecGOAT-LLM4Rec.
FLShield: A Validation Based Federated Learning Framework to Defend Against Poisoning Attacks
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is revolutionizing how we learn from data. With its growing popularity, it is now being used in many safety-critical domains such as autonomous vehicles and healthcare. Since thousands of participants can contribute in this collaborative setting, it is, however, challenging to ensure security and reliability of such systems. This highlights the need to design FL systems that are secure and robust against malicious participants' actions while also ensuring high utility, privacy of local data, and efficiency. In this paper, we propose a novel FL framework dubbed as FLShield that utilizes benign data from FL participants to validate the local models before taking them into account for generating the global model. This is in stark contrast with existing defenses relying on server's access to clean datasets -- an assumption often impractical in real-life scenarios and conflicting with the fundamentals of FL. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate our FLShield framework in different settings and demonstrate its effectiveness in thwarting various types of poisoning and backdoor attacks including a defense-aware one. FLShield also preserves privacy of local data against gradient inversion attacks.
CC-Loss: Channel Correlation Loss For Image Classification
Oct 12, 2020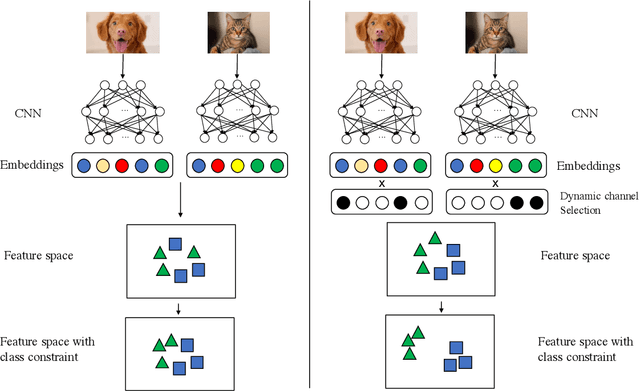
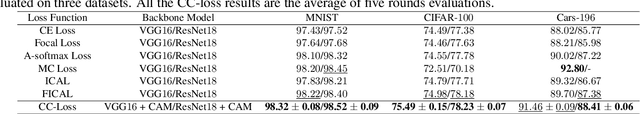
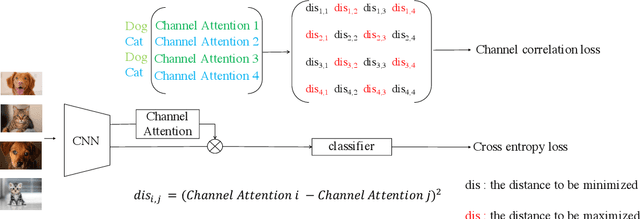
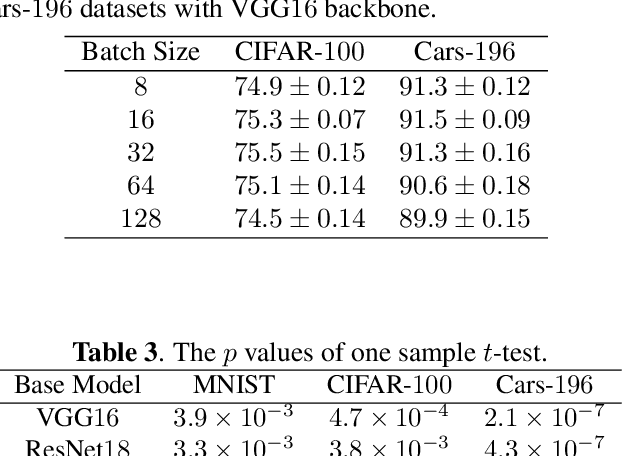
Abstract:The loss function is a key component in deep learning models. A commonly used loss function for classification is the cross entropy loss, which is a simple yet effective application of information theory for classification problems. Based on this loss, many other loss functions have been proposed,~\emph{e.g.}, by adding intra-class and inter-class constraints to enhance the discriminative ability of the learned features. However, these loss functions fail to consider the connections between the feature distribution and the model structure. Aiming at addressing this problem, we propose a channel correlation loss (CC-Loss) that is able to constrain the specific relations between classes and channels as well as maintain the intra-class and the inter-class separability. CC-Loss uses a channel attention module to generate channel attention of features for each sample in the training stage. Next, an Euclidean distance matrix is calculated to make the channel attention vectors associated with the same class become identical and to increase the difference between different classes. Finally, we obtain a feature embedding with good intra-class compactness and inter-class separability.Experimental results show that two different backbone models trained with the proposed CC-Loss outperform the state-of-the-art loss functions on three image classification datasets.
Deep Self-Supervised Representation Learning for Free-Hand Sketch
Feb 03, 2020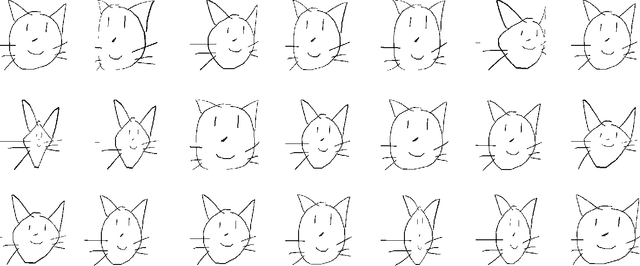
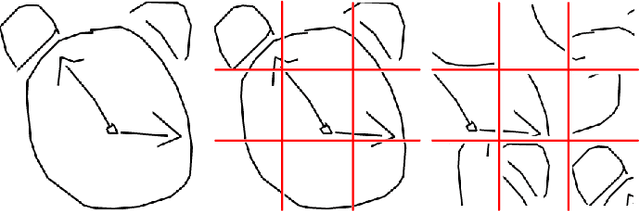
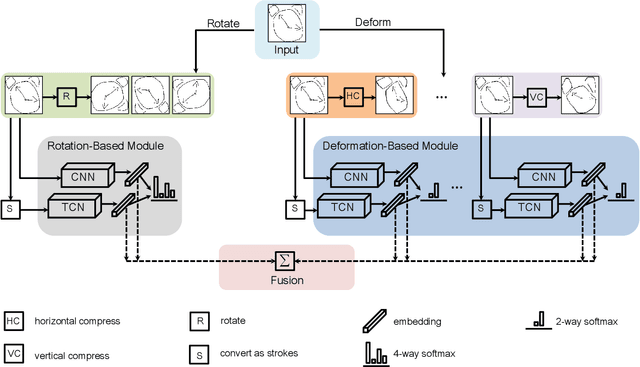
Abstract:In this paper, we tackle for the first time, the problem of self-supervised representation learning for free-hand sketches. This importantly addresses a common problem faced by the sketch community -- that annotated supervisory data are difficult to obtain. This problem is very challenging in that sketches are highly abstract and subject to different drawing styles, making existing solutions tailored for photos unsuitable. Key for the success of our self-supervised learning paradigm lies with our sketch-specific designs: (i) we propose a set of pretext tasks specifically designed for sketches that mimic different drawing styles, and (ii) we further exploit the use of a textual convolution network (TCN) in a dual-branch architecture for sketch feature learning, as means to accommodate the sequential stroke nature of sketches. We demonstrate the superiority of our sketch-specific designs through two sketch-related applications (retrieval and recognition) on a million-scale sketch dataset, and show that the proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art unsupervised representation learning methods, and significantly narrows the performance gap between with supervised representation learning.
Mobile big data analysis with machine learning
Aug 02, 2018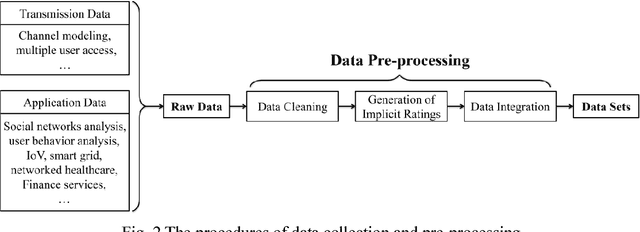
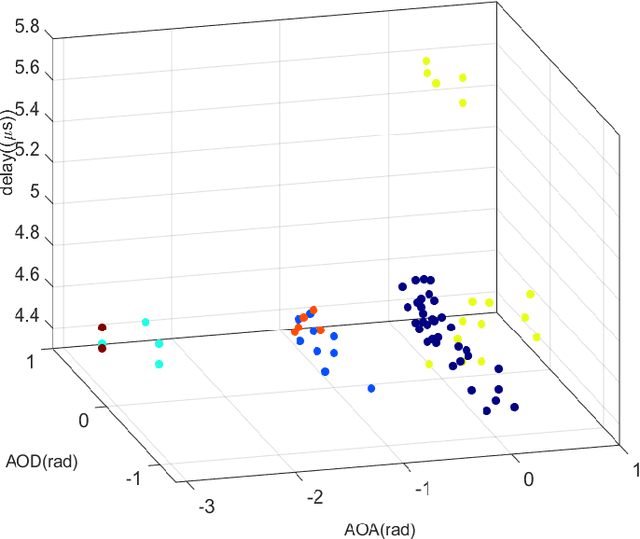

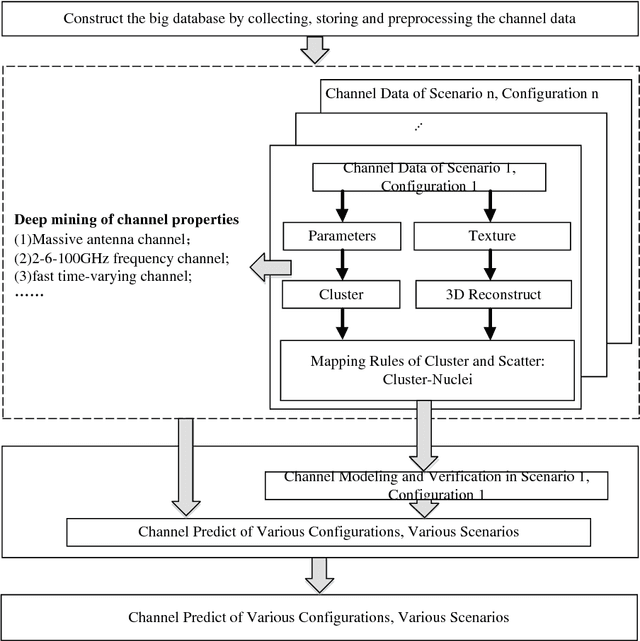
Abstract:This paper investigates to identify the requirement and the development of machine learning-based mobile big data analysis through discussing the insights of challenges in the mobile big data (MBD). Furthermore, it reviews the state-of-the-art applications of data analysis in the area of MBD. Firstly, we introduce the development of MBD. Secondly, the frequently adopted methods of data analysis are reviewed. Three typical applications of MBD analysis, namely wireless channel modeling, human online and offline behavior analysis, and speech recognition in the internet of vehicles, are introduced respectively. Finally, we summarize the main challenges and future development directions of mobile big data analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge