Yuxuan Yin
Large Language Models for EDA Cloud Job Resource and Lifetime Prediction
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of cloud computing in the Electronic Design Automation (EDA) industry has created a critical need for resource and job lifetime prediction to achieve optimal scheduling. Traditional machine learning methods often struggle with the complexity and heterogeneity of EDA workloads, requiring extensive feature engineering and domain expertise. We propose a novel framework that fine-tunes Large Language Models (LLMs) to address this challenge through text-to-text regression. We introduce the scientific notation and prefix filling to constrain the LLM, significantly improving output format reliability. Moreover, we found that full-attention finetuning and inference improves the prediction accuracy of sliding-window-attention LLMs. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework on real-world cloud datasets, setting a new baseline for performance prediction in the EDA domain.
Bishop: Sparsified Bundling Spiking Transformers on Heterogeneous Cores with Error-Constrained Pruning
May 18, 2025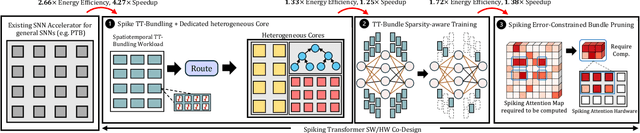
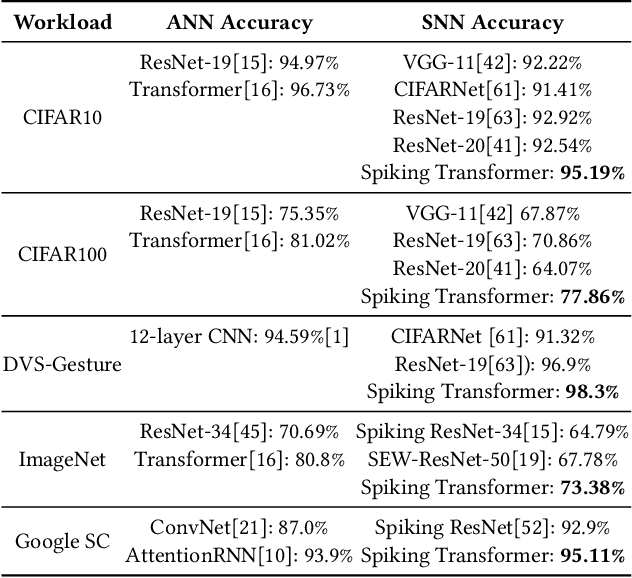
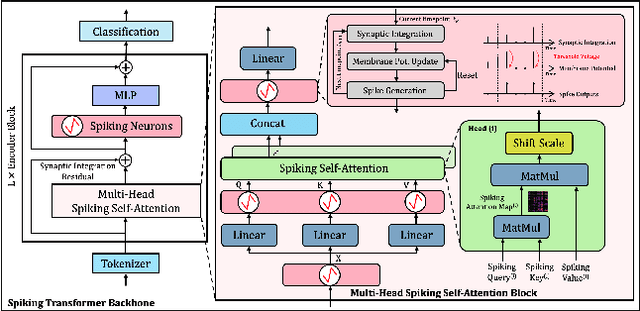
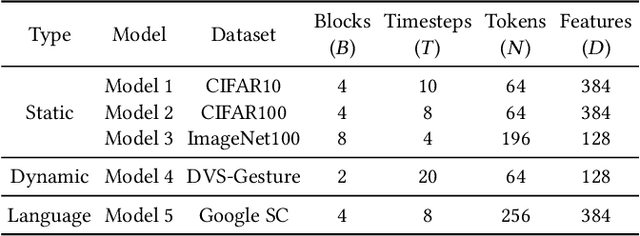
Abstract:We present Bishop, the first dedicated hardware accelerator architecture and HW/SW co-design framework for spiking transformers that optimally represents, manages, and processes spike-based workloads while exploring spatiotemporal sparsity and data reuse. Specifically, we introduce the concept of Token-Time Bundle (TTB), a container that bundles spiking data of a set of tokens over multiple time points. Our heterogeneous accelerator architecture Bishop concurrently processes workload packed in TTBs and explores intra- and inter-bundle multiple-bit weight reuse to significantly reduce memory access. Bishop utilizes a stratifier, a dense core array, and a sparse core array to process MLP blocks and projection layers. The stratifier routes high-density spiking activation workload to the dense core and low-density counterpart to the sparse core, ensuring optimized processing tailored to the given spatiotemporal sparsity level. To further reduce data access and computation, we introduce a novel Bundle Sparsity-Aware (BSA) training pipeline that enhances not only the overall but also structured TTB-level firing sparsity. Moreover, the processing efficiency of self-attention layers is boosted by the proposed Error-Constrained TTB Pruning (ECP), which trims activities in spiking queries, keys, and values both before and after the computation of spiking attention maps with a well-defined error bound. Finally, we design a reconfigurable TTB spiking attention core to efficiently compute spiking attention maps by executing highly simplified "AND" and "Accumulate" operations. On average, Bishop achieves a 5.91x speedup and 6.11x improvement in energy efficiency over previous SNN accelerators, while delivering higher accuracy across multiple datasets.
Towards 3D Acceleration for low-power Mixture-of-Experts and Multi-Head Attention Spiking Transformers
Dec 07, 2024Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks(SNNs) provide a brain-inspired and event-driven mechanism that is believed to be critical to unlock energy-efficient deep learning. The mixture-of-experts approach mirrors the parallel distributed processing of nervous systems, introducing conditional computation policies and expanding model capacity without scaling up the number of computational operations. Additionally, spiking mixture-of-experts self-attention mechanisms enhance representation capacity, effectively capturing diverse patterns of entities and dependencies between visual or linguistic tokens. However, there is currently a lack of hardware support for highly parallel distributed processing needed by spiking transformers, which embody a brain-inspired computation. This paper introduces the first 3D hardware architecture and design methodology for Mixture-of-Experts and Multi-Head Attention spiking transformers. By leveraging 3D integration with memory-on-logic and logic-on-logic stacking, we explore such brain-inspired accelerators with spatially stackable circuitry, demonstrating significant optimization of energy efficiency and latency compared to conventional 2D CMOS integration.
Towards the Mitigation of Confirmation Bias in Semi-supervised Learning: a Debiased Training Perspective
Sep 26, 2024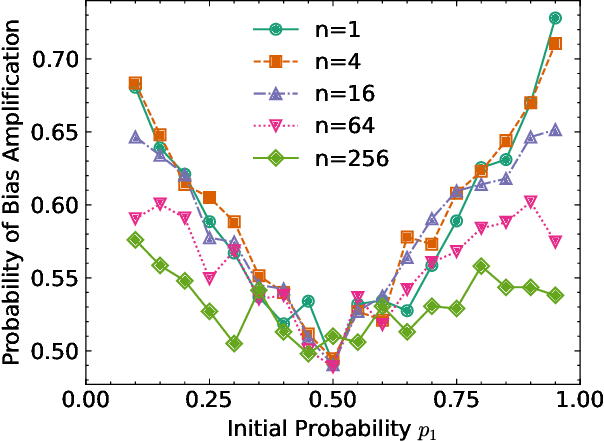
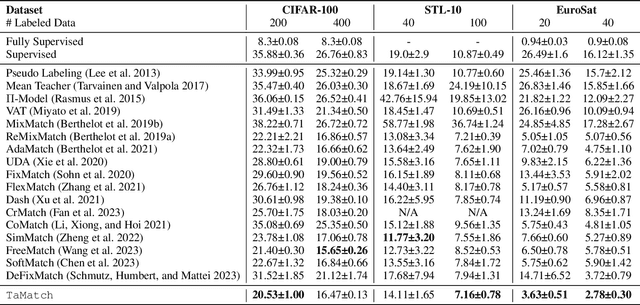
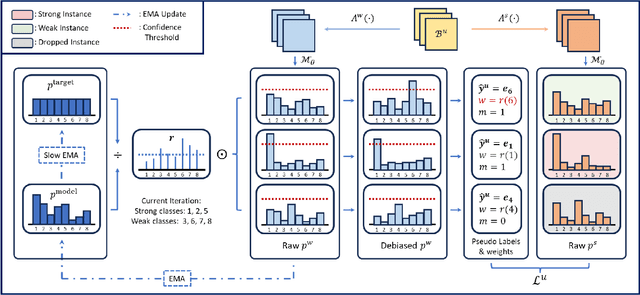
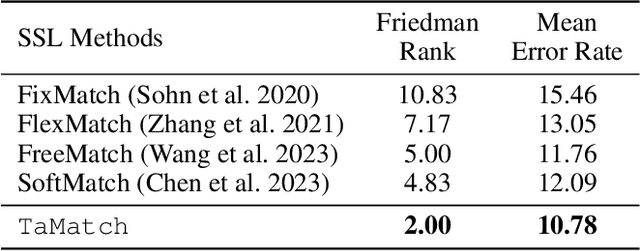
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) commonly exhibits confirmation bias, where models disproportionately favor certain classes, leading to errors in predicted pseudo labels that accumulate under a self-training paradigm. Unlike supervised settings, which benefit from a rich, static data distribution, SSL inherently lacks mechanisms to correct this self-reinforced bias, necessitating debiased interventions at each training step. Although the generation of debiased pseudo labels has been extensively studied, their effective utilization remains underexplored. Our analysis indicates that data from biased classes should have a reduced influence on parameter updates, while more attention should be given to underrepresented classes. To address these challenges, we introduce TaMatch, a unified framework for debiased training in SSL. TaMatch employs a scaling ratio derived from both a prior target distribution and the model's learning status to estimate and correct bias at each training step. This ratio adjusts the raw predictions on unlabeled data to produce debiased pseudo labels. In the utilization phase, these labels are differently weighted according to their predicted class, enhancing training equity and minimizing class bias. Additionally, TaMatch dynamically adjust the target distribution in response to the model's learning progress, facilitating robust handling of practical scenarios where the prior distribution is unknown. Empirical evaluations show that TaMatch significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across a range of challenging image classification tasks, highlighting the critical importance of both the debiased generation and utilization of pseudo labels in SSL.
ADO-LLM: Analog Design Bayesian Optimization with In-Context Learning of Large Language Models
Jun 26, 2024Abstract:Analog circuit design requires substantial human expertise and involvement, which is a significant roadblock to design productivity. Bayesian Optimization (BO), a popular machine learning based optimization strategy, has been leveraged to automate analog design given its applicability across various circuit topologies and technologies. Traditional BO methods employ black box Gaussian Process surrogate models and optimized labeled data queries to find optimization solutions by trading off between exploration and exploitation. However, the search for the optimal design solution in BO can be expensive from both a computational and data usage point of view, particularly for high dimensional optimization problems. This paper presents ADO-LLM, the first work integrating large language models (LLMs) with Bayesian Optimization for analog design optimization. ADO-LLM leverages the LLM's ability to infuse domain knowledge to rapidly generate viable design points to remedy BO's inefficiency in finding high value design areas specifically under the limited design space coverage of the BO's probabilistic surrogate model. In the meantime, sampling of design points evaluated in the iterative BO process provides quality demonstrations for the LLM to generate high quality design points while leveraging infused broad design knowledge. Furthermore, the diversity brought by BO's exploration enriches the contextual understanding of the LLM and allows it to more broadly search in the design space and prevent repetitive and redundant suggestions. We evaluate the proposed framework on two different types of analog circuits and demonstrate notable improvements in design efficiency and effectiveness.
DISTA: Denoising Spiking Transformer with intrinsic plasticity and spatiotemporal attention
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:Among the array of neural network architectures, the Vision Transformer (ViT) stands out as a prominent choice, acclaimed for its exceptional expressiveness and consistent high performance in various vision applications. Recently, the emerging Spiking ViT approach has endeavored to harness spiking neurons, paving the way for a more brain-inspired transformer architecture that thrives in ultra-low power operations on dedicated neuromorphic hardware. Nevertheless, this approach remains confined to spatial self-attention and doesn't fully unlock the potential of spiking neural networks. We introduce DISTA, a Denoising Spiking Transformer with Intrinsic Plasticity and SpatioTemporal Attention, designed to maximize the spatiotemporal computational prowess of spiking neurons, particularly for vision applications. DISTA explores two types of spatiotemporal attentions: intrinsic neuron-level attention and network-level attention with explicit memory. Additionally, DISTA incorporates an efficient nonlinear denoising mechanism to quell the noise inherent in computed spatiotemporal attention maps, thereby resulting in further performance gains. Our DISTA transformer undergoes joint training involving synaptic plasticity (i.e., weight tuning) and intrinsic plasticity (i.e., membrane time constant tuning) and delivers state-of-the-art performances across several static image and dynamic neuromorphic datasets. With only 6 time steps, DISTA achieves remarkable top-1 accuracy on CIFAR10 (96.26%) and CIFAR100 (79.15%), as well as 79.1% on CIFAR10-DVS using 10 time steps.
Semi-Supervised Learning of Dynamical Systems with Neural Ordinary Differential Equations: A Teacher-Student Model Approach
Oct 19, 2023Abstract:Modeling dynamical systems is crucial for a wide range of tasks, but it remains challenging due to complex nonlinear dynamics, limited observations, or lack of prior knowledge. Recently, data-driven approaches such as Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (NODE) have shown promising results by leveraging the expressive power of neural networks to model unknown dynamics. However, these approaches often suffer from limited labeled training data, leading to poor generalization and suboptimal predictions. On the other hand, semi-supervised algorithms can utilize abundant unlabeled data and have demonstrated good performance in classification and regression tasks. We propose TS-NODE, the first semi-supervised approach to modeling dynamical systems with NODE. TS-NODE explores cheaply generated synthetic pseudo rollouts to broaden exploration in the state space and to tackle the challenges brought by lack of ground-truth system data under a teacher-student model. TS-NODE employs an unified optimization framework that corrects the teacher model based on the student's feedback while mitigating the potential false system dynamics present in pseudo rollouts. TS-NODE demonstrates significant performance improvements over a baseline Neural ODE model on multiple dynamical system modeling tasks.
High-dimensional Bayesian Optimization via Semi-supervised Learning with Optimized Unlabeled Data Sampling
May 04, 2023Abstract:Bayesian optimization (BO) is a powerful tool for seeking the global optimum of black-box functions. While evaluations of the black-box functions can be highly costly, it is desirable to reduce the use of expensive labeled data. For the first time, we introduce a teacher-student model to exploit semi-supervised learning that can make use of large amounts of unlabelled data under the context of BO. Importantly, we show that the selection of the validation and unlabeled data is key to the performance of BO. To optimize the sampling of unlabeled data, we employ a black-box parameterized sampling distribution optimized as part of the employed bi-level optimization framework. Taking one step further, we demonstrate that the performance of BO can be further improved by selecting unlabeled data from a dynamically fitted extreme value distribution. Our BO method operates in a learned latent space with reduced dimensionality, making it scalable to high-dimensional problems. The proposed approach outperforms significantly the existing BO methods on several synthetic and real-world optimization tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge