Lianjun Liu
A Contemporary Overview: Trends and Applications of Large Language Models on Mobile Devices
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:With the rapid development of large language models (LLMs), which possess powerful natural language processing and generation capabilities, LLMs are poised to provide more natural and personalized user experiences. Their deployment on mobile devices is gradually becoming a significant trend in the field of intelligent devices. LLMs have demonstrated tremendous potential in applications such as voice assistants, real-time translation, and intelligent recommendations. Advancements in hardware technologies (such as neural network accelerators) and network infrastructure (such as 5G) have enabled efficient local inference and low-latency intelligent responses on mobile devices. This reduces reliance on cloud computing while enhancing data privacy and security. Developers can easily integrate LLM functionalities through open APIs and SDKs, enabling the creation of more innovative intelligent applications. The widespread use of LLMs not only enhances the intelligence of mobile devices but also fosters the integrated innovation of fields like augmented reality (AR) and the Internet of Things (IoT). This trend is expected to drive the development of the next generation of mobile intelligent applications.
PEP-GS: Perceptually-Enhanced Precise Structured 3D Gaussians for View-Adaptive Rendering
Nov 08, 2024
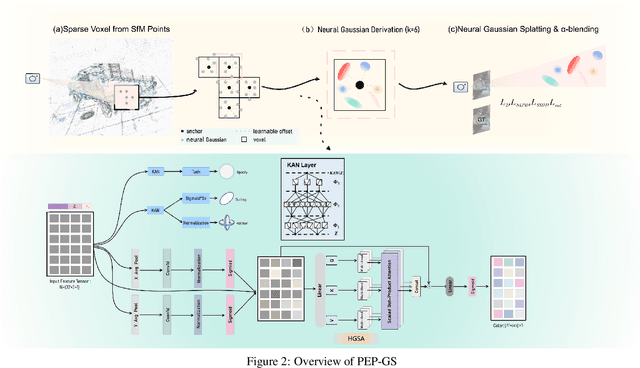
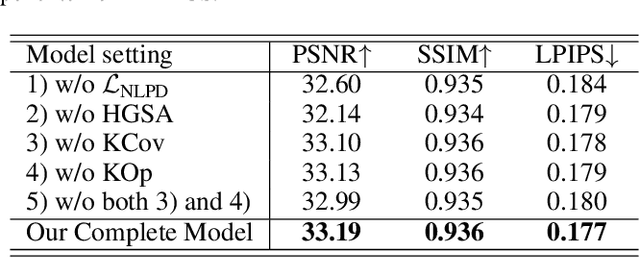
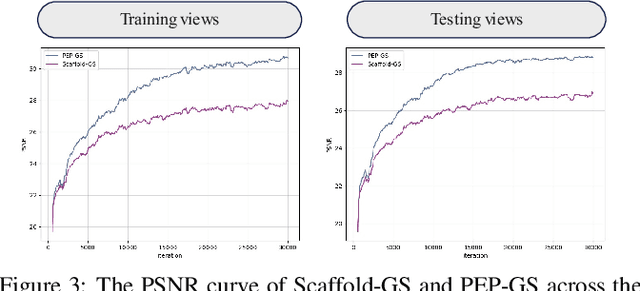
Abstract:Recent advances in structured 3D Gaussians for view-adaptive rendering, particularly through methods like Scaffold-GS, have demonstrated promising results in neural scene representation. However, existing approaches still face challenges in perceptual consistency and precise view-dependent effects. We present PEP-GS, a novel framework that enhances structured 3D Gaussians through three key innovations: (1) a Local-Enhanced Multi-head Self-Attention (LEMSA) mechanism that replaces spherical harmonics for more accurate view-dependent color decoding, and (2) Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) that optimize Gaussian opacity and covariance functions for enhanced interpretability and splatting precision. (3) a Neural Laplacian Pyramid Decomposition (NLPD) that improves perceptual similarity across views. Our comprehensive evaluation across multiple datasets indicates that, compared to the current state-of-the-art methods, these improvements are particularly evident in challenging scenarios such as view-dependent effects, specular reflections, fine-scale details and false geometry generation.
MV-Adapter: Enhancing Underwater Instance Segmentation via Adaptive Channel Attention
Nov 01, 2024Abstract:Underwater instance segmentation is a fundamental and critical step in various underwater vision tasks. However, the decline in image quality caused by complex underwater environments presents significant challenges to existing segmentation models. While the state-of-the-art USIS-SAM model has demonstrated impressive performance, it struggles to effectively adapt to feature variations across different channels in addressing issues such as light attenuation, color distortion, and complex backgrounds. This limitation hampers its segmentation performance in challenging underwater scenarios. To address these issues, we propose the MarineVision Adapter (MV-Adapter). This module introduces an adaptive channel attention mechanism that enables the model to dynamically adjust the feature weights of each channel based on the characteristics of underwater images. By adaptively weighting features, the model can effectively handle challenges such as light attenuation, color shifts, and complex backgrounds. Experimental results show that integrating the MV-Adapter module into the USIS-SAM network architecture further improves the model's overall performance, especially in high-precision segmentation tasks. On the USIS10K dataset, the module achieves improvements in key metrics such as mAP, AP50, and AP75 compared to competitive baseline models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge