Junxi Jin
CMR: Contractive Mapping Embeddings for Robust Humanoid Locomotion on Unstructured Terrains
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Robust disturbance rejection remains a longstanding challenge in humanoid locomotion, particularly on unstructured terrains where sensing is unreliable and model mismatch is pronounced. While perception information, such as height map, enhances terrain awareness, sensor noise and sim-to-real gaps can destabilize policies in practice. In this work, we provide theoretical analysis that bounds the return gap under observation noise, when the induced latent dynamics are contractive. Furthermore, we present Contractive Mapping for Robustness (CMR) framework that maps high-dimensional, disturbance-prone observations into a latent space, where local perturbations are attenuated over time. Specifically, this approach couples contrastive representation learning with Lipschitz regularization to preserve task-relevant geometry while explicitly controlling sensitivity. Notably, the formulation can be incorporated into modern deep reinforcement learning pipelines as an auxiliary loss term with minimal additional technical effort required. Further, our extensive humanoid experiments show that CMR potently outperforms other locomotion algorithms under increased noise.
Balancing Signal and Variance: Adaptive Offline RL Post-Training for VLA Flow Models
Sep 04, 2025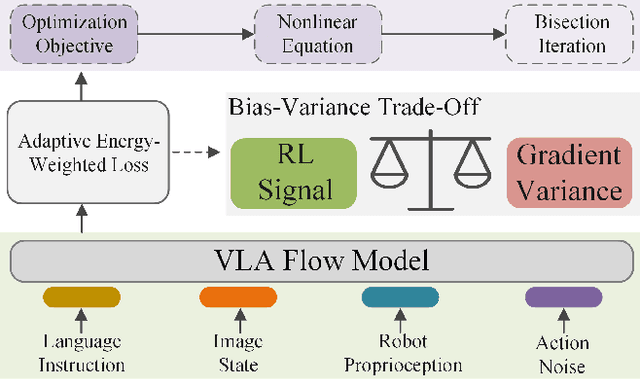
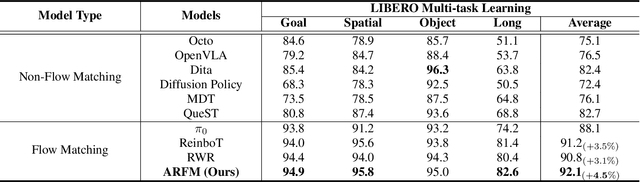
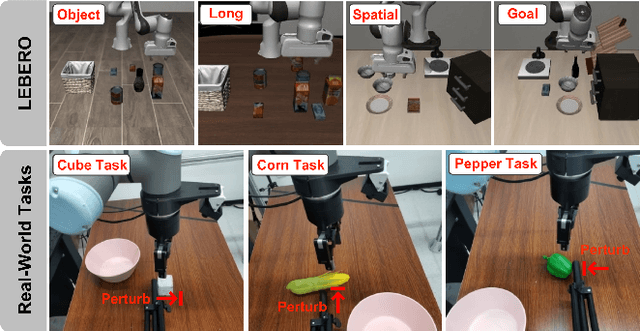
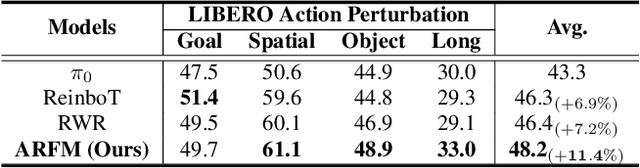
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models based on flow matching have shown excellent performance in general-purpose robotic manipulation tasks. However, the action accuracy of these models on complex downstream tasks is unsatisfactory. One important reason is that these models rely solely on the post-training paradigm of imitation learning, which makes it difficult to have a deeper understanding of the distribution properties of data quality, which is exactly what Reinforcement Learning (RL) excels at. In this paper, we theoretically propose an offline RL post-training objective for VLA flow models and induce an efficient and feasible offline RL fine-tuning algorithm -- Adaptive Reinforced Flow Matching (ARFM). By introducing an adaptively adjusted scaling factor in the VLA flow model loss, we construct a principled bias-variance trade-off objective function to optimally control the impact of RL signal on flow loss. ARFM adaptively balances RL advantage preservation and flow loss gradient variance control, resulting in a more stable and efficient fine-tuning process. Extensive simulation and real-world experimental results show that ARFM exhibits excellent generalization, robustness, few-shot learning, and continuous learning performance.
PEP-GS: Perceptually-Enhanced Precise Structured 3D Gaussians for View-Adaptive Rendering
Nov 08, 2024
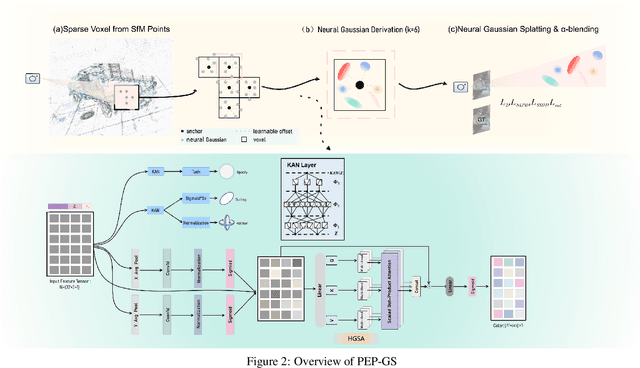
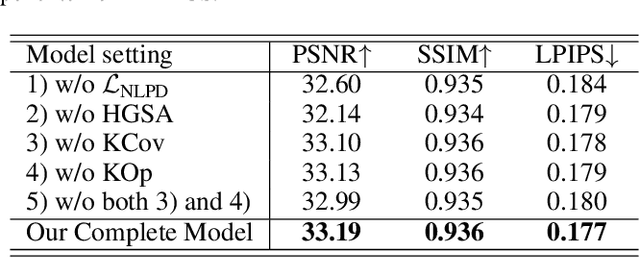
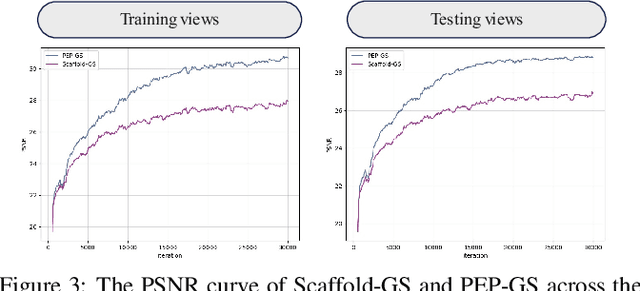
Abstract:Recent advances in structured 3D Gaussians for view-adaptive rendering, particularly through methods like Scaffold-GS, have demonstrated promising results in neural scene representation. However, existing approaches still face challenges in perceptual consistency and precise view-dependent effects. We present PEP-GS, a novel framework that enhances structured 3D Gaussians through three key innovations: (1) a Local-Enhanced Multi-head Self-Attention (LEMSA) mechanism that replaces spherical harmonics for more accurate view-dependent color decoding, and (2) Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KAN) that optimize Gaussian opacity and covariance functions for enhanced interpretability and splatting precision. (3) a Neural Laplacian Pyramid Decomposition (NLPD) that improves perceptual similarity across views. Our comprehensive evaluation across multiple datasets indicates that, compared to the current state-of-the-art methods, these improvements are particularly evident in challenging scenarios such as view-dependent effects, specular reflections, fine-scale details and false geometry generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge