Yushi Sun
MedKGI: Iterative Differential Diagnosis with Medical Knowledge Graphs and Information-Guided Inquiring
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant promise in clinical diagnosis. However, current models struggle to emulate the iterative, diagnostic hypothesis-driven reasoning of real clinical scenarios. Specifically, current LLMs suffer from three critical limitations: (1) generating hallucinated medical content due to weak grounding in verified knowledge, (2) asking redundant or inefficient questions rather than discriminative ones that hinder diagnostic progress, and (3) losing coherence over multi-turn dialogues, leading to contradictory or inconsistent conclusions. To address these challenges, we propose MedKGI, a diagnostic framework grounded in clinical practices. MedKGI integrates a medical knowledge graph (KG) to constrain reasoning to validated medical ontologies, selects questions based on information gain to maximize diagnostic efficiency, and adopts an OSCE-format structured state to maintain consistent evidence tracking across turns. Experiments on clinical benchmarks show that MedKGI outperforms strong LLM baselines in both diagnostic accuracy and inquiry efficiency, improving dialogue efficiency by 30% on average while maintaining state-of-the-art accuracy.
KERAG: Knowledge-Enhanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Advanced Question Answering
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) mitigates hallucination in Large Language Models (LLMs) by incorporating external data, with Knowledge Graphs (KGs) offering crucial information for question answering. Traditional Knowledge Graph Question Answering (KGQA) methods rely on semantic parsing, which typically retrieves knowledge strictly necessary for answer generation, thus often suffer from low coverage due to rigid schema requirements and semantic ambiguity. We present KERAG, a novel KG-based RAG pipeline that enhances QA coverage by retrieving a broader subgraph likely to contain relevant information. Our retrieval-filtering-summarization approach, combined with fine-tuned LLMs for Chain-of-Thought reasoning on knowledge sub-graphs, reduces noises and improves QA for both simple and complex questions. Experiments demonstrate that KERAG surpasses state-of-the-art solutions by about 7% in quality and exceeds GPT-4o (Tool) by 10-21%.
Are Large Language Models a Good Replacement of Taxonomies?
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate an impressive ability to internalize knowledge and answer natural language questions. Although previous studies validate that LLMs perform well on general knowledge while presenting poor performance on long-tail nuanced knowledge, the community is still doubtful about whether the traditional knowledge graphs should be replaced by LLMs. In this paper, we ask if the schema of knowledge graph (i.e., taxonomy) is made obsolete by LLMs. Intuitively, LLMs should perform well on common taxonomies and at taxonomy levels that are common to people. Unfortunately, there lacks a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates the LLMs over a wide range of taxonomies from common to specialized domains and at levels from root to leaf so that we can draw a confident conclusion. To narrow the research gap, we constructed a novel taxonomy hierarchical structure discovery benchmark named TaxoGlimpse to evaluate the performance of LLMs over taxonomies. TaxoGlimpse covers ten representative taxonomies from common to specialized domains with in-depth experiments of different levels of entities in this taxonomy from root to leaf. Our comprehensive experiments of eighteen state-of-the-art LLMs under three prompting settings validate that LLMs can still not well capture the knowledge of specialized taxonomies and leaf-level entities.
Cross-domain-aware Worker Selection with Training for Crowdsourced Annotation
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:Annotation through crowdsourcing draws incremental attention, which relies on an effective selection scheme given a pool of workers. Existing methods propose to select workers based on their performance on tasks with ground truth, while two important points are missed. 1) The historical performances of workers in other tasks. In real-world scenarios, workers need to solve a new task whose correlation with previous tasks is not well-known before the training, which is called cross-domain. 2) The dynamic worker performance as workers will learn from the ground truth. In this paper, we consider both factors in designing an allocation scheme named cross-domain-aware worker selection with training approach. Our approach proposes two estimation modules to both statistically analyze the cross-domain correlation and simulate the learning gain of workers dynamically. A framework with a theoretical analysis of the worker elimination process is given. To validate the effectiveness of our methods, we collect two novel real-world datasets and generate synthetic datasets. The experiment results show that our method outperforms the baselines on both real-world and synthetic datasets.
CRAG -- Comprehensive RAG Benchmark
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has recently emerged as a promising solution to alleviate Large Language Model (LLM)'s deficiency in lack of knowledge. Existing RAG datasets, however, do not adequately represent the diverse and dynamic nature of real-world Question Answering (QA) tasks. To bridge this gap, we introduce the Comprehensive RAG Benchmark (CRAG), a factual question answering benchmark of 4,409 question-answer pairs and mock APIs to simulate web and Knowledge Graph (KG) search. CRAG is designed to encapsulate a diverse array of questions across five domains and eight question categories, reflecting varied entity popularity from popular to long-tail, and temporal dynamisms ranging from years to seconds. Our evaluation on this benchmark highlights the gap to fully trustworthy QA. Whereas most advanced LLMs achieve <=34% accuracy on CRAG, adding RAG in a straightforward manner improves the accuracy only to 44%. State-of-the-art industry RAG solutions only answer 63% questions without any hallucination. CRAG also reveals much lower accuracy in answering questions regarding facts with higher dynamism, lower popularity, or higher complexity, suggesting future research directions. The CRAG benchmark laid the groundwork for a KDD Cup 2024 challenge, attracting thousands of participants and submissions within the first 50 days of the competition. We commit to maintaining CRAG to serve research communities in advancing RAG solutions and general QA solutions.
Fake News Detection with Heterogeneous Transformer
May 06, 2022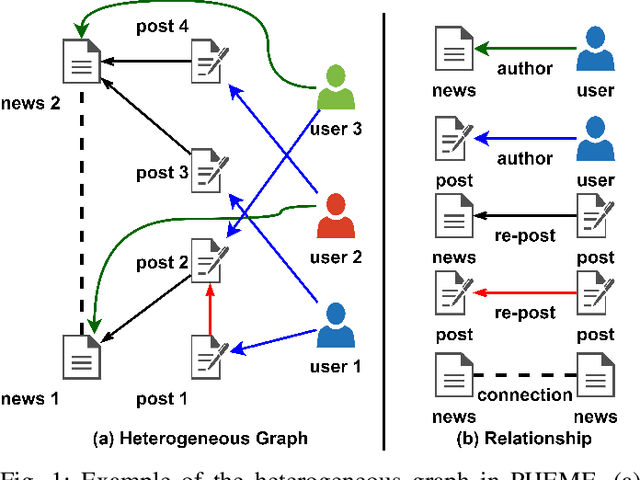
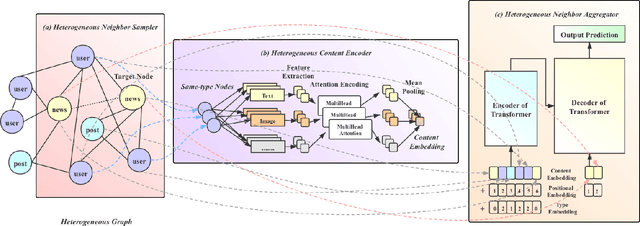
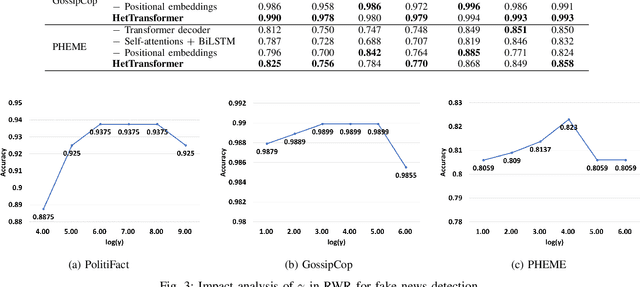
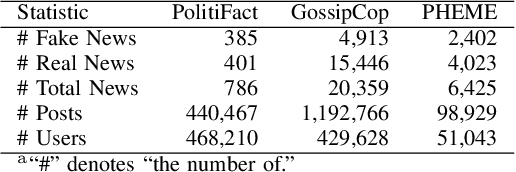
Abstract:The dissemination of fake news on social networks has drawn public need for effective and efficient fake news detection methods. Generally, fake news on social networks is multi-modal and has various connections with other entities such as users and posts. The heterogeneity in both news content and the relationship with other entities in social networks brings challenges to designing a model that comprehensively captures the local multi-modal semantics of entities in social networks and the global structural representation of the propagation patterns, so as to classify fake news effectively and accurately. In this paper, we propose a novel Transformer-based model: HetTransformer to solve the fake news detection problem on social networks, which utilises the encoder-decoder structure of Transformer to capture the structural information of news propagation patterns. We first capture the local heterogeneous semantics of news, post, and user entities in social networks. Then, we apply Transformer to capture the global structural representation of the propagation patterns in social networks for fake news detection. Experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that our model is able to outperform the state-of-the-art baselines in fake news detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge