Yuefeng Li
GeRe: Towards Efficient Anti-Forgetting in Continual Learning of LLM via General Samples Replay
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:The continual learning capability of large language models (LLMs) is crucial for advancing artificial general intelligence. However, continual fine-tuning LLMs across various domains often suffers from catastrophic forgetting, characterized by: 1) significant forgetting of their general capabilities, and 2) sharp performance declines in previously learned tasks. To simultaneously address both issues in a simple yet stable manner, we propose General Sample Replay (GeRe), a framework that use usual pretraining texts for efficient anti-forgetting. Beyond revisiting the most prevalent replay-based practices under GeRe, we further leverage neural states to introduce a enhanced activation states constrained optimization method using threshold-based margin (TM) loss, which maintains activation state consistency during replay learning. We are the first to validate that a small, fixed set of pre-collected general replay samples is sufficient to resolve both concerns--retaining general capabilities while promoting overall performance across sequential tasks. Indeed, the former can inherently facilitate the latter. Through controlled experiments, we systematically compare TM with different replay strategies under the GeRe framework, including vanilla label fitting, logit imitation via KL divergence and feature imitation via L1/L2 losses. Results demonstrate that TM consistently improves performance and exhibits better robustness. Our work paves the way for efficient replay of LLMs for the future. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/Qznan/GeRe.
Display Content, Display Methods and Evaluation Methods of the HCI in Explainable Recommender Systems: A Survey
May 14, 2025Abstract:Explainable Recommender Systems (XRS) aim to provide users with understandable reasons for the recommendations generated by these systems, representing a crucial research direction in artificial intelligence (AI). Recent research has increasingly focused on the algorithms, display, and evaluation methodologies of XRS. While current research and reviews primarily emphasize the algorithmic aspects, with fewer studies addressing the Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) layer of XRS. Additionally, existing reviews lack a unified taxonomy for XRS and there is insufficient attention given to the emerging area of short video recommendations. In this study, we synthesize existing literature and surveys on XRS, presenting a unified framework for its research and development. The main contributions are as follows: 1) We adopt a lifecycle perspective to systematically summarize the technologies and methods used in XRS, addressing challenges posed by the diversity and complexity of algorithmic models and explanation techniques. 2) For the first time, we highlight the application of multimedia, particularly video-based explanations, along with its potential, technical pathways, and challenges in XRS. 3) We provide a structured overview of evaluation methods from both qualitative and quantitative dimensions. These findings provide valuable insights for the systematic design, progress, and testing of XRS.
Random Forest-of-Thoughts: Uncertainty-aware Reasoning for Computational Social Science
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Social surveys in computational social science are well-designed by elaborate domain theories that can effectively reflect the interviewee's deep thoughts without concealing their true feelings. The candidate questionnaire options highly depend on the interviewee's previous answer, which results in the complexity of social survey analysis, the time, and the expertise required. The ability of large language models (LLMs) to perform complex reasoning is well-enhanced by prompting learning such as Chain-of-thought (CoT) but still confined to left-to-right decision-making processes or limited paths during inference. This means they can fall short in problems that require exploration and uncertainty searching. In response, a novel large language model prompting method, called Random Forest of Thoughts (RFoT), is proposed for generating uncertainty reasoning to fit the area of computational social science. The RFoT allows LLMs to perform deliberate decision-making by generating diverse thought space and randomly selecting the sub-thoughts to build the forest of thoughts. It can extend the exploration and prediction of overall performance, benefiting from the extensive research space of response. The method is applied to optimize computational social science analysis on two datasets covering a spectrum of social survey analysis problems. Our experiments show that RFoT significantly enhances language models' abilities on two novel social survey analysis problems requiring non-trivial reasoning.
Nonnegative Matrix Factorization in Dimensionality Reduction: A Survey
May 06, 2024



Abstract:Dimensionality Reduction plays a pivotal role in improving feature learning accuracy and reducing training time by eliminating redundant features, noise, and irrelevant data. Nonnegative Matrix Factorization (NMF) has emerged as a popular and powerful method for dimensionality reduction. Despite its extensive use, there remains a need for a comprehensive analysis of NMF in the context of dimensionality reduction. To address this gap, this paper presents a comprehensive survey of NMF, focusing on its applications in both feature extraction and feature selection. We introduce a classification of dimensionality reduction, enhancing understanding of the underlying concepts. Subsequently, we delve into a thorough summary of diverse NMF approaches used for feature extraction and selection. Furthermore, we discuss the latest research trends and potential future directions of NMF in dimensionality reduction, aiming to highlight areas that need further exploration and development.
DE-CGAN: Boosting rTMS Treatment Prediction with Diversity Enhancing Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) is a well-supported, evidence-based treatment for depression. However, patterns of response to this treatment are inconsistent. Emerging evidence suggests that artificial intelligence can predict rTMS treatment outcomes for most patients using fMRI connectivity features. While these models can reliably predict treatment outcomes for many patients for some underrepresented fMRI connectivity measures DNN models are unable to reliably predict treatment outcomes. As such we propose a novel method, Diversity Enhancing Conditional General Adversarial Network (DE-CGAN) for oversampling these underrepresented examples. DE-CGAN creates synthetic examples in difficult-to-classify regions by first identifying these data points and then creating conditioned synthetic examples to enhance data diversity. Through empirical experiments we show that a classification model trained using a diversity enhanced training set outperforms traditional data augmentation techniques and existing benchmark results. This work shows that increasing the diversity of a training dataset can improve classification model performance. Furthermore, this work provides evidence for the utility of synthetic patients providing larger more robust datasets for both AI researchers and psychiatrists to explore variable relationships.
Graph-enabled Reinforcement Learning for Time Series Forecasting with Adaptive Intelligence
Sep 18, 2023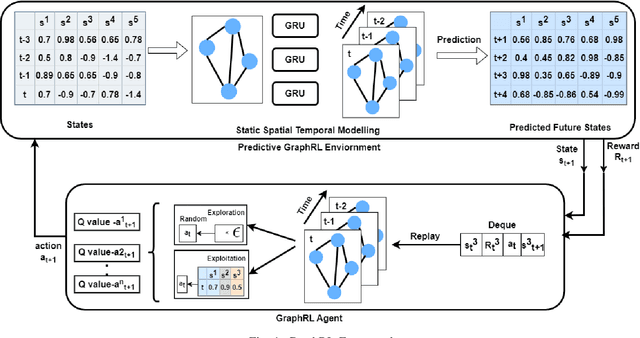
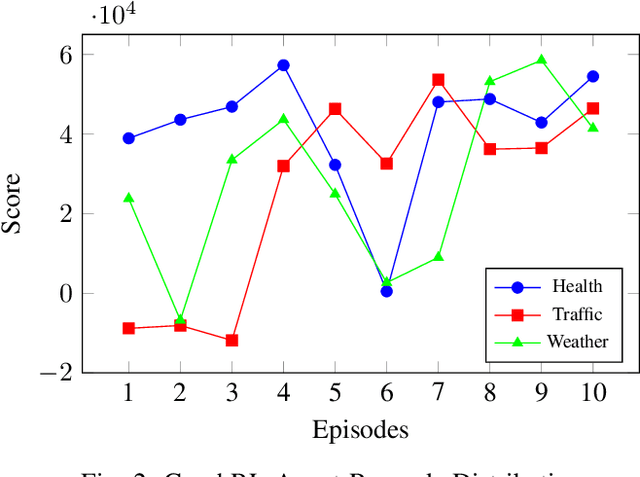
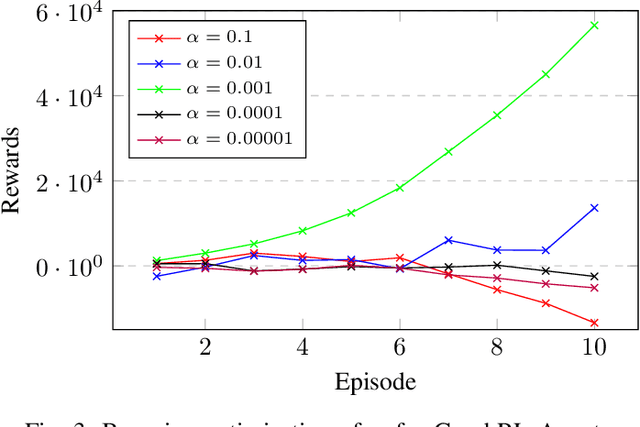
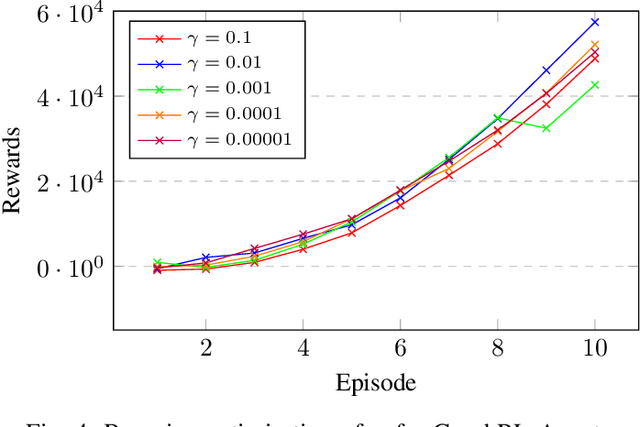
Abstract:Reinforcement learning is well known for its ability to model sequential tasks and learn latent data patterns adaptively. Deep learning models have been widely explored and adopted in regression and classification tasks. However, deep learning has its limitations such as the assumption of equally spaced and ordered data, and the lack of ability to incorporate graph structure in terms of time-series prediction. Graphical neural network (GNN) has the ability to overcome these challenges and capture the temporal dependencies in time-series data. In this study, we propose a novel approach for predicting time-series data using GNN and monitoring with Reinforcement Learning (RL). GNNs are able to explicitly incorporate the graph structure of the data into the model, allowing them to capture temporal dependencies in a more natural way. This approach allows for more accurate predictions in complex temporal structures, such as those found in healthcare, traffic and weather forecasting. We also fine-tune our GraphRL model using a Bayesian optimisation technique to further improve performance. The proposed framework outperforms the baseline models in time-series forecasting and monitoring. The contributions of this study include the introduction of a novel GraphRL framework for time-series prediction and the demonstration of the effectiveness of GNNs in comparison to traditional deep learning models such as RNNs and LSTMs. Overall, this study demonstrates the potential of GraphRL in providing accurate and efficient predictions in dynamic RL environments.
FedStack: Personalized activity monitoring using stacked federated learning
Sep 27, 2022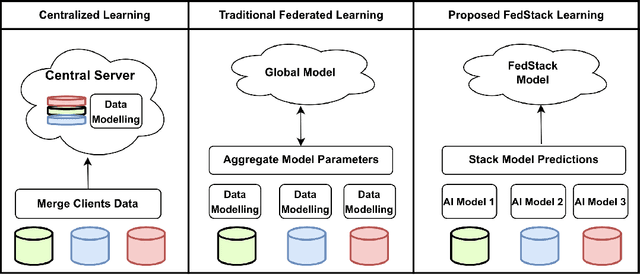
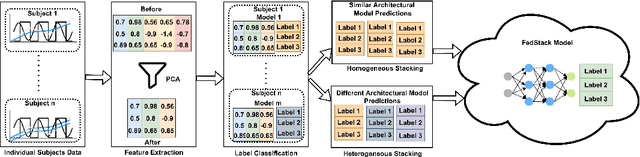
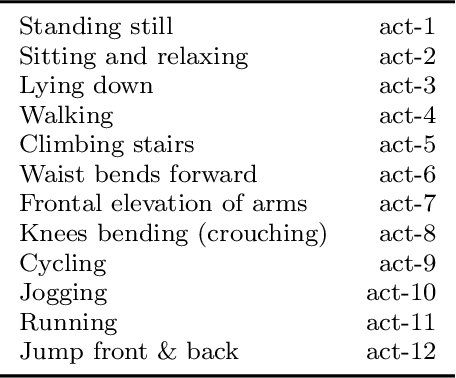
Abstract:Recent advances in remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems can recognize various human activities to measure vital signs, including subtle motions from superficial vessels. There is a growing interest in applying artificial intelligence (AI) to this area of healthcare by addressing known limitations and challenges such as predicting and classifying vital signs and physical movements, which are considered crucial tasks. Federated learning is a relatively new AI technique designed to enhance data privacy by decentralizing traditional machine learning modeling. However, traditional federated learning requires identical architectural models to be trained across the local clients and global servers. This limits global model architecture due to the lack of local models heterogeneity. To overcome this, a novel federated learning architecture, FedStack, which supports ensembling heterogeneous architectural client models was proposed in this study. This work offers a protected privacy system for hospitalized in-patients in a decentralized approach and identifies optimum sensor placement. The proposed architecture was applied to a mobile health sensor benchmark dataset from 10 different subjects to classify 12 routine activities. Three AI models, ANN, CNN, and Bi-LSTM were trained on individual subject data. The federated learning architecture was applied to these models to build local and global models capable of state of the art performances. The local CNN model outperformed ANN and Bi-LSTM models on each subject data. Our proposed work has demonstrated better performance for heterogeneous stacking of the local models compared to homogeneous stacking. This work sets the stage to build an enhanced RPM system that incorporates client privacy to assist with clinical observations for patients in an acute mental health facility and ultimately help to prevent unexpected death.
A Preference Random Walk Algorithm for Link Prediction through Mutual Influence Nodes in Complex Networks
May 20, 2021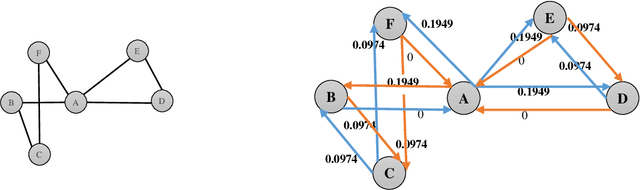
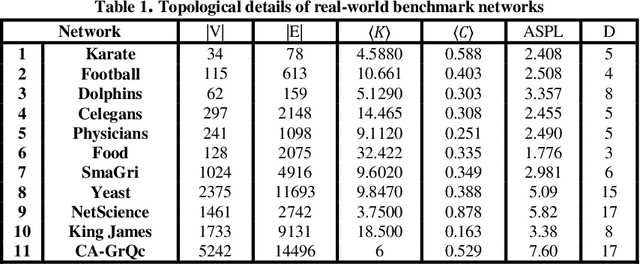
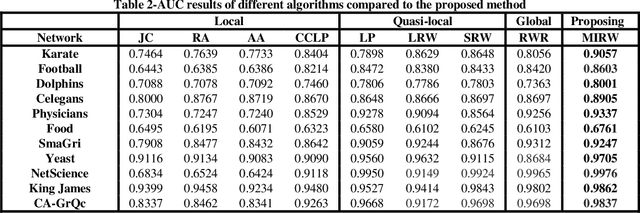
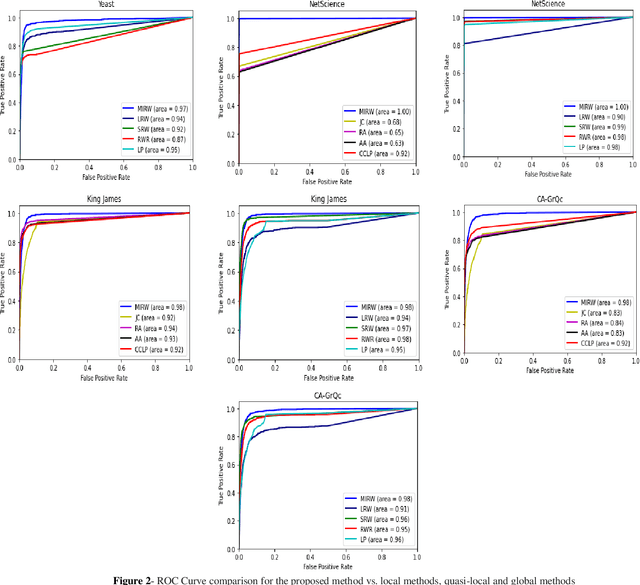
Abstract:Predicting links in complex networks has been one of the essential topics within the realm of data mining and science discovery over the past few years. This problem remains an attempt to identify future, deleted, and redundant links using the existing links in a graph. Local random walk is considered to be one of the most well-known algorithms in the category of quasi-local methods. It traverses the network using the traditional random walk with a limited number of steps, randomly selecting one adjacent node in each step among the nodes which have equal importance. Then this method uses the transition probability between node pairs to calculate the similarity between them. However, in most datasets, this method is not able to perform accurately in scoring remarkably similar nodes. In the present article, an efficient method is proposed for improving local random walk by encouraging random walk to move, in every step, towards the node which has a stronger influence. Therefore, the next node is selected according to the influence of the source node. To do so, using mutual information, the concept of the asymmetric mutual influence of nodes is presented. A comparison between the proposed method and other similarity-based methods (local, quasi-local, and global) has been performed, and results have been reported for 11 real-world networks. It had a higher prediction accuracy compared with other link prediction approaches.
Aspect-Based Opinion Extraction from Customer reviews
Apr 08, 2014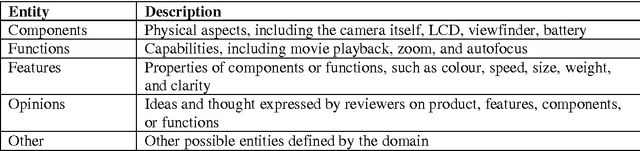
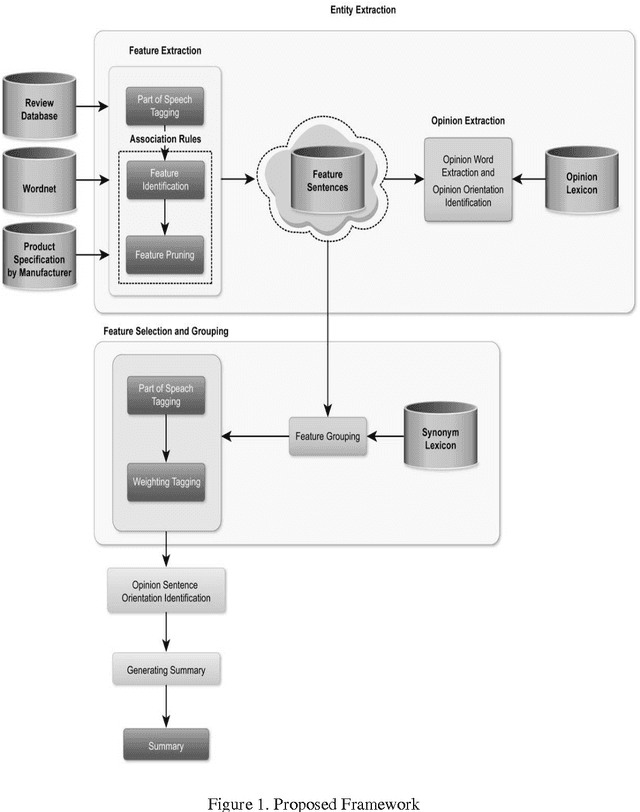
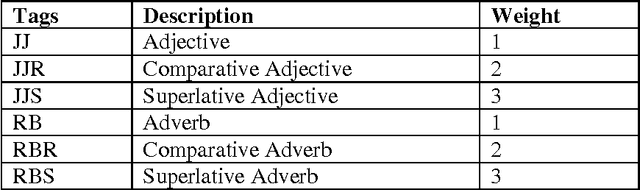
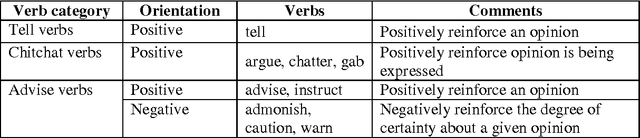
Abstract:Text is the main method of communicating information in the digital age. Messages, blogs, news articles, reviews, and opinionated information abound on the Internet. People commonly purchase products online and post their opinions about purchased items. This feedback is displayed publicly to assist others with their purchasing decisions, creating the need for a mechanism with which to extract and summarize useful information for enhancing the decision-making process. Our contribution is to improve the accuracy of extraction by combining different techniques from three major areas, named Data Mining, Natural Language Processing techniques and Ontologies. The proposed framework sequentially mines products aspects and users opinions, groups representative aspects by similarity, and generates an output summary. This paper focuses on the task of extracting product aspects and users opinions by extracting all possible aspects and opinions from reviews using natural language, ontology, and frequent (tag) sets. The proposed framework, when compared with an existing baseline model, yielded promising results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge