Yujie Sun
PEP-GS: Perceptually-Enhanced Precise Structured 3D Gaussians for View-Adaptive Rendering
Nov 08, 2024
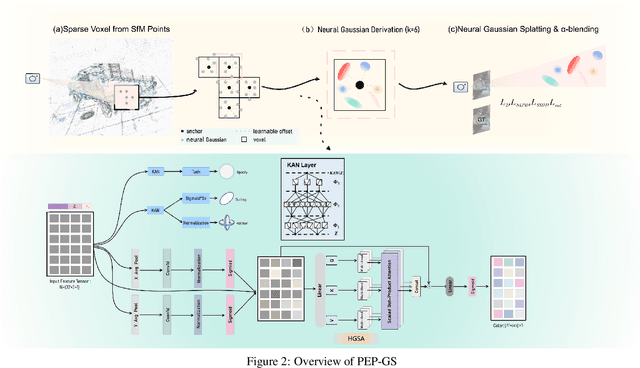
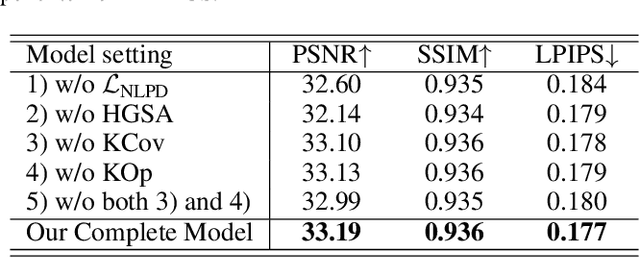
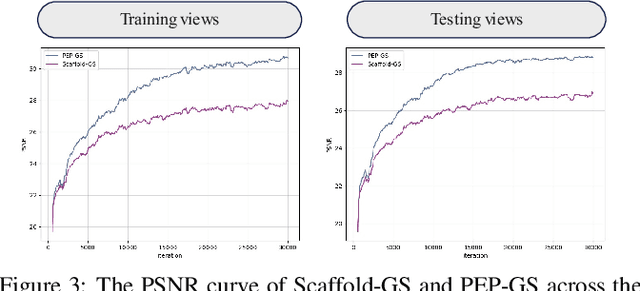
Abstract:Recent advances in structured 3D Gaussians for view-adaptive rendering, particularly through methods like Scaffold-GS, have demonstrated promising results in neural scene representation. However, existing approaches still face challenges in perceptual consistency and precise view-dependent effects. We present PEP-GS, a novel framework that enhances structured 3D Gaussians through three key innovations: (1) a Local-Enhanced Multi-head Self-Attention (LEMSA) mechanism that replaces spherical harmonics for more accurate view-dependent color decoding, and (2) Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) that optimize Gaussian opacity and covariance functions for enhanced interpretability and splatting precision. (3) a Neural Laplacian Pyramid Decomposition (NLPD) that improves perceptual similarity across views. Our comprehensive evaluation across multiple datasets indicates that, compared to the current state-of-the-art methods, these improvements are particularly evident in challenging scenarios such as view-dependent effects, specular reflections, fine-scale details and false geometry generation.
Large Language Models for Mobility in Transportation Systems: A Survey on Forecasting Tasks
May 03, 2024

Abstract:Mobility analysis is a crucial element in the research area of transportation systems. Forecasting traffic information offers a viable solution to address the conflict between increasing transportation demands and the limitations of transportation infrastructure. Predicting human travel is significant in aiding various transportation and urban management tasks, such as taxi dispatch and urban planning. Machine learning and deep learning methods are favored for their flexibility and accuracy. Nowadays, with the advent of large language models (LLMs), many researchers have combined these models with previous techniques or applied LLMs to directly predict future traffic information and human travel behaviors. However, there is a lack of comprehensive studies on how LLMs can contribute to this field. This survey explores existing approaches using LLMs for mobility forecasting problems. We provide a literature review concerning the forecasting applications within transportation systems, elucidating how researchers utilize LLMs, showcasing recent state-of-the-art advancements, and identifying the challenges that must be overcome to fully leverage LLMs in this domain.
Form 10-Q Itemization
Apr 23, 2021



Abstract:Form 10-Q, the quarterly financial statement, is one of the most crucial filings for US public firms to disclose their financial and other relevant business operation information. Due to the gigantic number of 10-Q filings prevailing in the market for each quarter and diverse variations in the implementation of format given company-specific nature, it has long been a problem in the field to provide a generalized way to dissect and retrieve the itemized information. In this paper, we create a tool to itemize 10-Q filings using multi-stage processes, blending a rule-based algorithm with a CNN deep learning model. The implementation is an integrated pipeline which provides a solution to the item retrieval on a large scale. This would enable cross sectional and longitudinal textual analysis on massive number of companies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge